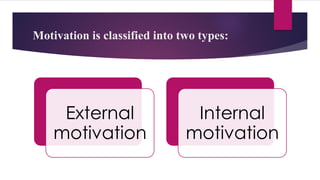
Motivation refers to the factors that energize and direct behavior. There are internal and external motivators. Basic motivational processes involve needs and drives like hunger, thirst, sex, and pain avoidance. Maslow's hierarchy of needs categorizes human motivations. Motivating factors include recognition, respect, interesting work, listening, and empowering others. Demotivating factors are unfair criticism, negative criticism, rewarding non-performers, fear of failure, complacency from success, lack of direction, and low self-esteem. The greatest motivator is self-motivation through belief in one's own responsibility for actions.