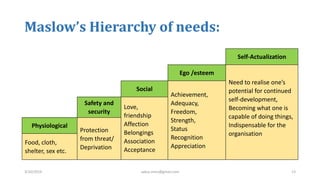
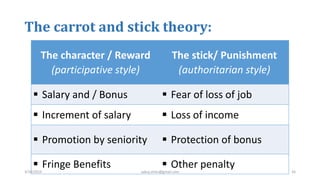
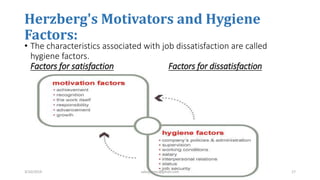
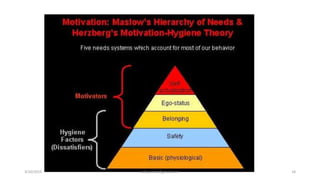
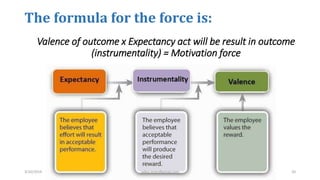
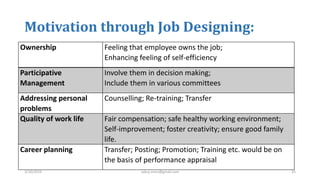
The document discusses motivation in the workplace. It defines motivation as the desires within individuals that stimulate behavior and action. It outlines several theories of motivation, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg's motivator-hygiene theory. The document also discusses the importance of motivation for employee performance and organizational goals and provides tips for motivating employees such as rewarding good performance, ensuring fair treatment, and fostering a participative environment.