More Related Content
PDF
3 Generative models for discrete data PDF
PDF
Support Vector Machine Tutorial 한국어 PDF
PPTX
머피's 머신러닝: Latent Linear Model PPTX
머피's 머신러닝, Mixture model and EM algorithm PPTX
머피의 머신러닝 : Gaussian Processes PDF
Eigenvalues of regular graphs What's hot
PPTX
머피's 머신러닝: Latent Linear Model PPTX
Murpy's Machine Learing: 10. Directed Graphical Model PPTX
PDF
머피의 머신러닝: Undirencted Graphical Model PPTX
Efficient linear skyline algorithm in two dimensional space PDF
Lecture 3: Unsupervised Learning PDF
PDF
PDF
Lecture 4: Neural Networks I PDF
PPTX
Variational AutoEncoder(VAE) PPTX
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PPTX
Recurrent Neural Net의 이론과 설명 PPTX
PDF
Energy based models and boltzmann machines - v2.0 PDF
Chapter 19 Variational Inference Viewers also liked
PDF
Jensen's inequality, EM 알고리즘 PDF
ThinkBayes: Chapter 9 two_dimensions PPTX
PPTX
Murpy's Machine Learning:14. Kernel PDF
ThinkBayes: chapter 13 simulation PPTX
TETRIS AI WITH REINFORCEMENT LEARNING PPTX
머피의 머신러닝 13 Sparse Linear Model PDF
PDF
PPTX
머피의 머신러닝: 17장 Markov Chain and HMM PPTX
From A Neural Probalistic Language Model to Word2vec PDF
Similar to Murpy's Machine Learning 9. Generalize Linear Model
PDF
PDF
PDF
Lecture 2: Supervised Learning PDF
PDF
04. logistic regression ( 로지스틱 회귀 ) PPTX
[Probability for machine learning] PPTX
[PRML 3.1~3.2] Linear Regression / Bias-Variance Decomposition PDF
PPTX
2.supervised learning(epoch#2)-1 PDF
Machine learning bysogood PPTX
PDF
PPTX
PDF
캐빈머피 머신러닝 Kevin Murphy Machine Learning Statistic PDF
PPTX
PDF
From maching learning to deep learning PDF
PDF
PPTX
[한글] Tutorial: Sparse variational dropout Murpy's Machine Learning 9. Generalize Linear Model
- 1.
- 2.
8.1 Introduction, overview
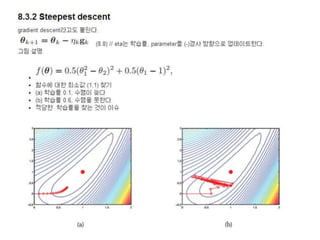
8.2Model specification
8.3 Model fitting
8.3.1 MLE
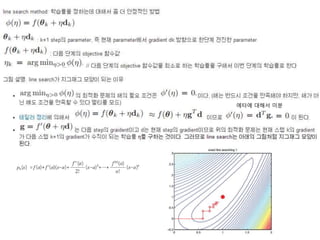
8.3.2 Steepest descent
8.3.3 Newton's method
8.3.6 l2 regularization
8.3.7 Multi-class logistic regression
8.4 Bayesian logistic regression
8.4.1 Laplace approximation
8.4.2 Derivation of the BIC(Bayesian Information
Criterion)
8.4.3 Gaussian approximation for logistic regression
8.4.4 Approximating the posterior predictive
8.5 Online learning and stochastic optimization
8.5.3 The LMS algorithm
8.5.4 The perceptron algorithm
8.5.5 A Bayesian view
8.6 Generative vs discriminative classifiers
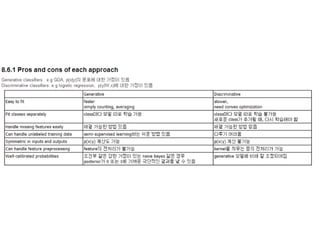
8.6.1 Pros and cons of each approach
- 5.
- 6.
- 8.
- 11.
- 16.
- 19.
- 21.
9.1 Introduction
9.2 Theexponential family
9.2.1 Definition
9.2.2.1 Bernoulli
9.2.2.2 Multinoulli
9.2.2.3 Univariate Gaussian
9.2.3 Log partition function
9.2.3.1 Example: the Bernoulli distribution
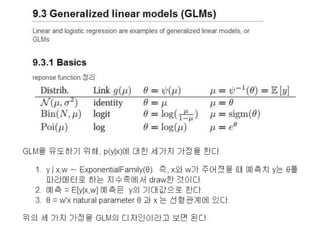
9.3 Generalized linear models (GLMs)
9.3.1 Basics
9.3.2 ML and MAP estimation
9.3.3 Bayesian inference
- 23.
- 29.
- 30.
- 35.
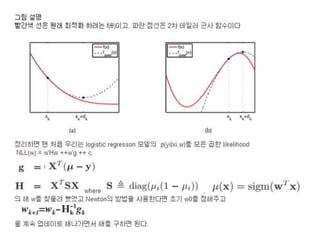
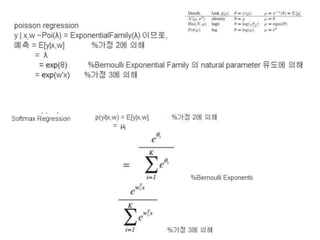
logistic regression 의경우 μ
= 1/(1+exp(-w'x)) 이므로 S는 섹션 8.3.1
의 결과와 같아진다.
Logistic R의 gradient
부호가 바뀐건 위의 결과는 NLL에 대해서 한거라