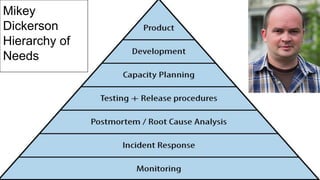
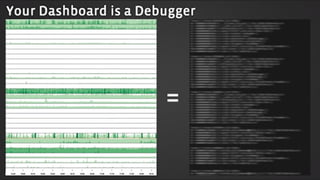
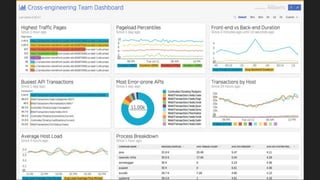
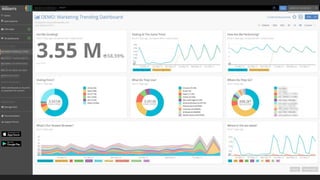
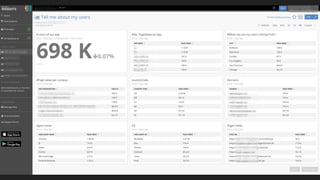
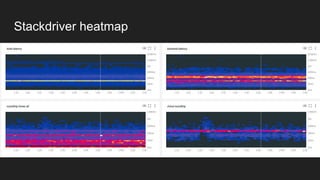
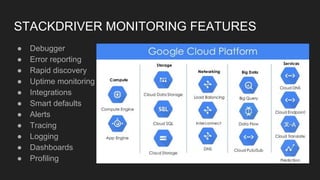
The document discusses various aspects of monitoring systems including:
- What monitoring involves such as collecting data, processing it, and displaying metrics.
- Why monitoring is important for analyzing trends, comparing performance, and debugging.
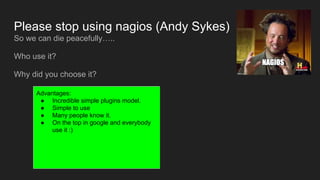
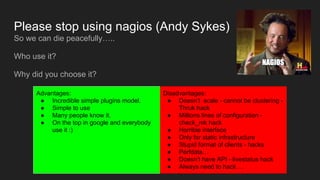
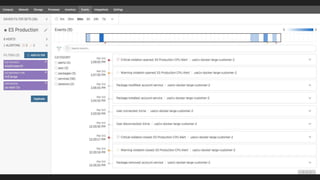
- Some advantages and disadvantages of the Nagios monitoring tool and why it may be time to stop using it.
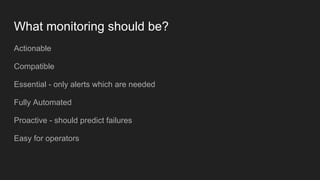
- What makes for good state and metric monitoring in terms of being actionable, automated, proactive, and easy for operators.
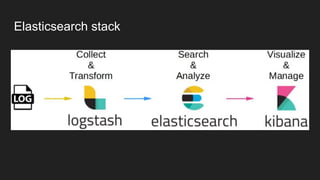
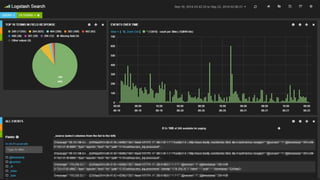
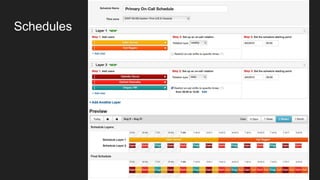
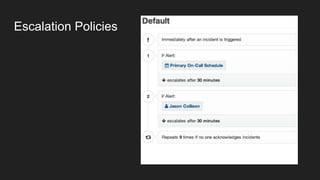
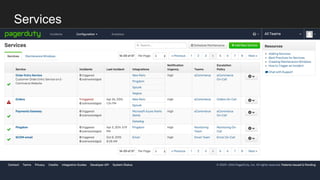
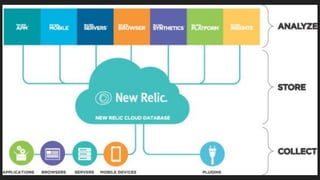
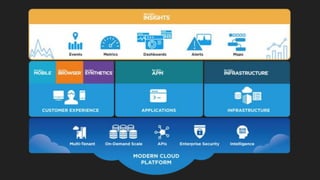
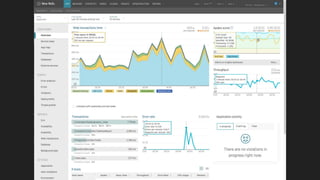
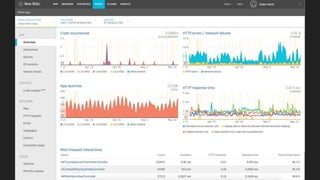
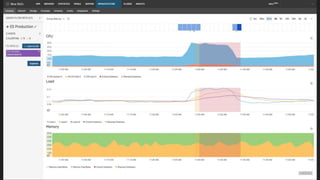
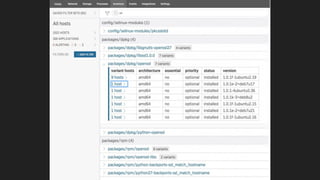
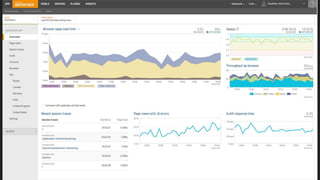
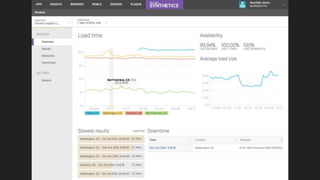
- Potential monitoring tools and strategies including Icinga2, Prometheus, Elasticsearch, PagerDuty, and New Relic.