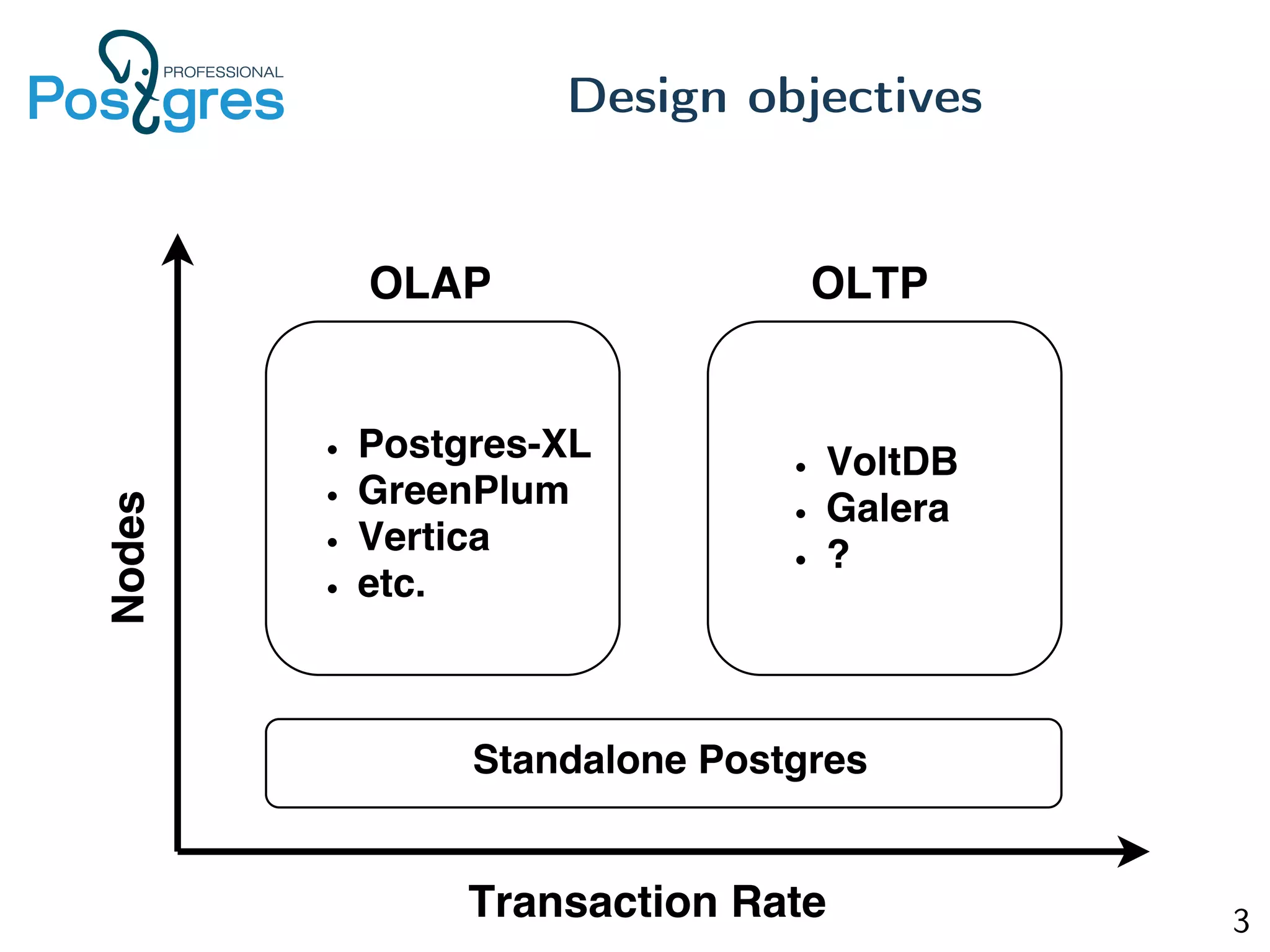
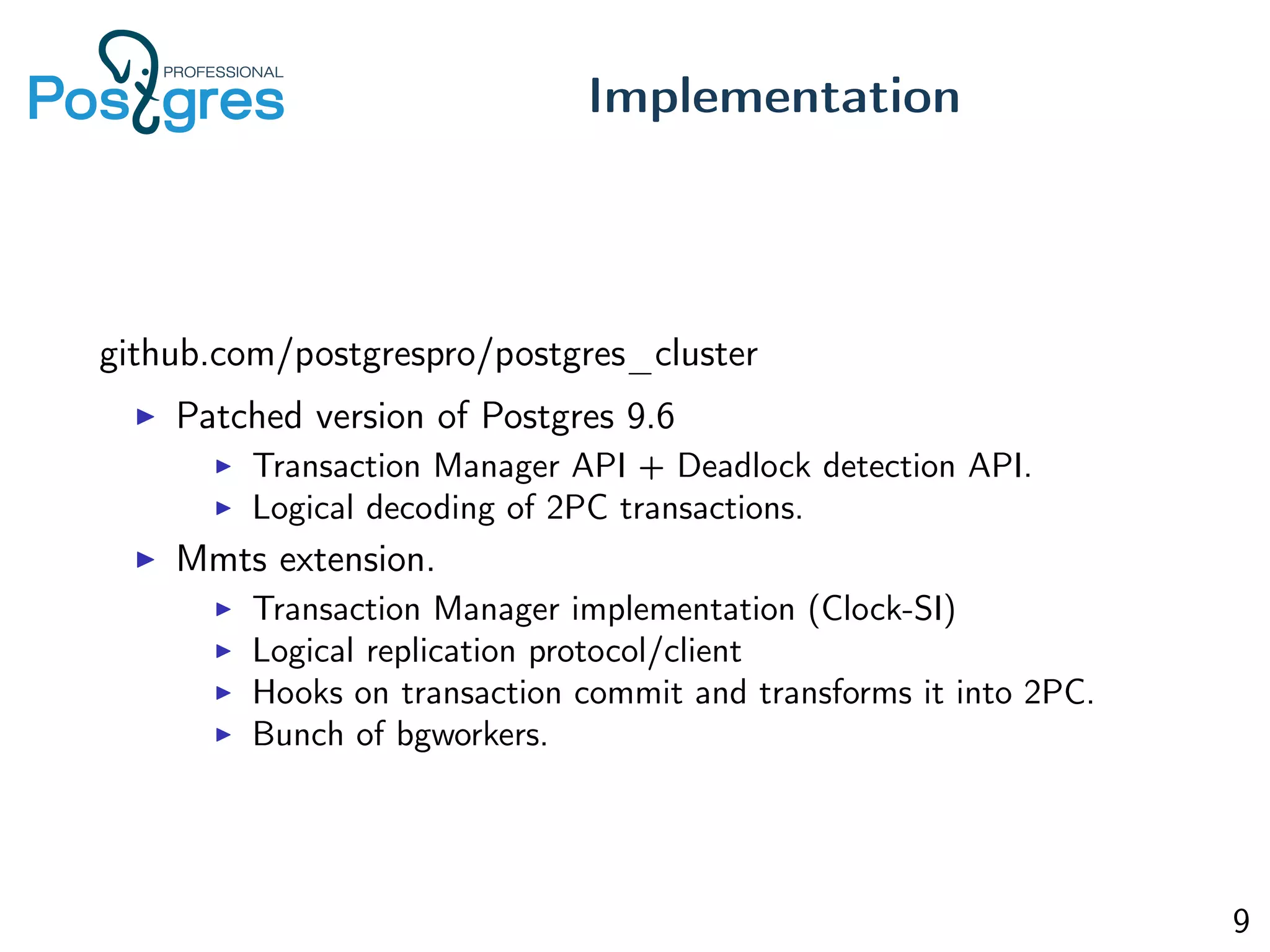
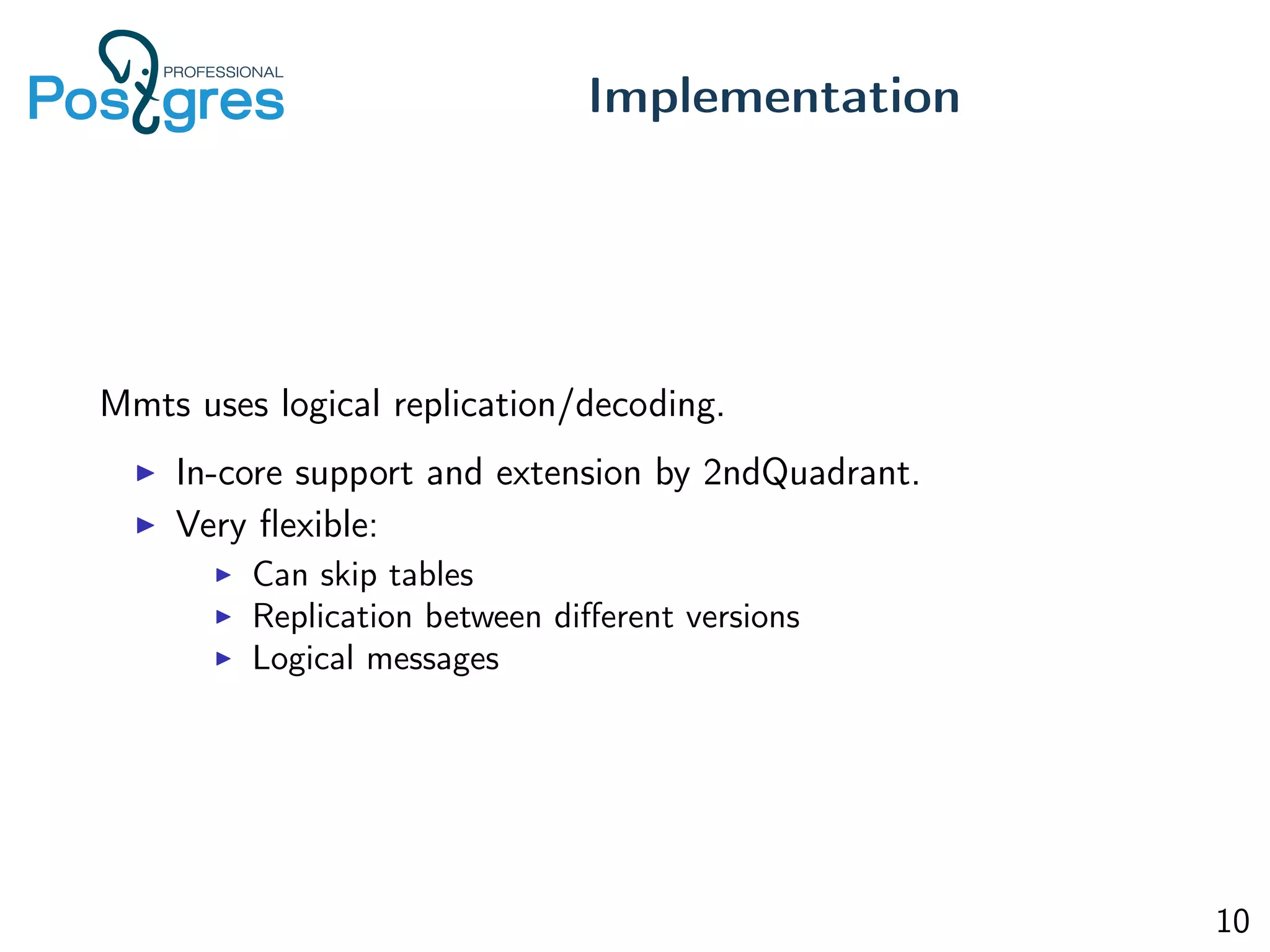
