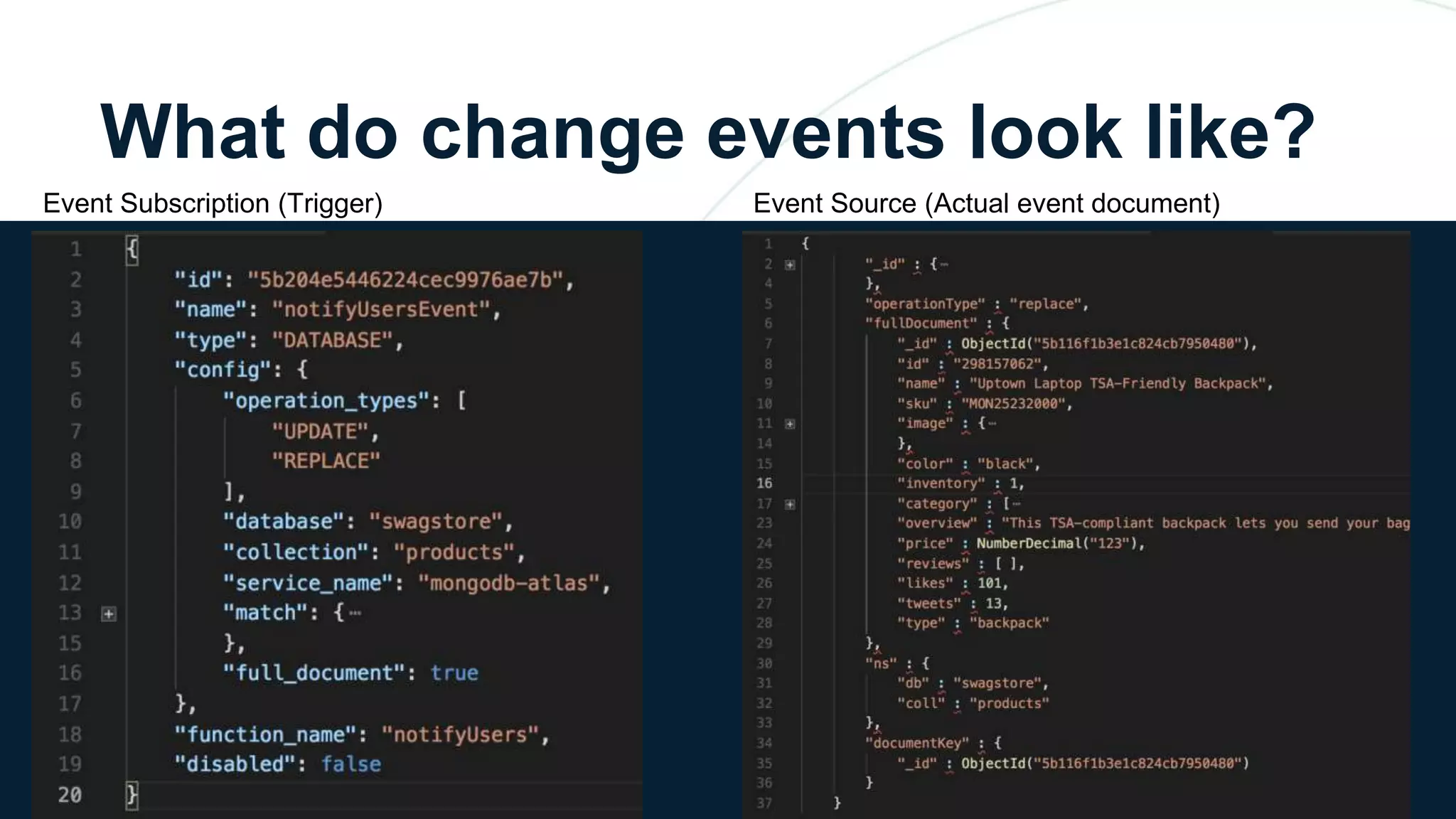
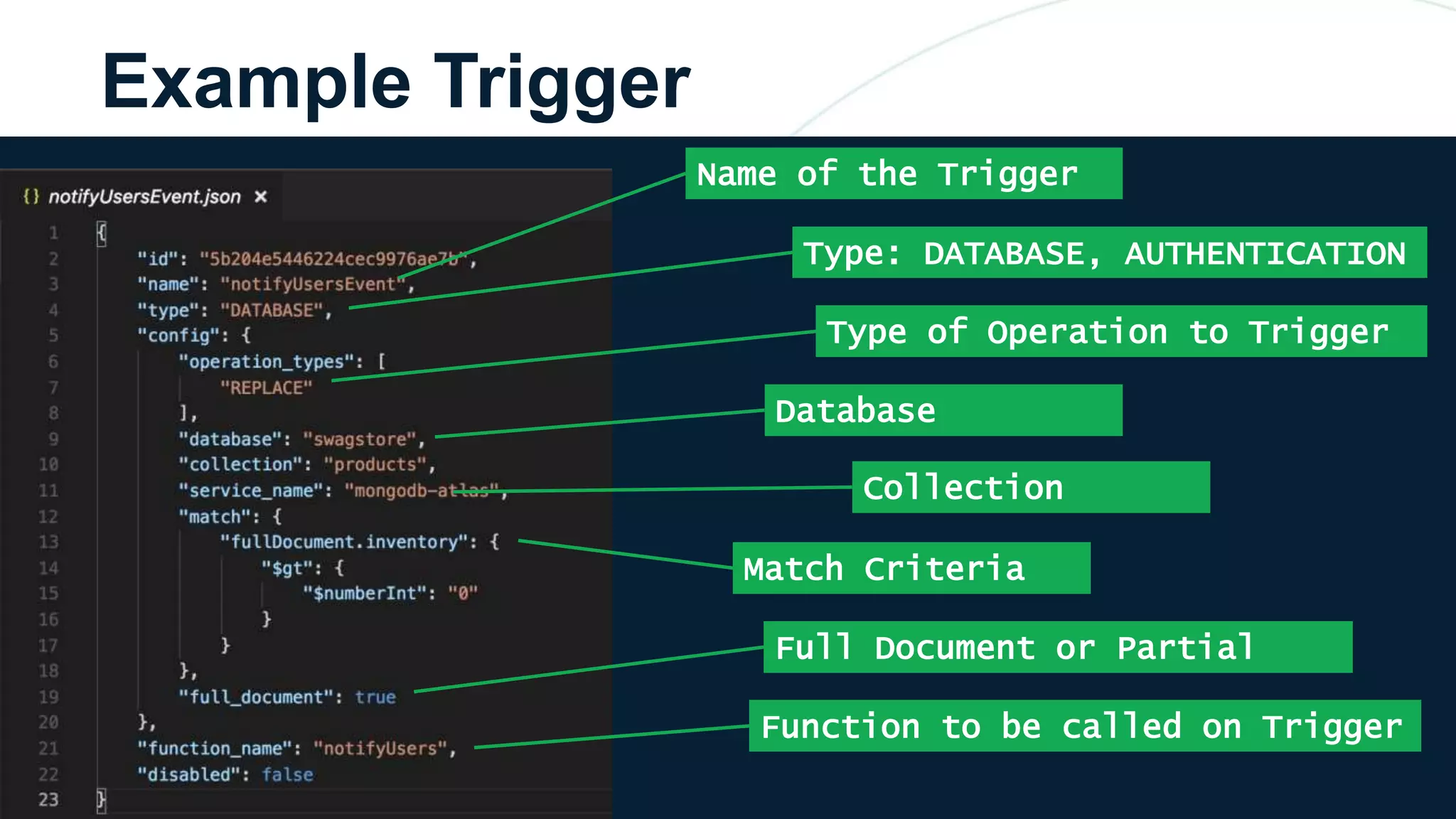
