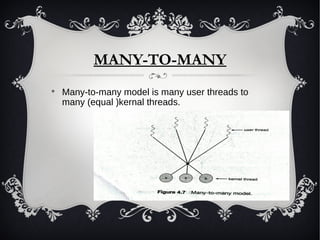
This document discusses different threading models and examples of threading implementations in operating systems. There are three dominant threading models: many-to-one maps many user threads to one kernel thread; one-to-one maps each user thread to a kernel thread and allows more concurrency; many-to-many maps many user threads to many kernel threads but true concurrency is not gained. Windows XP uses a one-to-one model where each thread has an ID and separate stacks. Linux refers to threads as tasks and uses clone() to create child tasks that share the parent's address space.