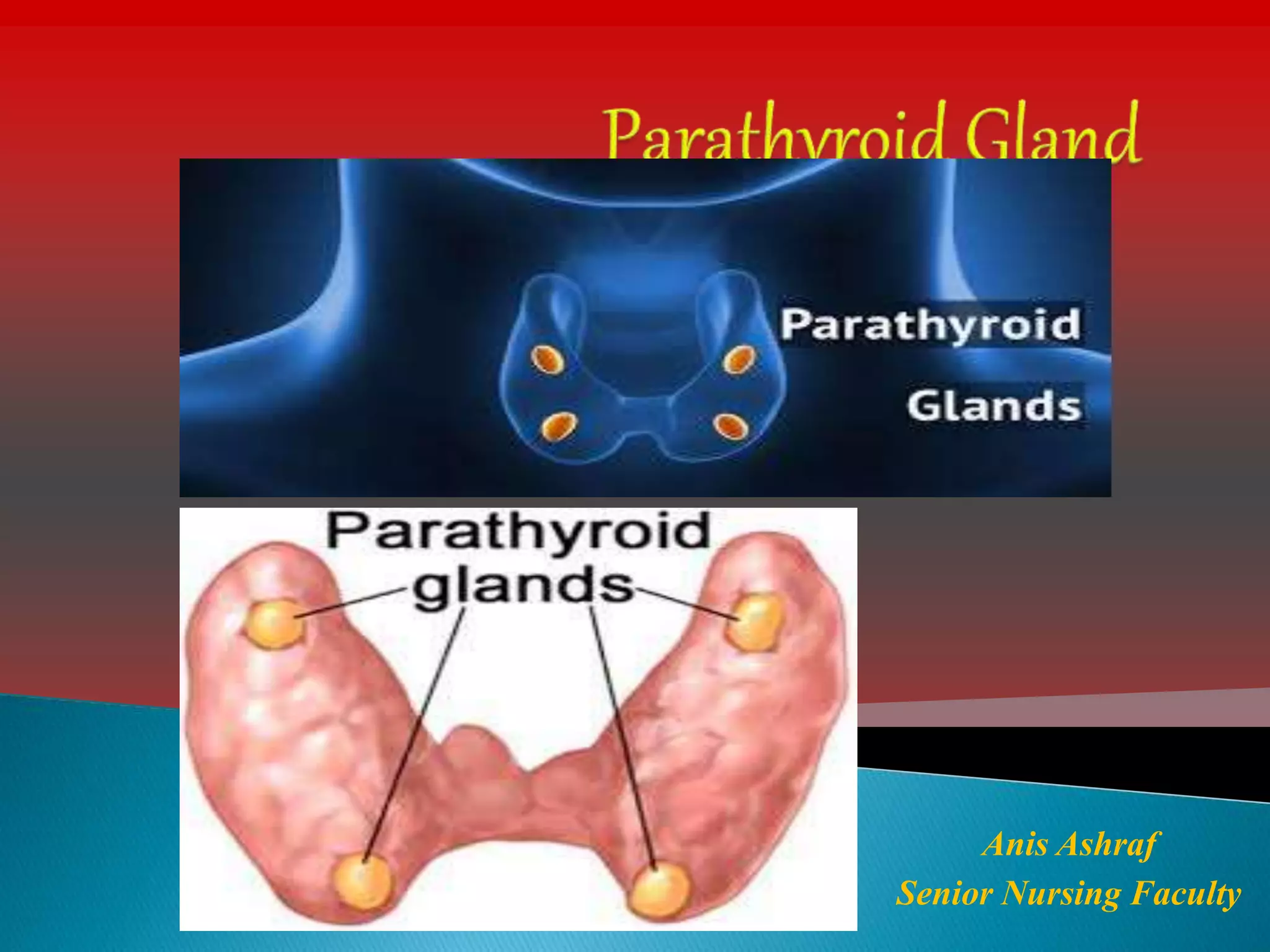
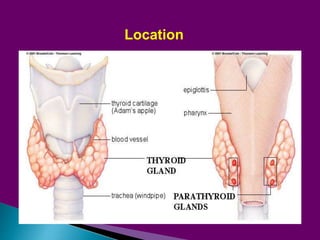
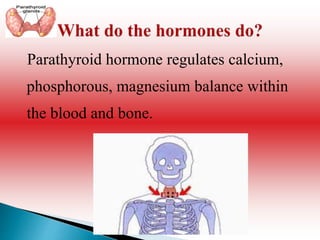
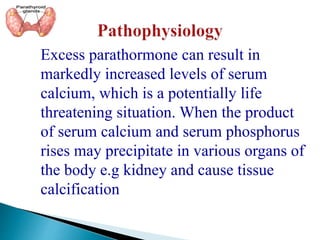
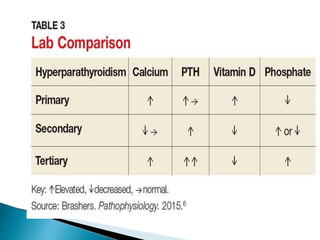
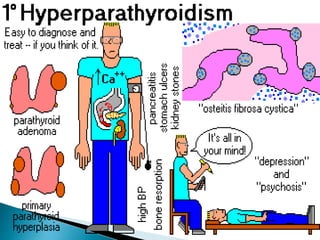
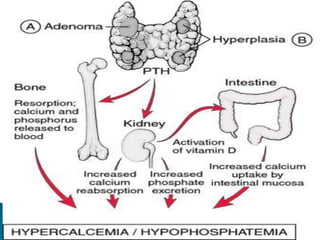
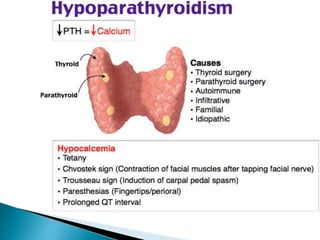
This document provides an overview of the parathyroid gland and its role in regulating calcium and phosphorus levels. It discusses three key learning objectives: 1) the anatomy and physiology of the parathyroid gland, 2) complications of thyroid disorders and appropriate treatment, and 3) hyperparathyroidism, hypothyroidism, and their management. The parathyroid gland, located in the neck, produces parathyroid hormone which regulates calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium balance. Issues like hyperparathyroidism can cause high calcium levels, potentially damaging organs. The summary discusses causes, symptoms, and treatments for hyperparathyroidism and hypothyroidism.