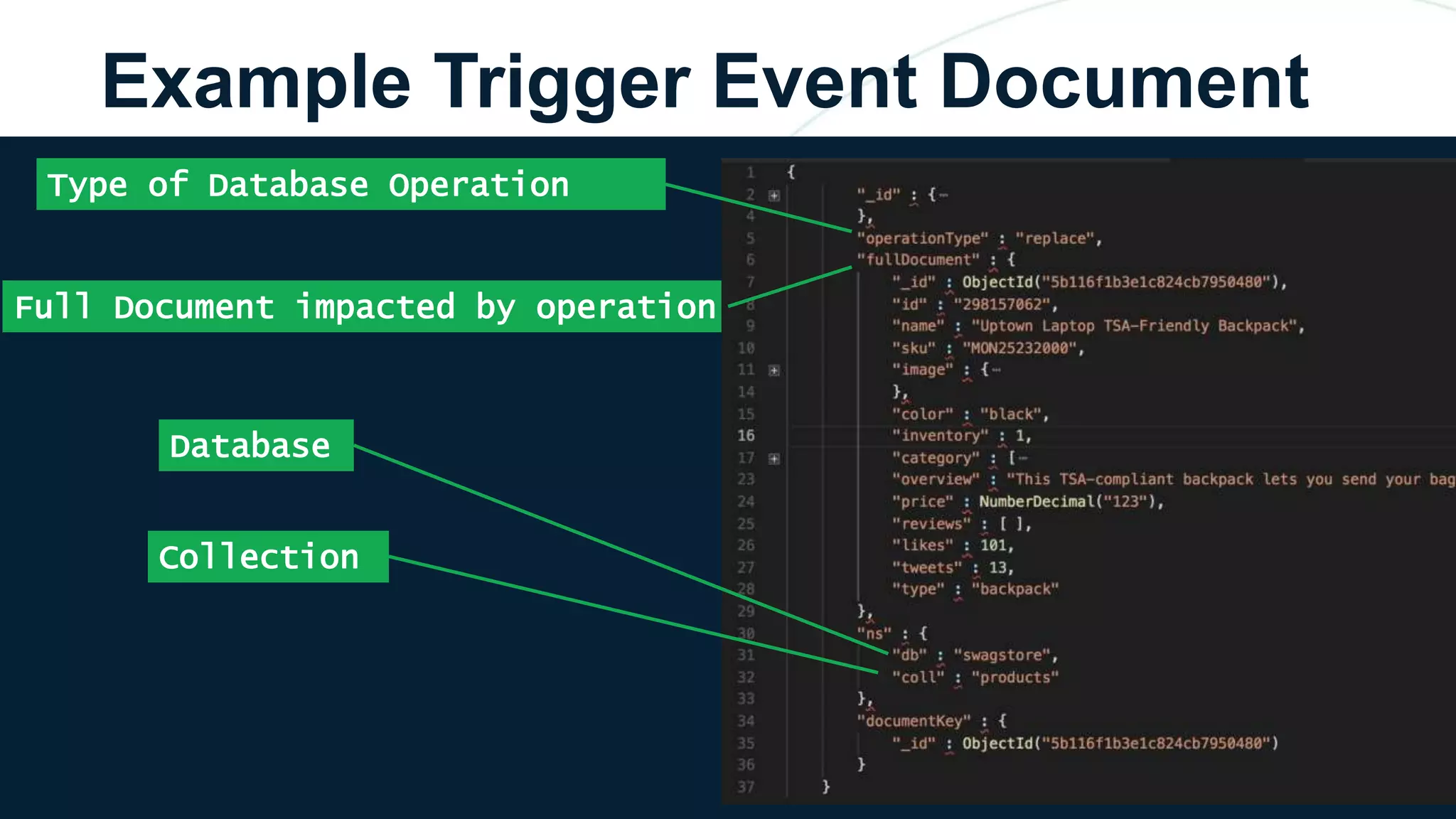