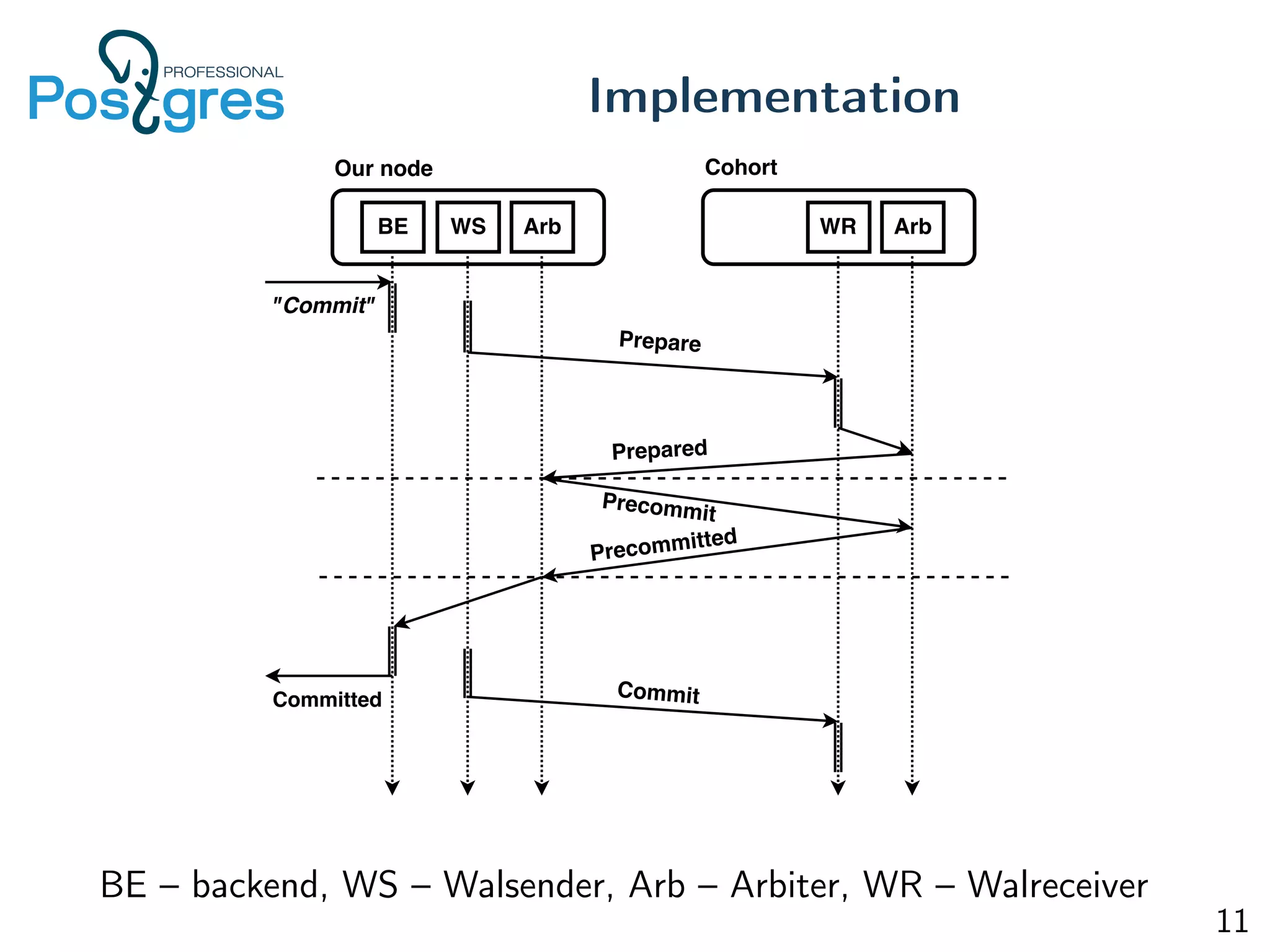
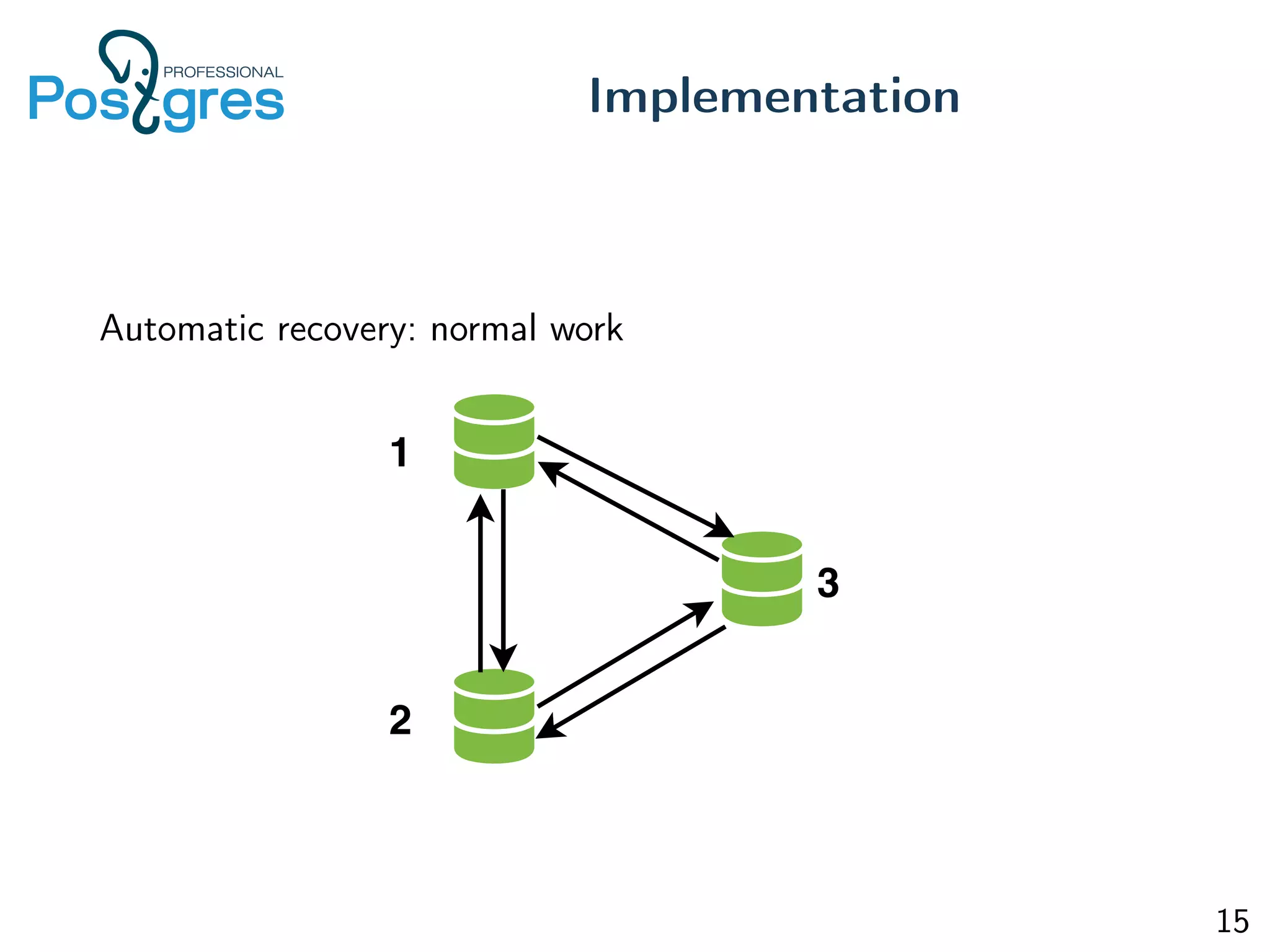
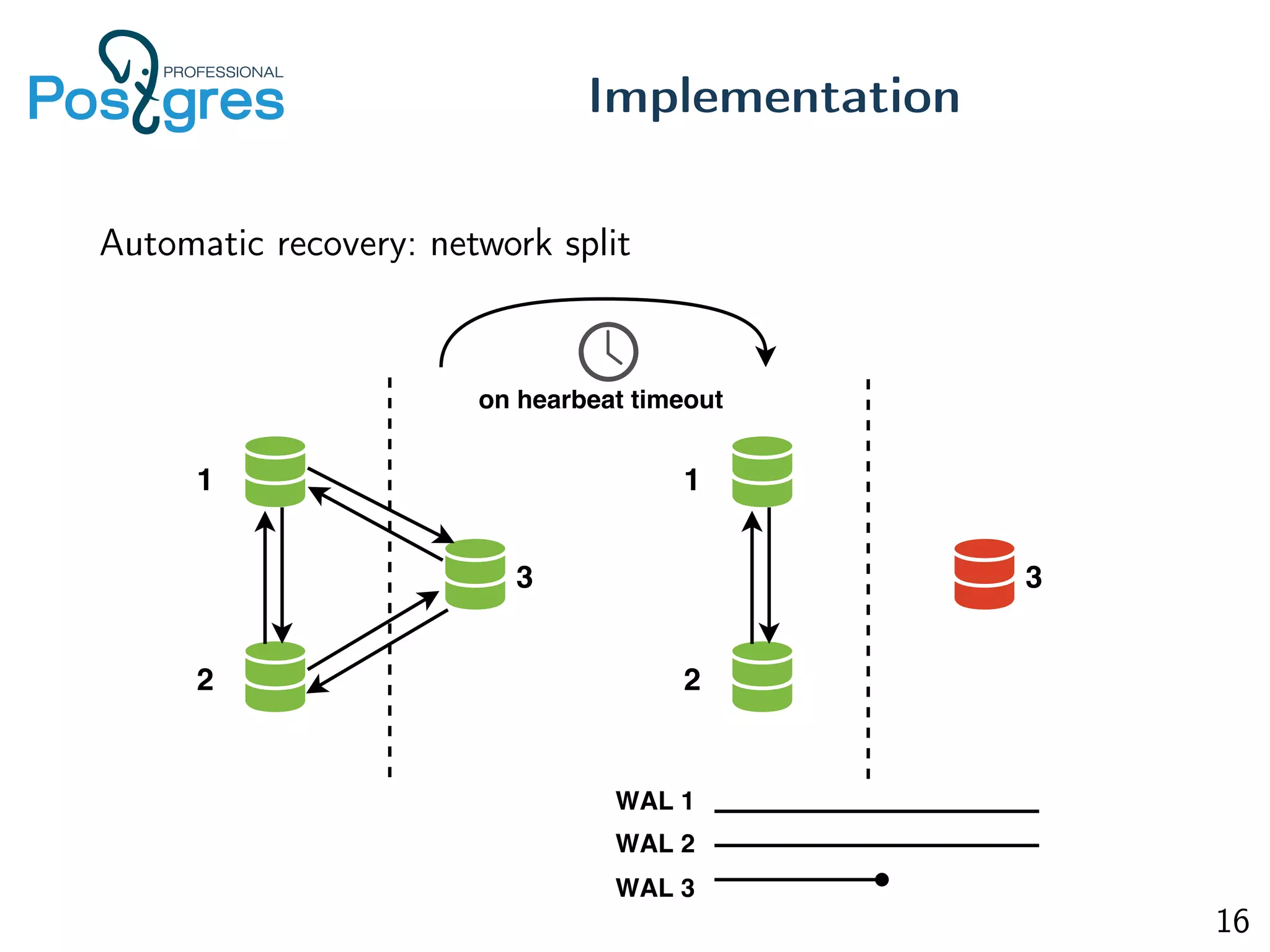
