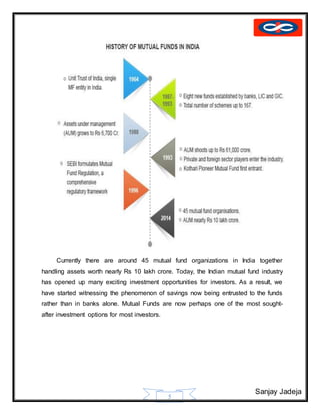
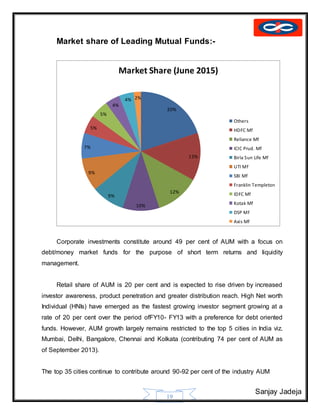
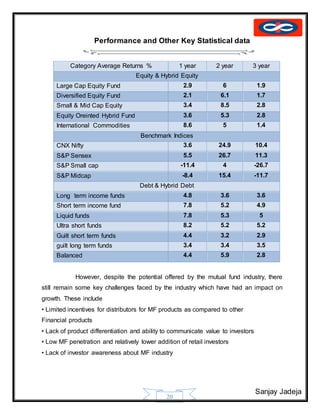
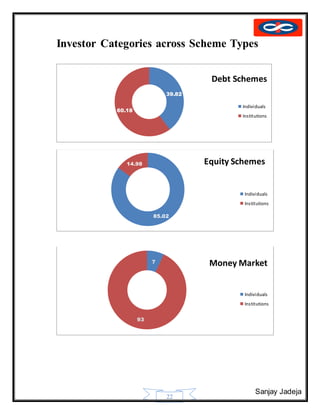
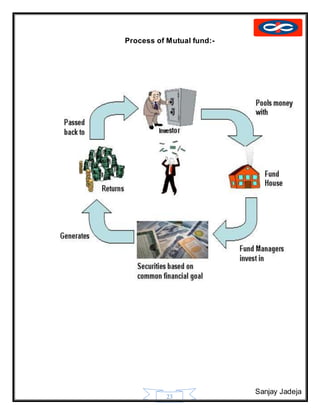
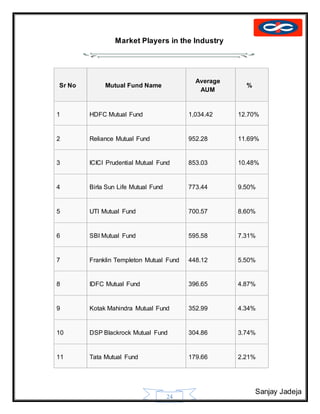
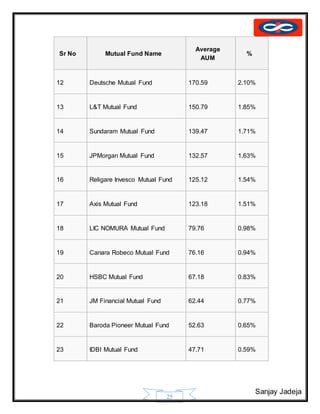
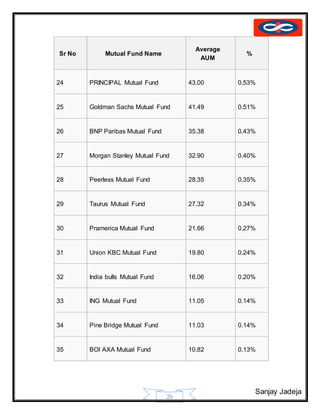
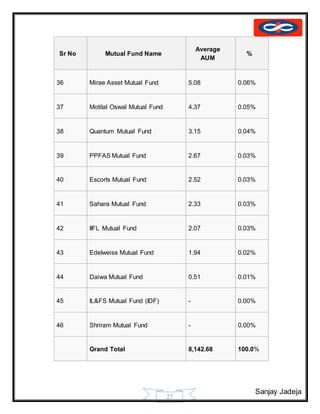
The document provides a history of mutual funds in India from 1964 to the present. It discusses the evolution of the industry through 5 phases: (1) 1964-1987 with only UTI operating, (2) 1987-1993 when public sector funds entered, (3) 1993-1996 emergence of private funds, (4) 1996 when SEBI regulation was introduced, and (5) 2003 onwards marked by rapid growth. It also outlines the structure of mutual funds in India including sponsors, trustees, asset management companies, and schemes. Overall, the document traces the development of India's mutual fund industry from a sole player to a growing sector with many private and public funds.