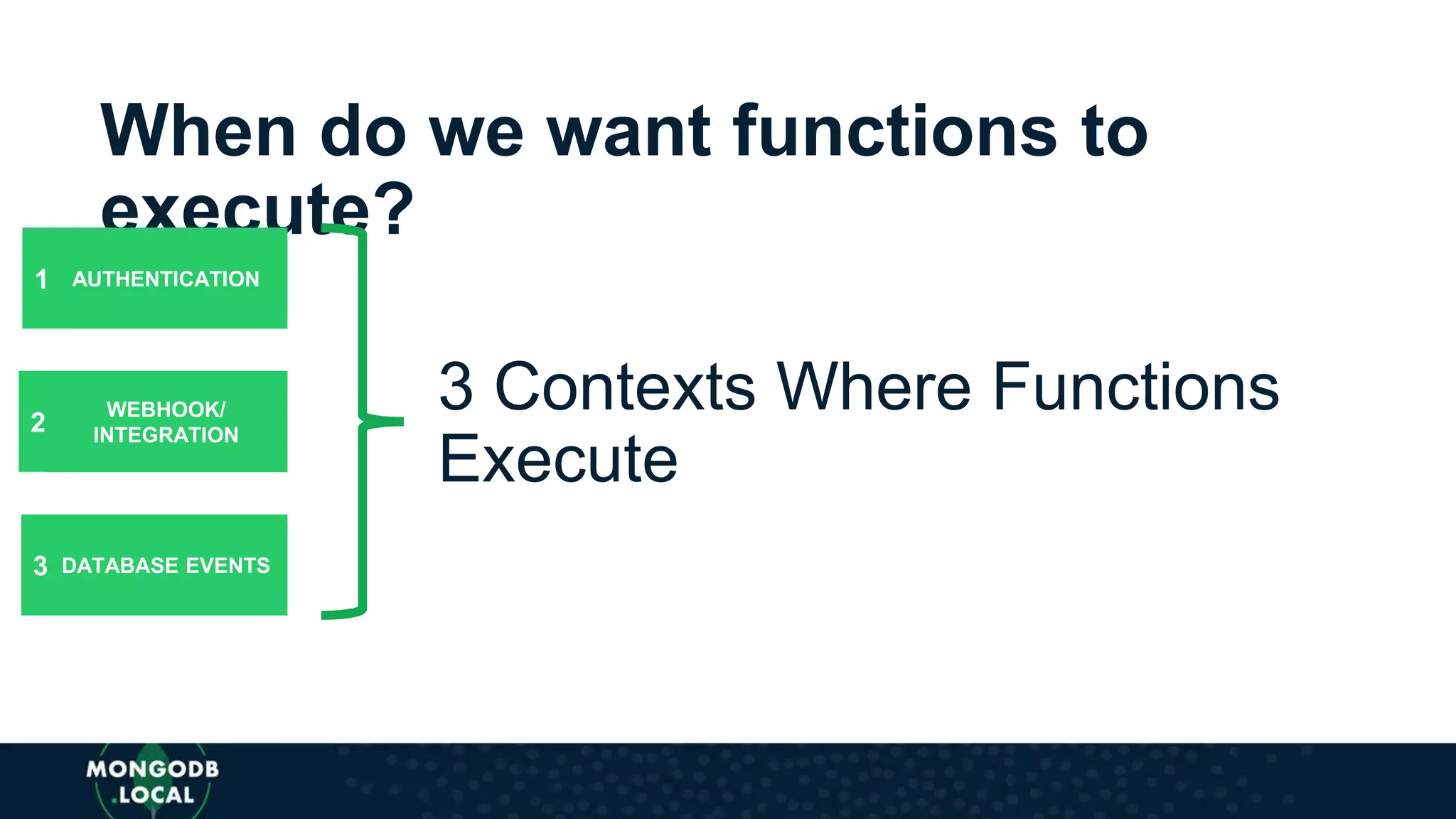
