This document provides information on multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), including its global and national burden, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Some key points include:
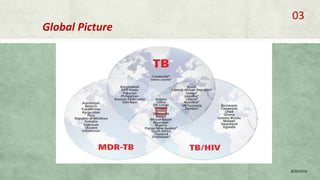
- MDR-TB affects about 490,000 people globally each year and is a major public health issue, especially in countries like India, China, and Russia.
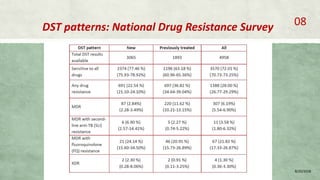
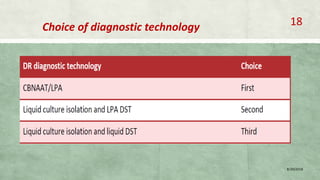
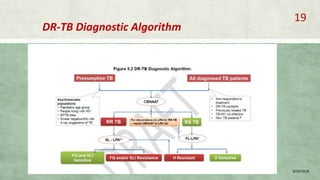
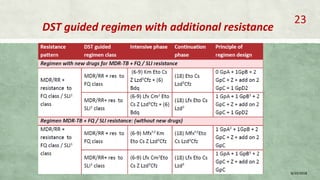
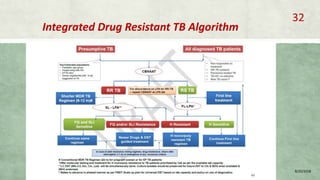
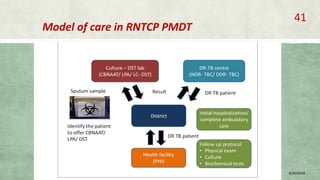
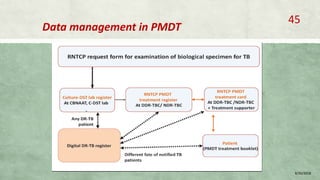
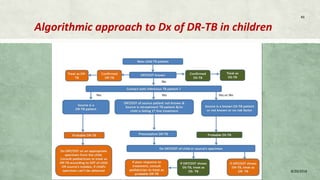
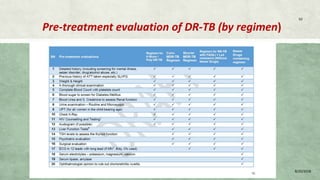
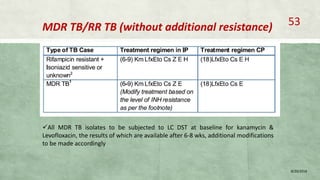
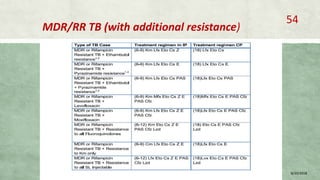
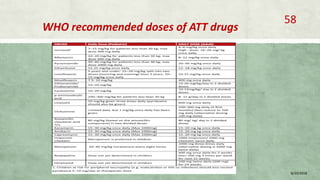
- Diagnosis involves laboratory tests like phenotypic drug susceptibility testing (DST) or genotypic tests like line probe assays (LPA) and cartridge-based nucleic acid amplification tests (CBNAAT). DST guided treatment regimens are recommended.
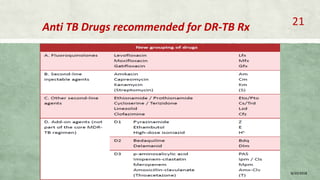
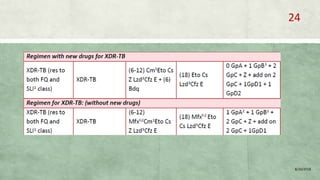
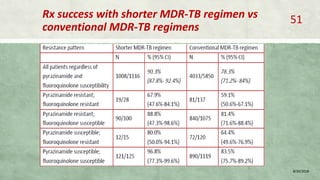
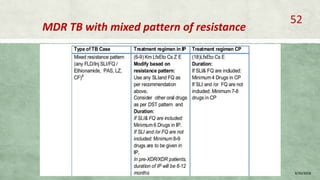
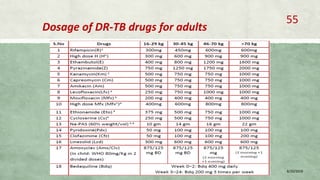
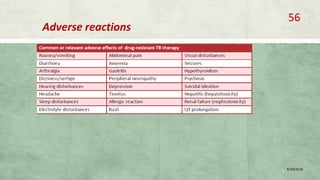
- Treatment of MDR-TB requires longer and more toxic drug regimens than drug-sensitive TB.