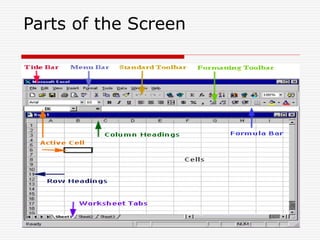
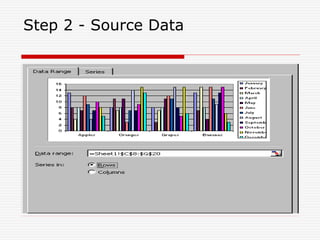
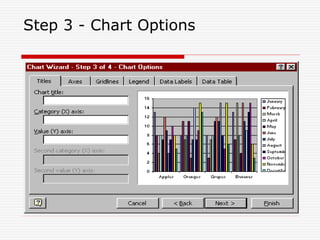
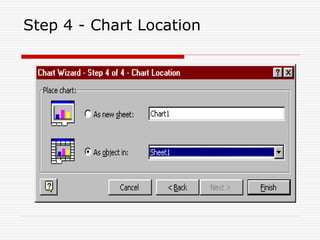
MS Excel is an electronic spreadsheet used to maintain small office activities like accounts. It allows automatic recalculation of data, data storage, built-in functions, charts, basic database capabilities, what-if analysis, macros, pivot tables, and importing/exporting data. Excel screens contain sheets where different types of data like labels, numbers, and formulas can be entered and edited. Charts can be created using a 4-step wizard to visualize data and common applications include accounting, budgets, and calculations.