![Sanjay Jadeja
39
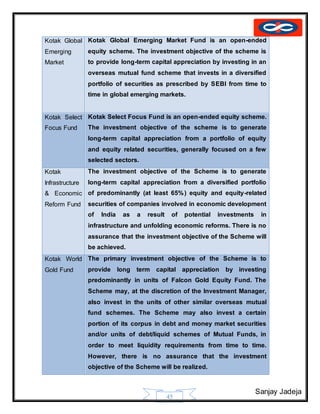
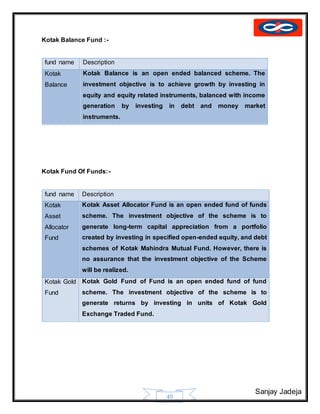
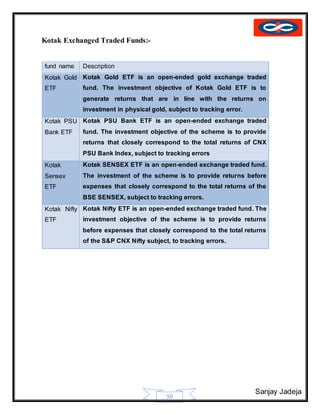
Growth and Development of Kotak Group:-
Year Milestone
1985 Kotak Mahindra Finance Limited commences bill discounting business
1987 Kotak Mahindra Finance Limited enters leasing and hire purchase business
1990 Starts the auto finance division for financing passenger cars
1991 Launches investment banking business
1992 Enters the funds syndication business
1995 Commenced joint venture with Goldman Sachs Group Inc.
Investment Banking division incorporated into a separate company - Kotak
Mahindra Capital Company
1996 The auto finance business is hived off into a separate company - Kotak
Mahindra Prime Limited (formerly known as Kotak Mahindra Primus Limited).
Kotak Mahindra takes a significant stake in Ford Credit Kotak Mahindra
Limited, for financing Ford vehicles.
1998 Launches mutual fund through Kotak Mahindra Asset Management Company
(KMAMC).
2000 Kotak Securities launches online broking business
2001 Launches insurance business, partners Old Mutual from South Africa to form
Kotak Mahindra Old Mutual Life Insurance Ltd.
2003 Kotak Mahindra Finance Ltd. (KMFL), the group's flagship company, receives
banking license from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). With this, KMFL
becomes the first non-banking finance company to be converted into a
commercial bank - Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd.
2004 Enters alternate assets business with the launch of a private equity fund.
2005 Kotak Mahindra Group realigns joint venture in Ford Credit; takes 100%
ownership of Kotak Mahindra Prime (formerly known as Kotak Mahindra
Primus Limited) and sells its stake in Ford credit Mahindra to Ford.
2005 Launches a real estate fund
2006 Buys out Goldman Sachs' equity stake in Kotak Mahindra Capital Company
and Kotak Securities Ltd.
2008 Launched a Pension Fund under India's National Pension System (NPS)
2009 Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd. opens a representative office in Dubai
Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd. becomes anchor investor in Ahmedabad
Commodities Exchange (ACE)
2015 ING Vysya Bank has merged with Kotak Mahindra Bank with effect from April
1, 2015.[7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sanjayfinalproject-151028114148-lva1-app6891/85/mutual-fund-project-39-320.jpg)
![Sanjay Jadeja
40
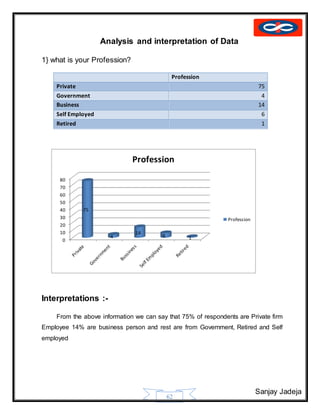
Mergerwith ING Vysya Bank
In 2014, Kotak Bank acquired ING Vysaya Bank for a deal valued at ₹15000 crore
(US$2.4 billion). With the merger, the total human resource count will jump to almost 40,000
heads and the branch was expected to rise over 1200.[8] Post the merger, ING Group which
controlled ING Vysya Bank will own 7% share in Kotak Mahindra Bank.[9]
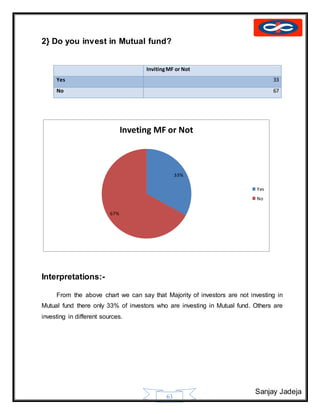
Symbol :-
The symbol of the infinite Ka reflects our global Indian personality. The Ka is
uniquely Indian while its curve forms the infinity sign, which is universal. One of the basic
tenets of economists is that man's needs are unlimited. The infinite Kasymbolises that we have
infinite number of ways to meet those needs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sanjayfinalproject-151028114148-lva1-app6891/85/mutual-fund-project-40-320.jpg)