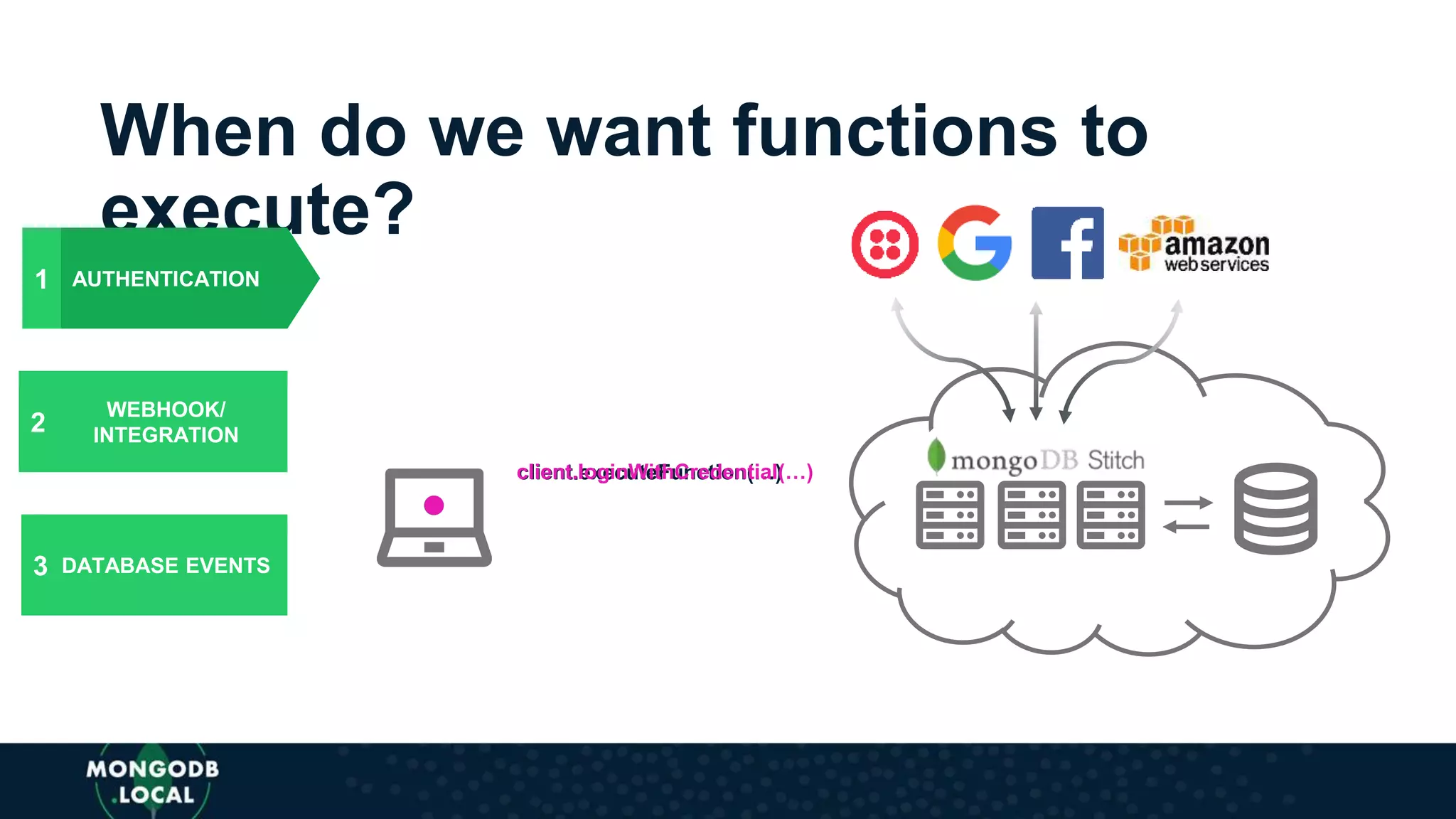
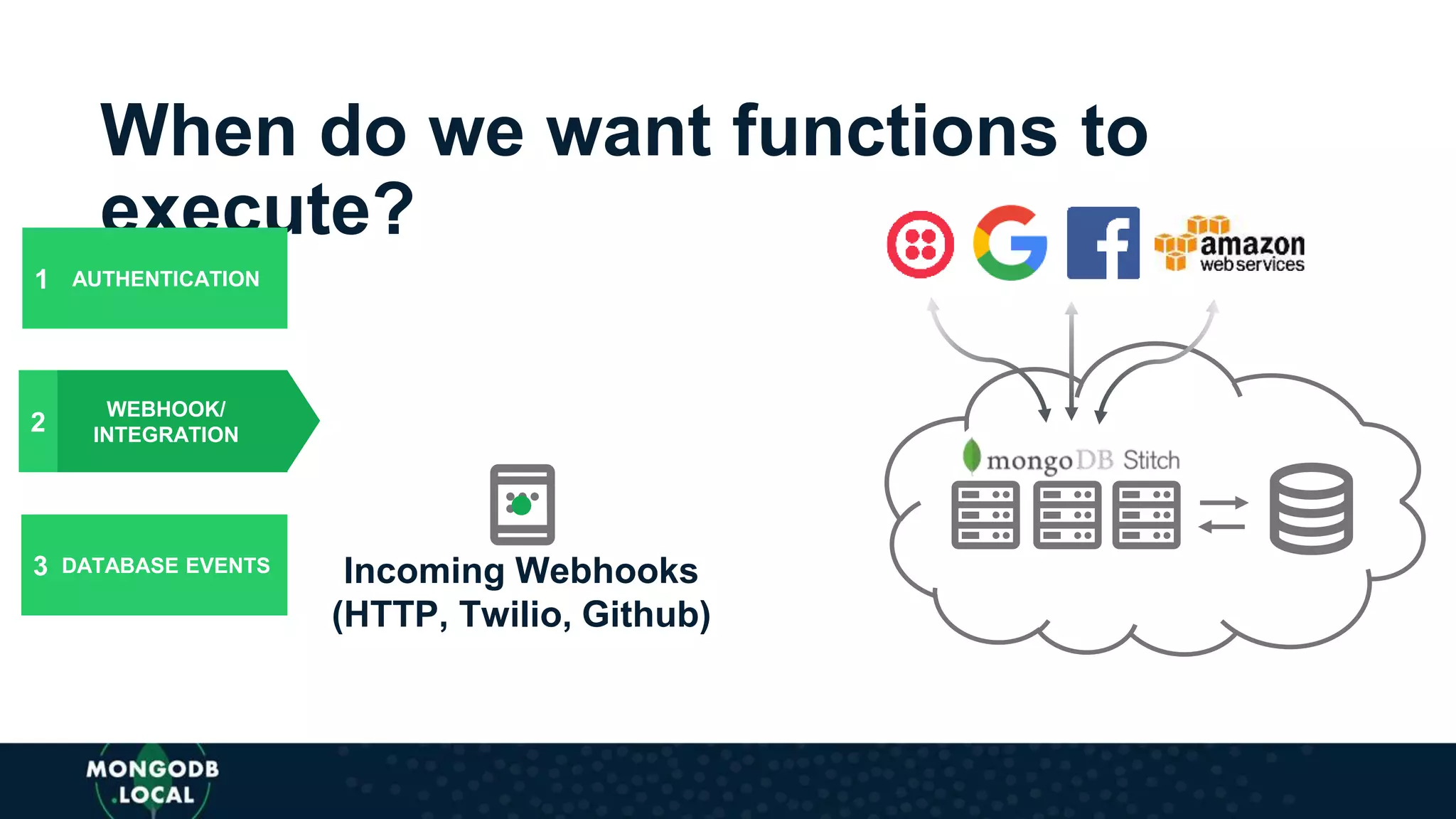
