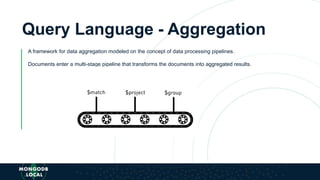
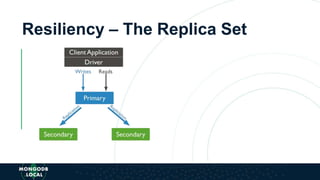
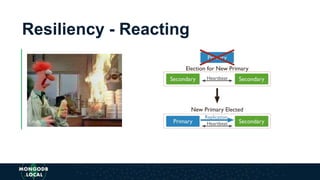
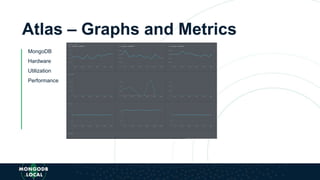
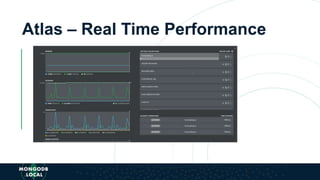
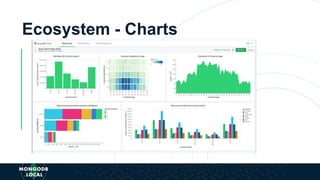
The document is an introduction to MongoDB, a cross-platform, open-source document-oriented database that uses JSON-like documents with dynamic schemas. It covers the features of MongoDB, including its document model, query language, and ecosystem, highlighting its flexibility and ease of use compared to traditional databases. Additionally, it discusses the importance of resiliency through replica sets and the various tools available within the MongoDB ecosystem.













![Not just key-
valueMongoDB’s document model is not just a key-value
store.
Rich document composition is possible, and
encouraged.
Store embedded objects, arrays, rich data types, and
more.
{
"title": "The Martian",
"year": 2015,
"runtime": 130,
"released": ISODate("2015-10-
02T00:00:00Z"),
"cast": [
"Kate Mara",
"Matt Damon",
"Jessica Chastain",
"Kristen Wiig"
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/800amnorthintrotodocumentdatabases-brettgray-190326065358/85/MongoDB-local-Sydney-An-Introduction-to-Document-Databases-with-MongoDB-14-320.jpg)





![Query Language
ALTER TABLE movies ADD cast
ARRAY
UPDATE movies SET cast =
["Morgan Freeman", "Tim
Robbins"] WHERE title = "The
Shawshank Redemption"
db.movies.updateOne(
{title: "The Shawshank
Redemption"},
{$set: { "cast": ["Morgan
Freeman", "Tim Robbins" ] } }
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/800amnorthintrotodocumentdatabases-brettgray-190326065358/85/MongoDB-local-Sydney-An-Introduction-to-Document-Databases-with-MongoDB-22-320.jpg)
![Query Language
ALTER TABLE movies ADD cast
ARRAY
UPDATE movies SET cast =
["Morgan Freeman", "Tim
Robbins"] WHERE title = "The
Shawshank Redemption"
db.movies.updateOne(
{title: "The Shawshank
Redemption"},
{$set: { "cast": ["Morgan
Freeman", "Tim Robbins" ] } }
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/800amnorthintrotodocumentdatabases-brettgray-190326065358/85/MongoDB-local-Sydney-An-Introduction-to-Document-Databases-with-MongoDB-23-320.jpg)