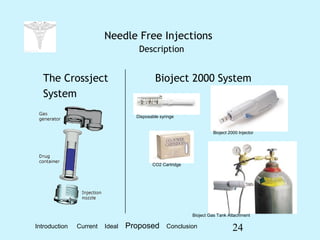
The document discusses the advantages and proposals for needle-free injection technology as an alternative to traditional hypodermic needles, highlighting its benefits such as reduced needle phobia, safety, and reliability in medication delivery. It compares needle-free injectors to traditional needles, noting the disadvantages of the latter, including training requirements and disposal issues. The document concludes that while needle-free systems may initially be more expensive, they are ultimately more efficient and safe for administering vaccinations and medications.