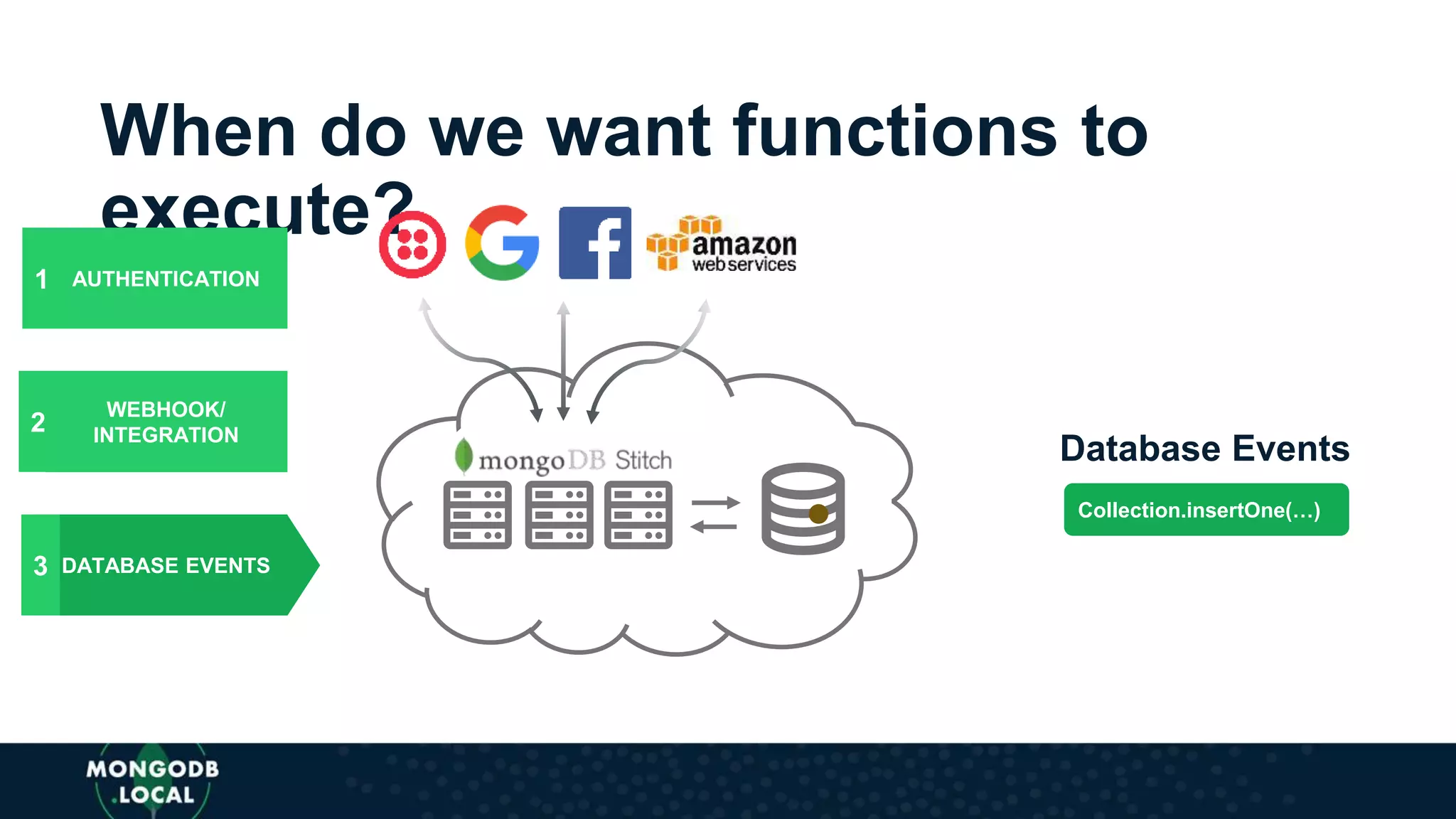
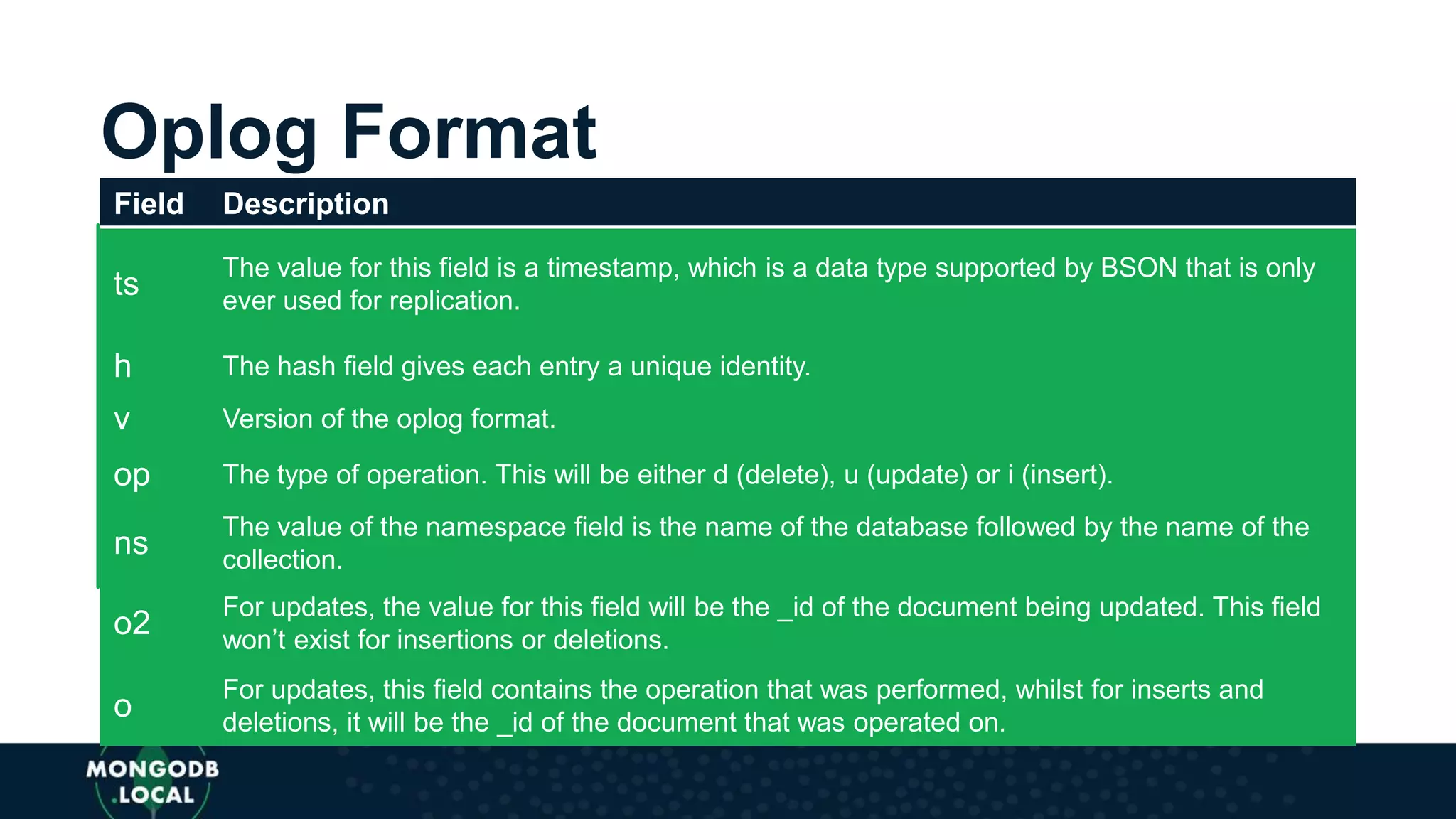
