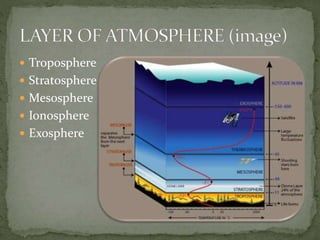
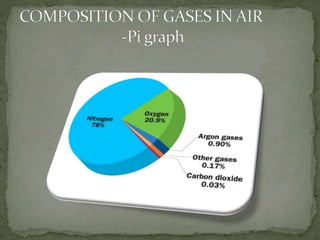
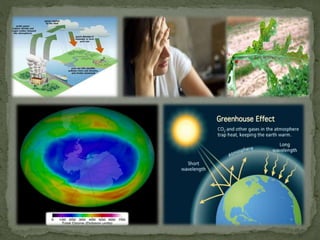
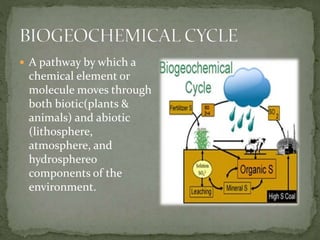
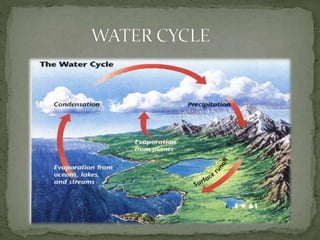
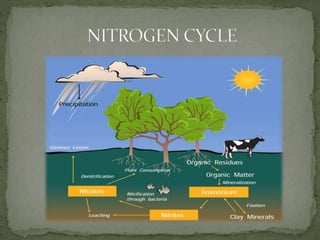
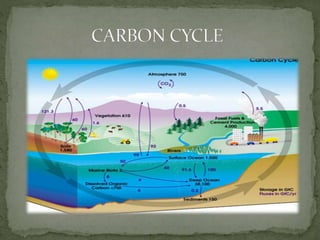
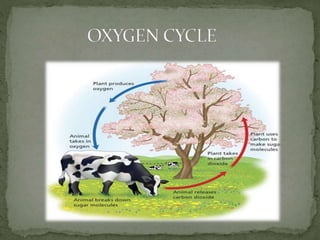
The document summarizes key components of Earth's biosphere. It describes the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere and explains how they interact to support life. It also discusses various environmental issues like air pollution, water pollution, soil degradation, and their impacts on human health, plants, and aquatic life. Additionally, it provides a brief overview of different layers of the atmosphere and processes like greenhouse effect, ozone depletion, and carbon dioxide emissions that affect Earth's climate.