This document discusses four approaches to storing multilingual content in a database:
1. The column approach duplicates content across language-specific columns, keeping data on each row but becoming difficult to maintain with many languages.
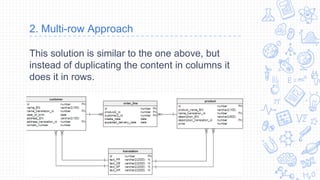
2. The multi-row approach stores each language's content in a separate row, avoiding duplicate columns but requiring duplicating other data across rows.
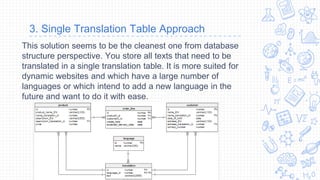
3. The single translation table stores all language content together and references it from the main tables, keeping the data normalized but requiring complex joins.
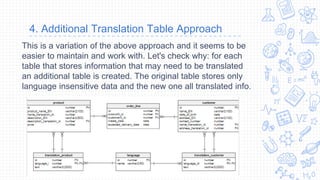
4. The additional translation table adds a separate table per main table to store translations, allowing simpler joins while doubling the number of tables. The best approach depends on an application's requirements regarding languages and queries.