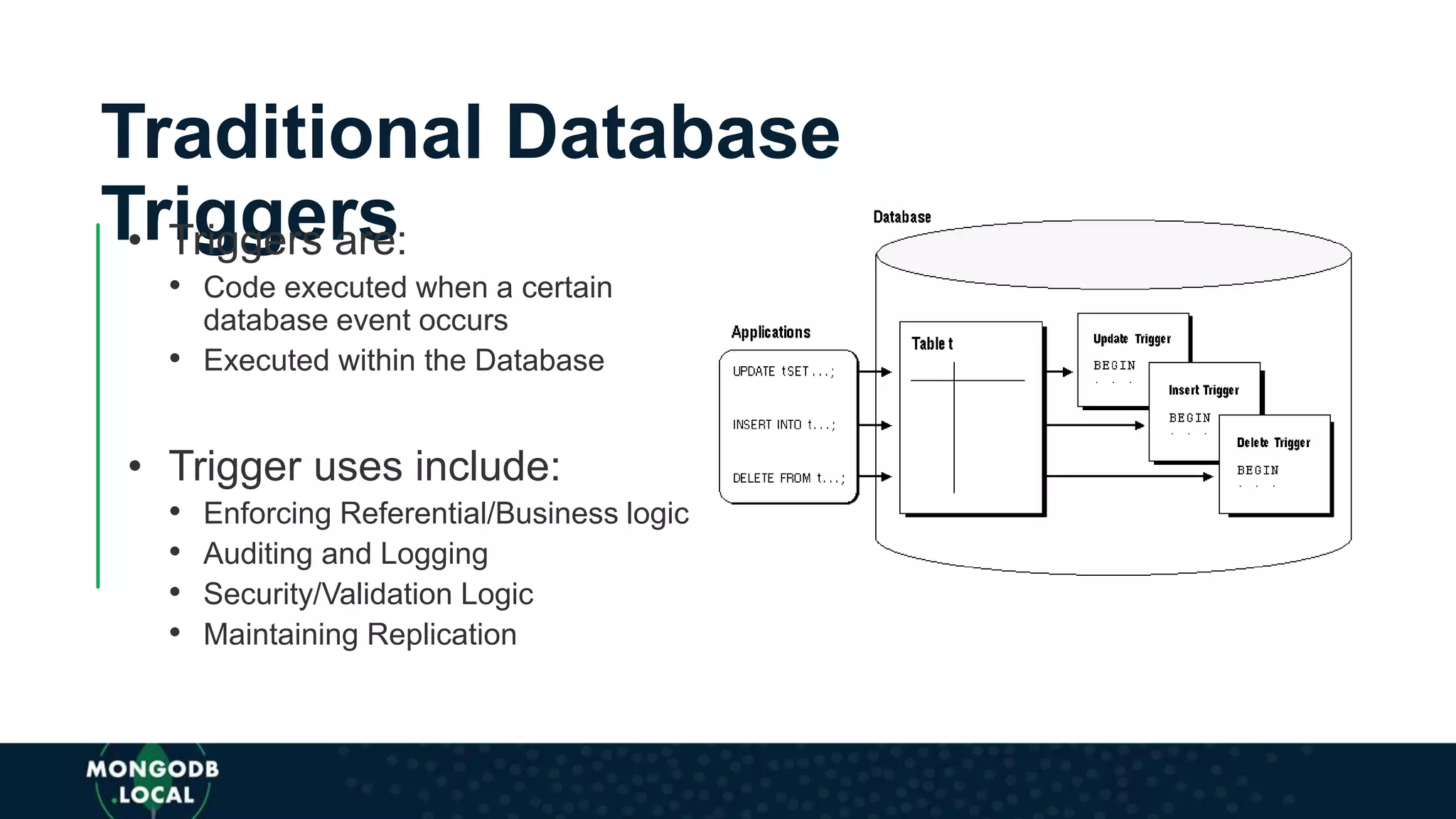