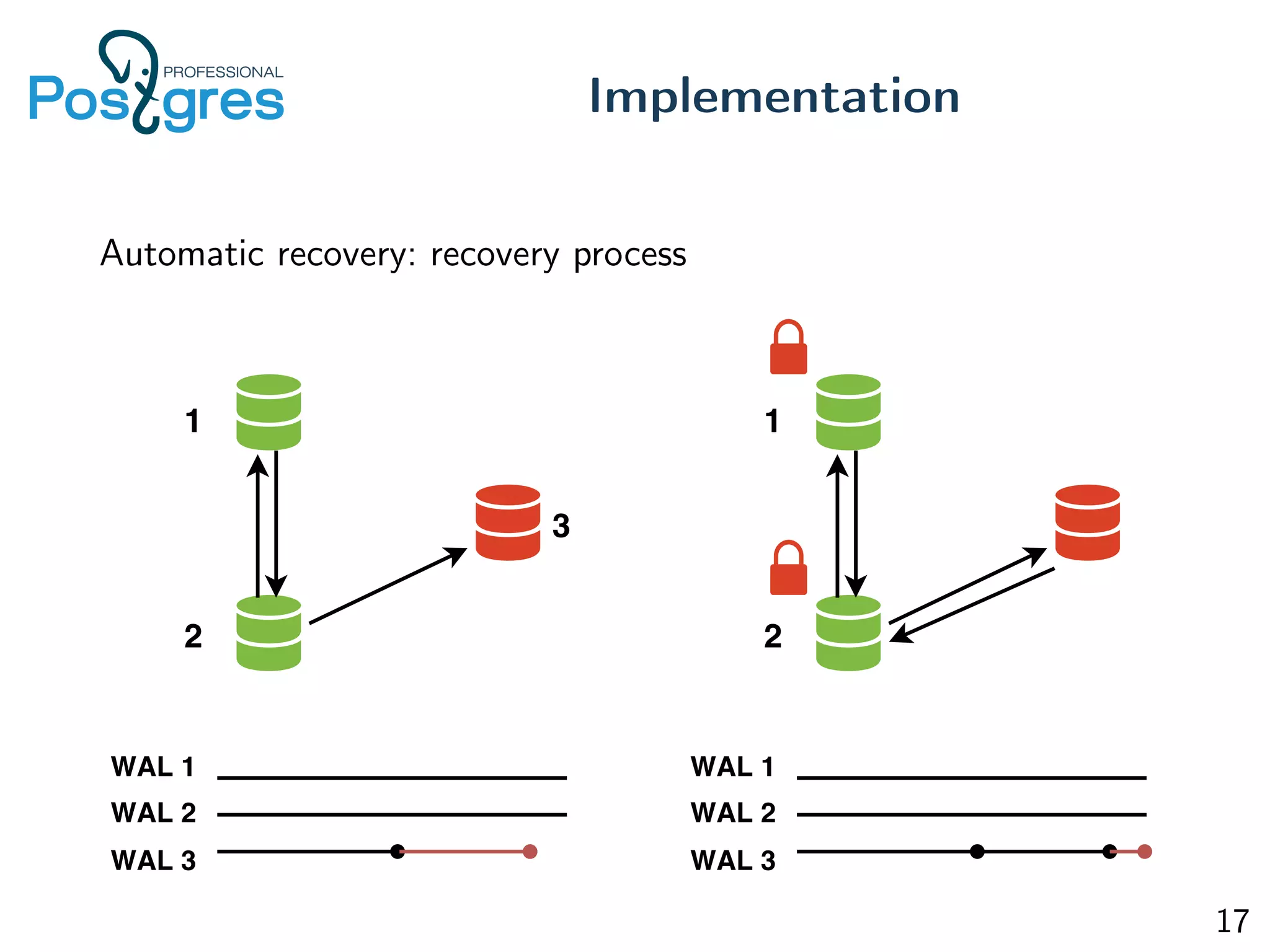
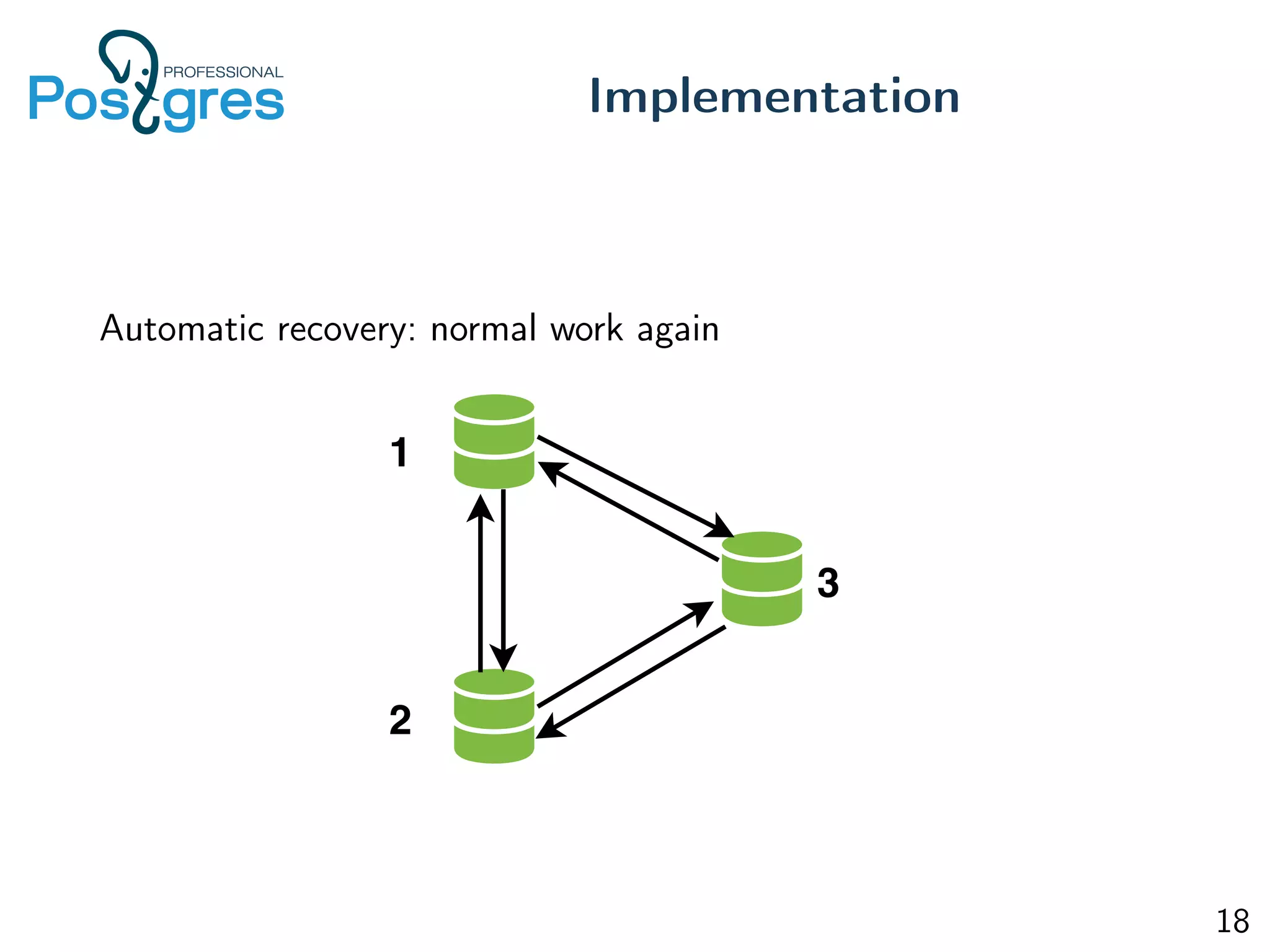
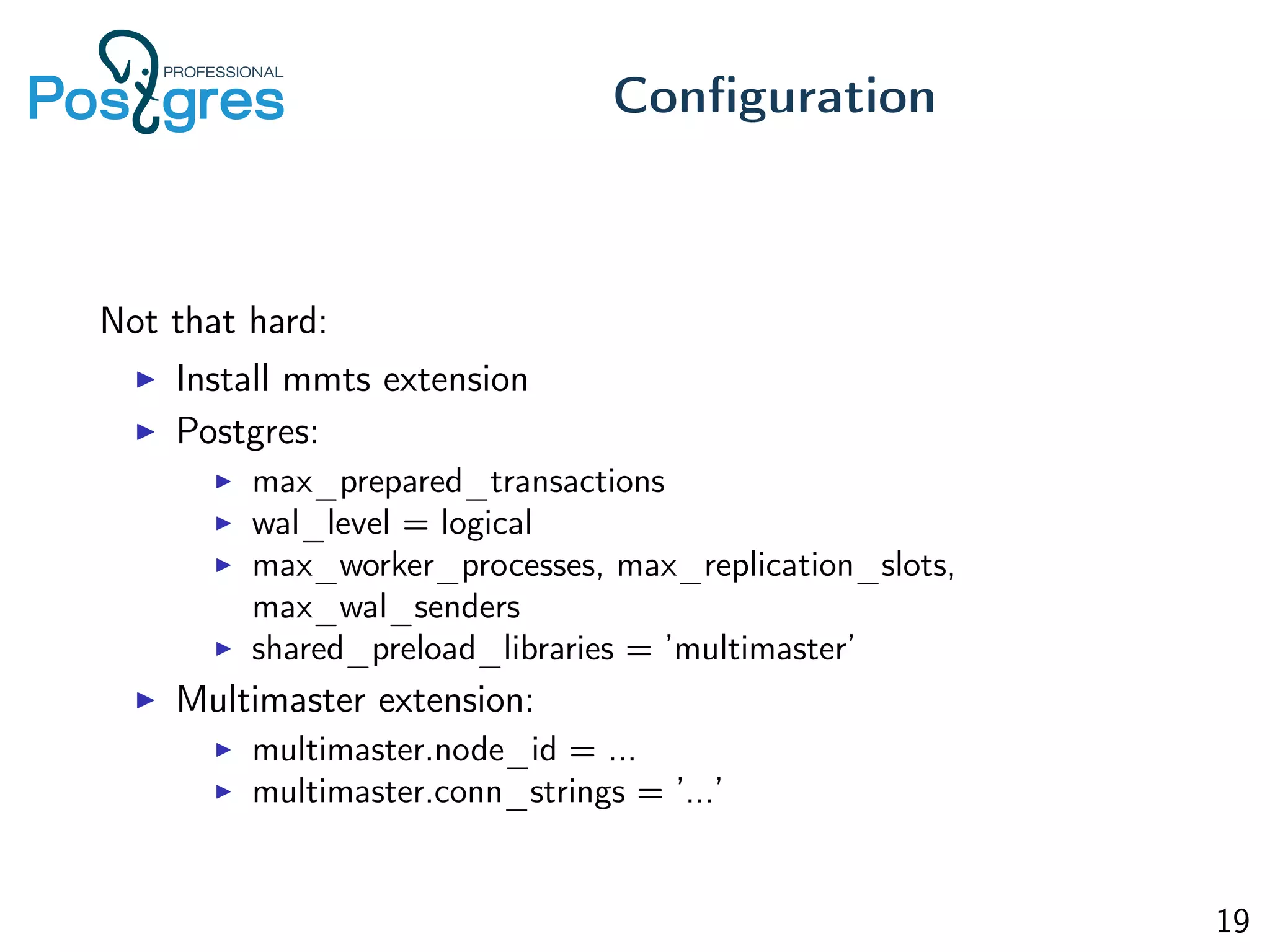
