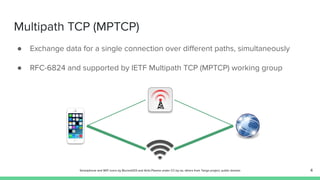
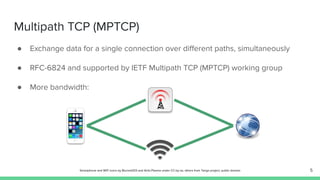
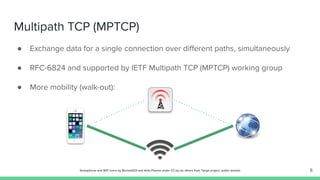
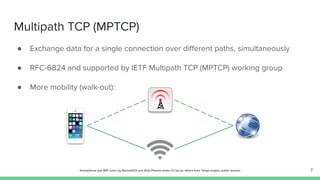
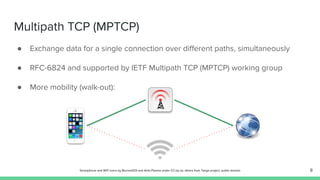
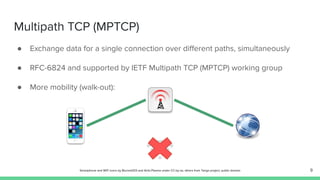
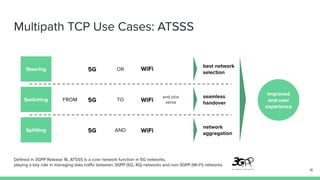
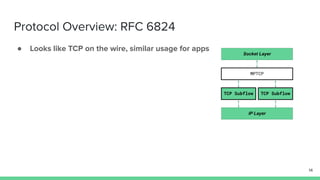
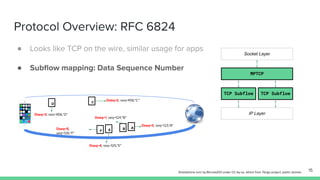
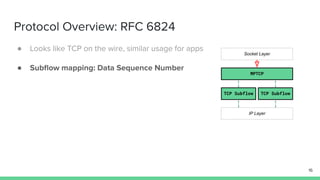
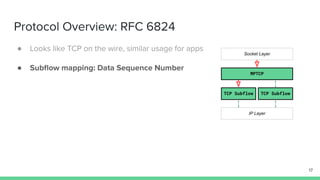
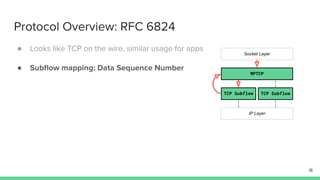
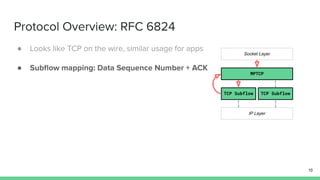
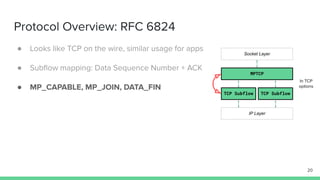
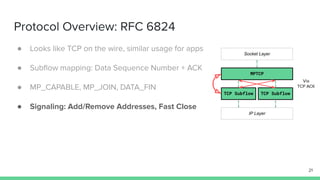
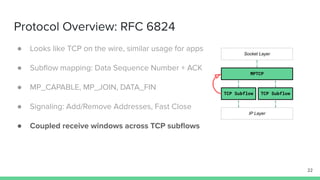
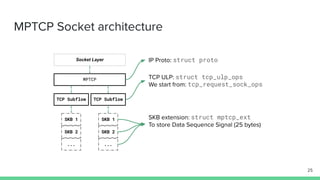
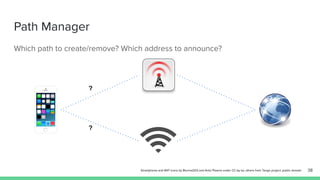
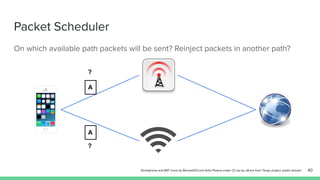
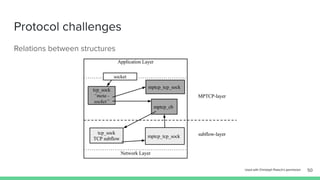
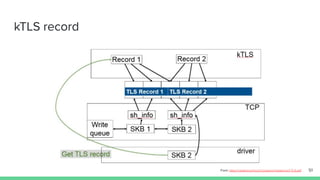
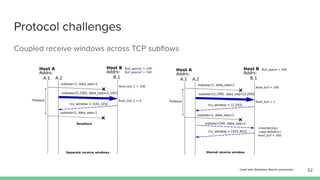
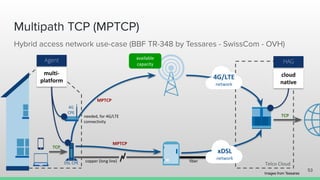
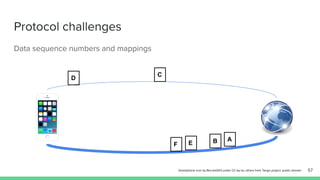
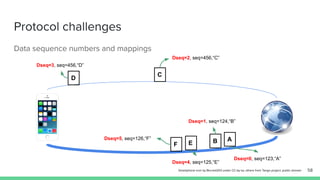
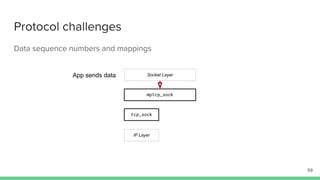
The document outlines the roadmap and technical overview for Multipath TCP (MPTCP), which enables simultaneous data transmission over multiple paths to enhance bandwidth and mobility. It discusses use cases, particularly in smartphones and 5G networks, along with upstreaming guidelines and existing implementations. Advanced features and optimizations for MPTCP, along with diagnostic capabilities and initial testing strategies, are also highlighted.