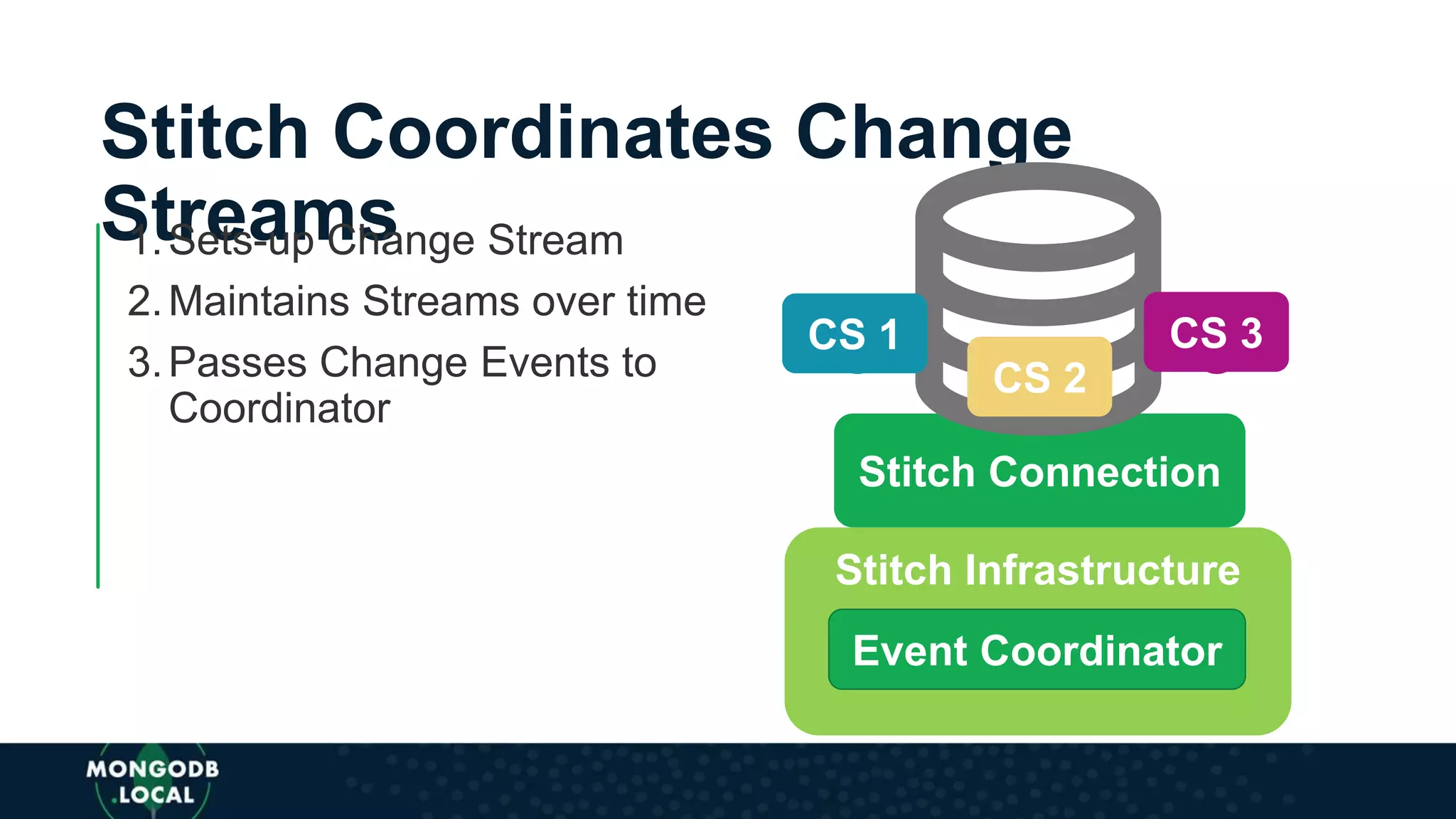
