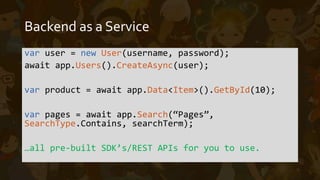
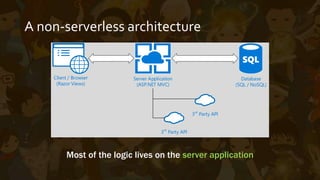
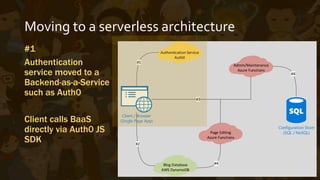
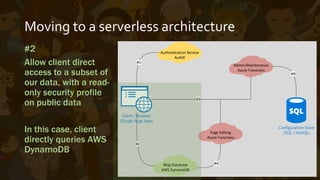
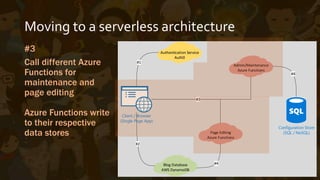
This document provides an overview of Azure Functions, a serverless computing service. It describes serverless architectures and how they differ from traditional server-based architectures by relying on third-party backend services. It then explains how Azure Functions allows developers to write short-lived, event-triggered functions using C# or other languages. The document outlines some pros and cons of Azure Functions, such as its reliance on App Services and ability to deploy code via source control. It concludes with a demonstration of Azure Functions.