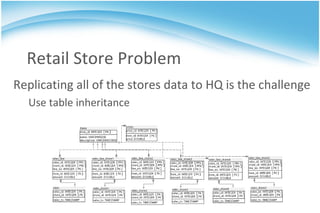
The document discusses multi-master replication in database systems, highlighting the benefits of increased availability and performance. It introduces Slony, an asynchronous master-slave replication solution especially effective for retail scenarios, and describes how it can manage data consistency and conflict resolution across multiple geographic locations. The document emphasizes the complexity of implementing such systems and advises caution in using multi-master configurations unless necessary.