Embed presentation
Download to read offline





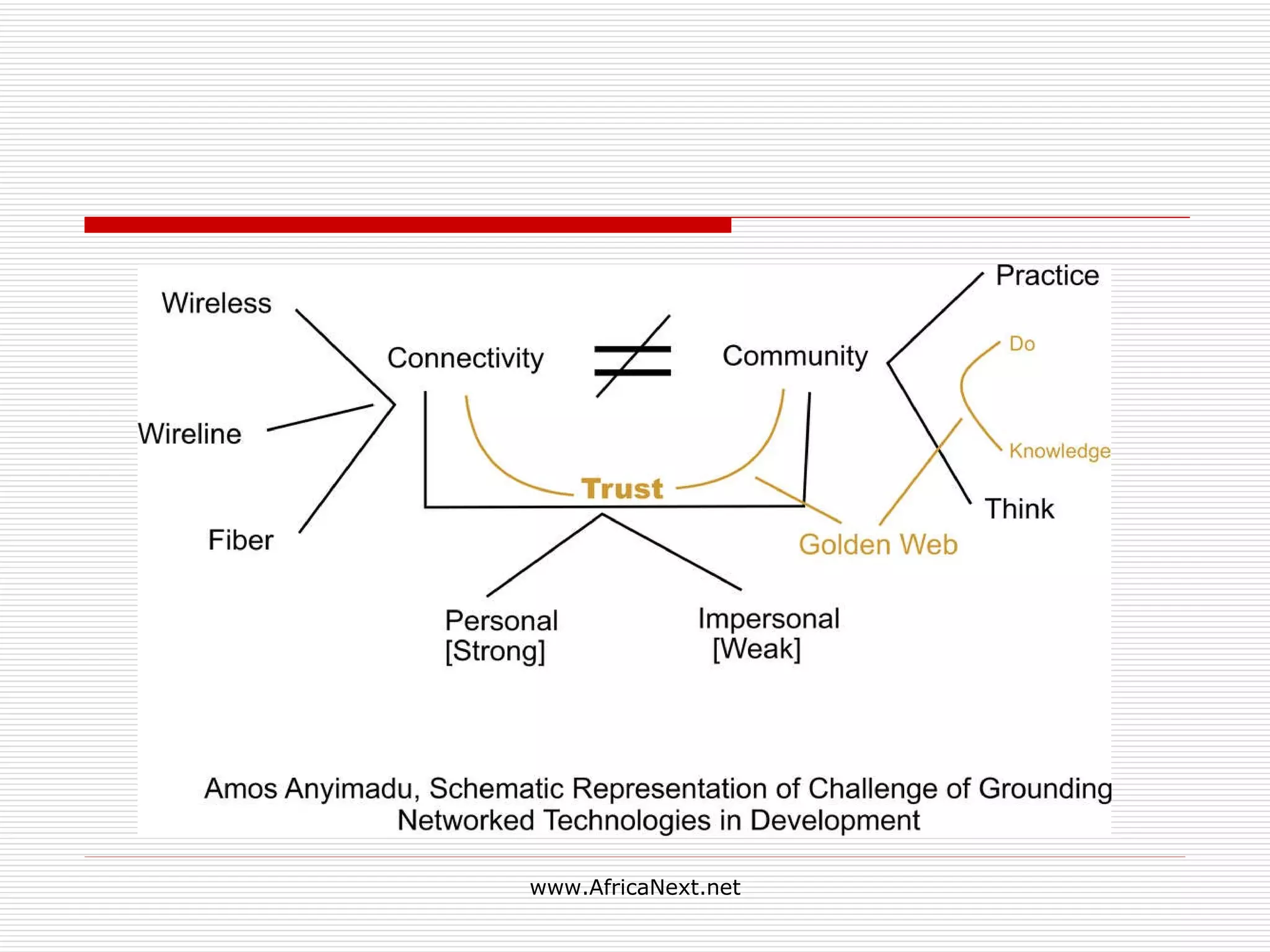

The document discusses the challenges of addressing local digital divides in Ghana given opportunities presented by new mobile technologies and the internet. It explores policy and regulatory challenges around universal access and equity. It also discusses possible applications of mobile and internet platforms in Ghana and the need for technology foresight to balance market forces and regulation.