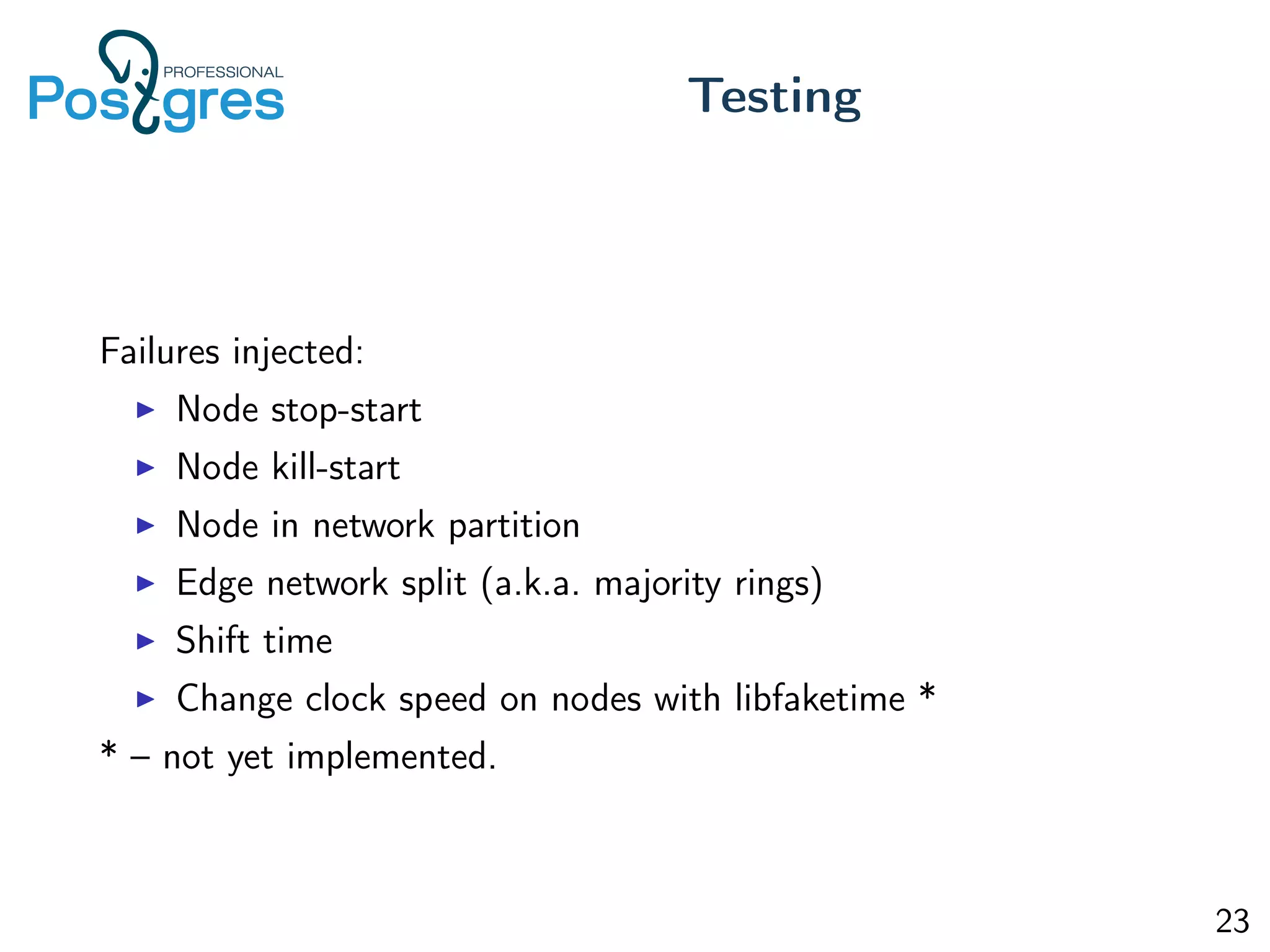
This document discusses the objectives, implementation, testing, and roadmap for multi-master replication in Postgres. The key goals are fault tolerance, allowing writes to any node, and compatibility with standalone Postgres. It uses logical replication and a transaction manager based on ClockSI to allow transactions to commit on any node. Testing involves starting docker containers to inject failures like network partitions and verify automatic recovery works as expected. The roadmap includes releasing a public beta, contributing patches to upstream Postgres, and discussing replication of catalog content.