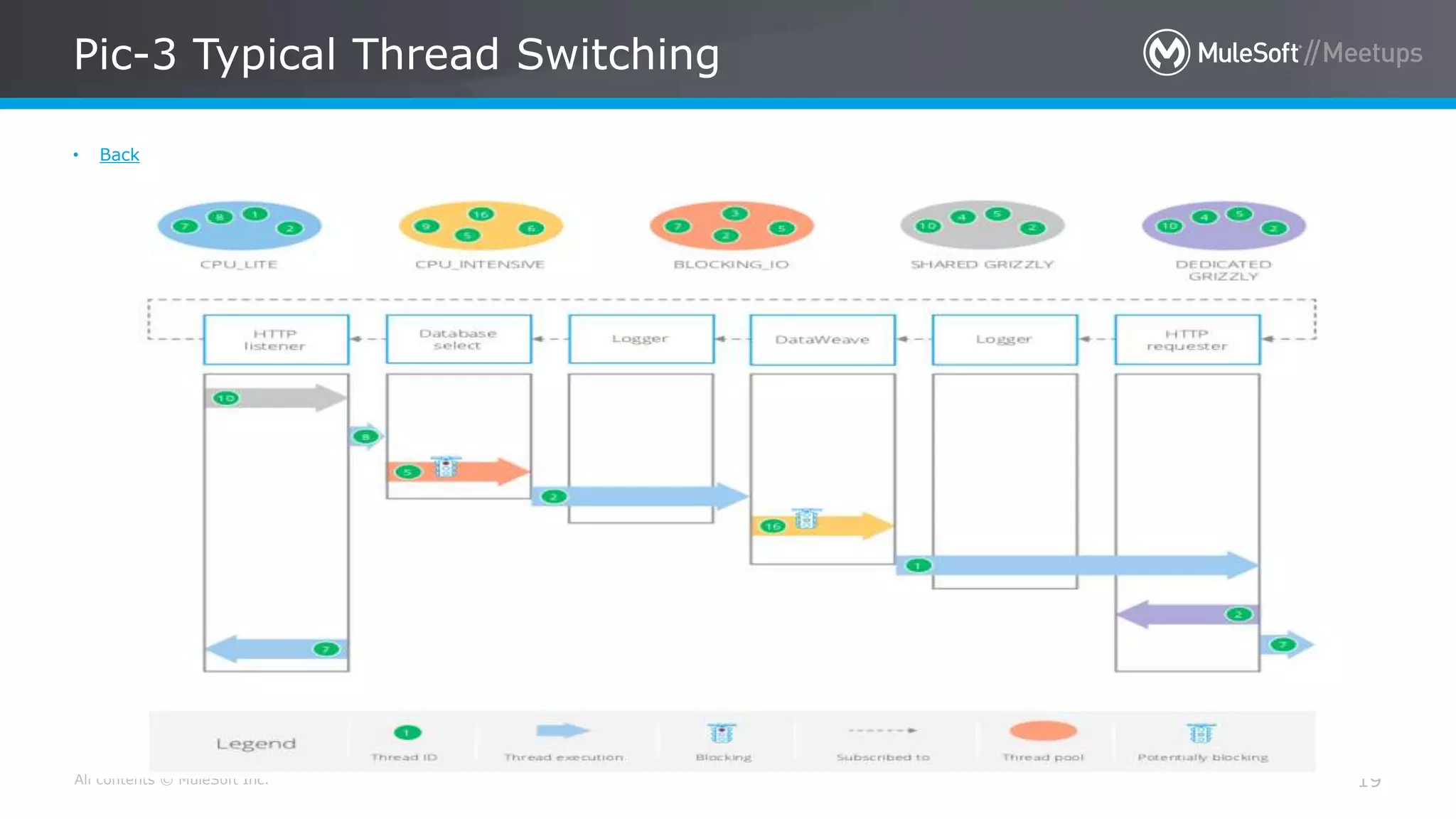
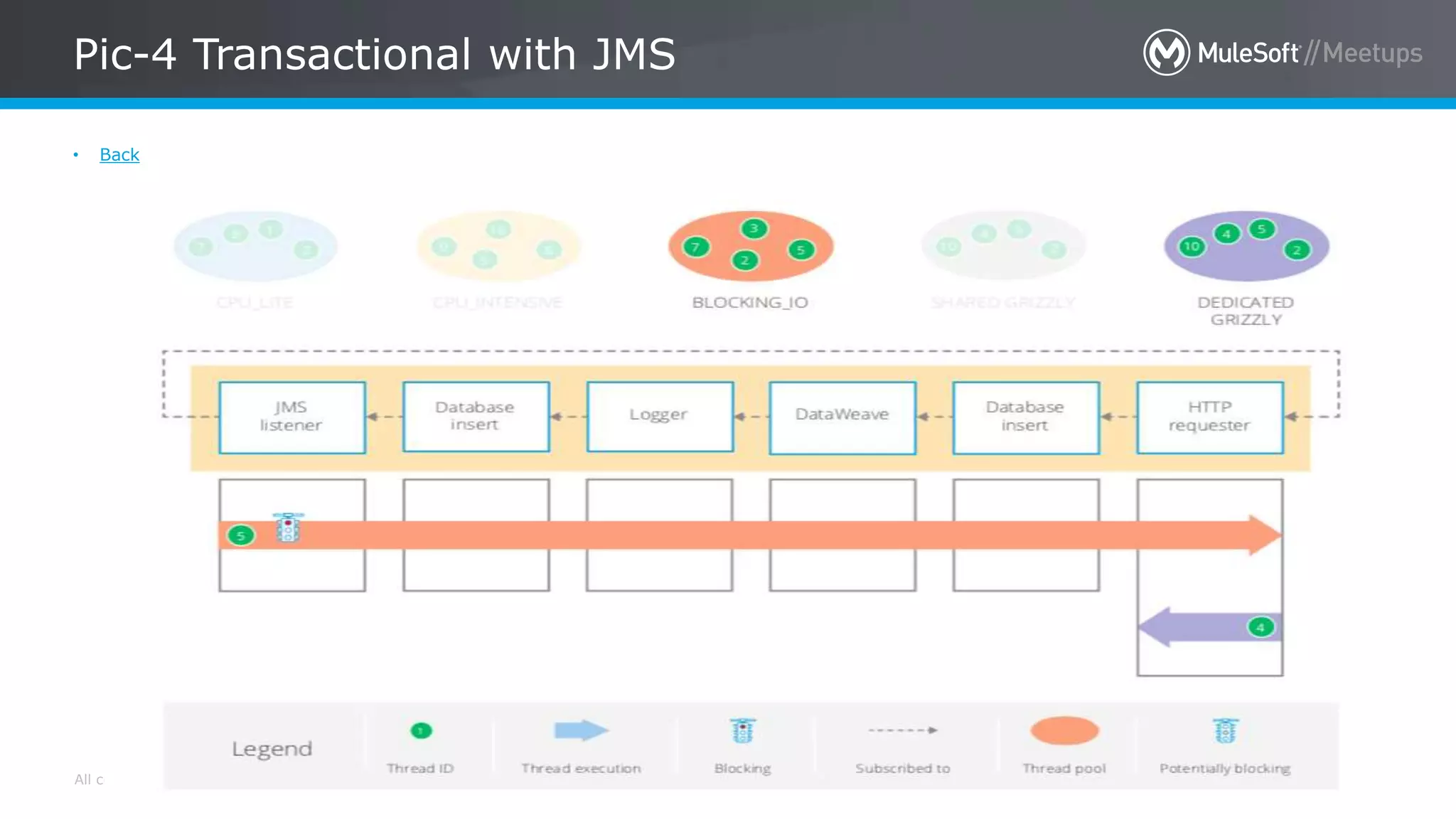
The document summarizes an agenda for a MuleSoft meetup discussing the new foundations of Mule 4. The agenda includes introductions of the organizers and speakers, two sessions on reactive programming and non-blocking operations in Mule 4, and a Q&A. Key points about Mule 4 include using reactive programming with non-blocking operations for improved scalability, new threading management, and support for streaming large payloads without holding entire objects in memory.