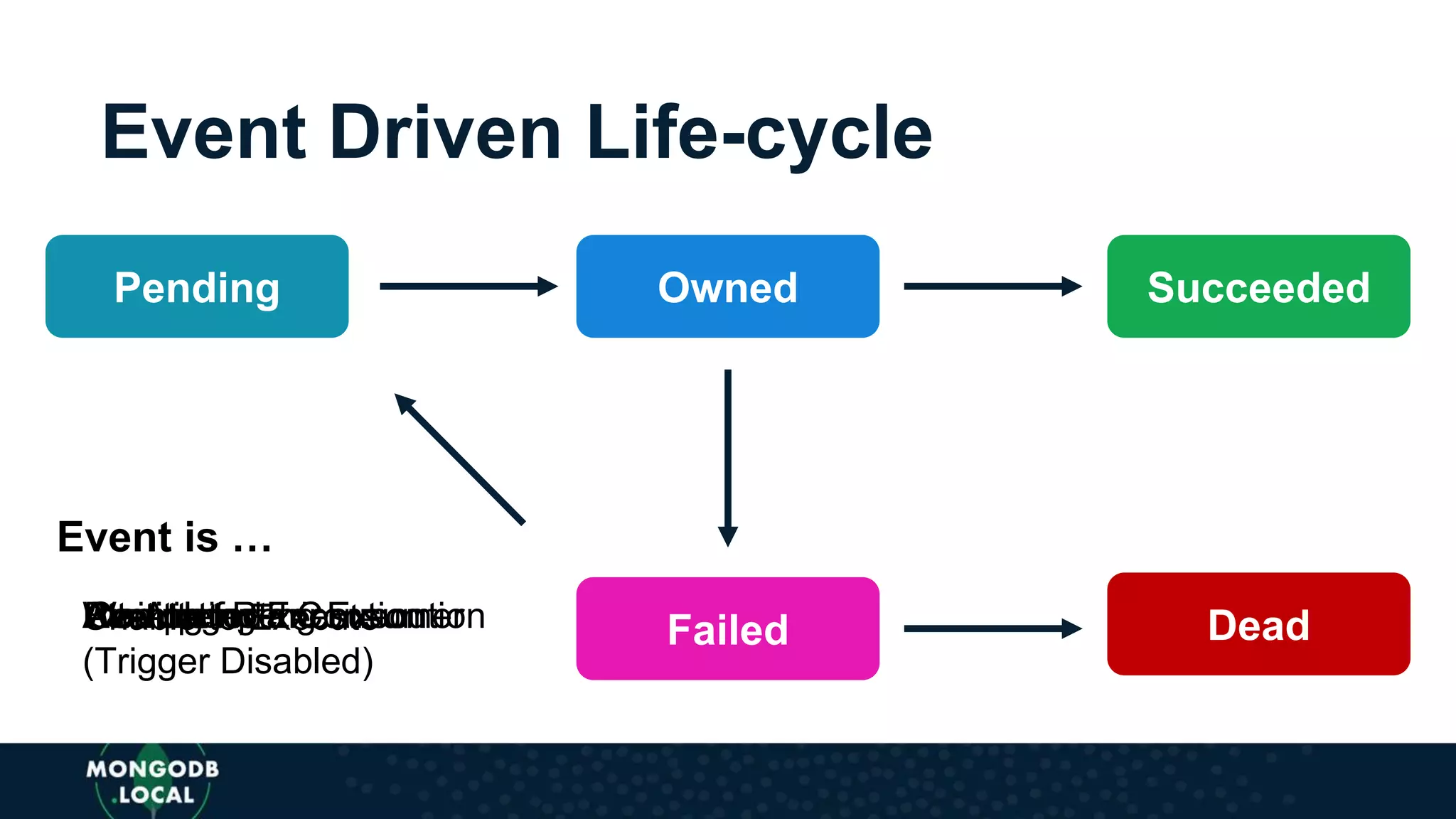
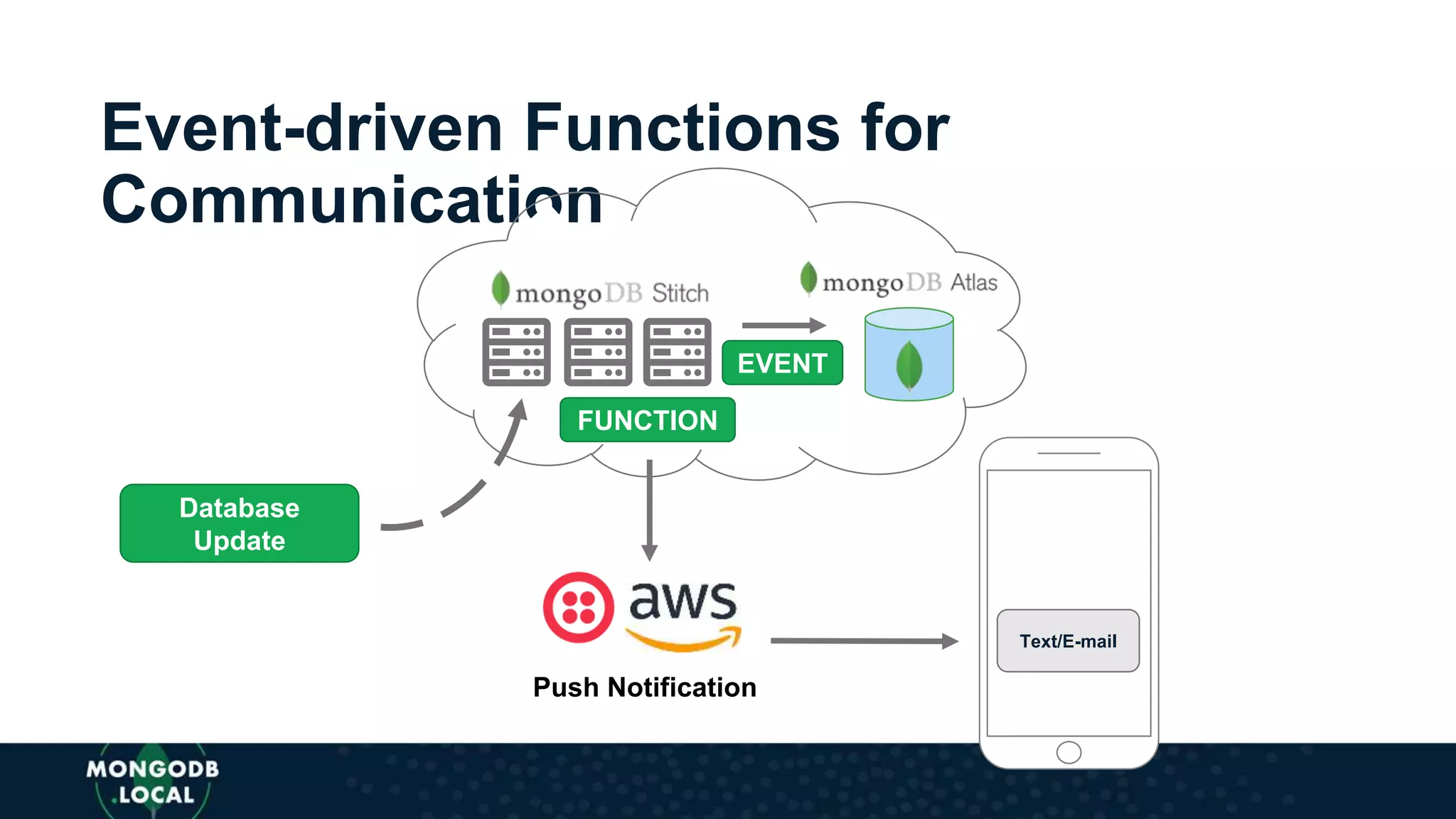
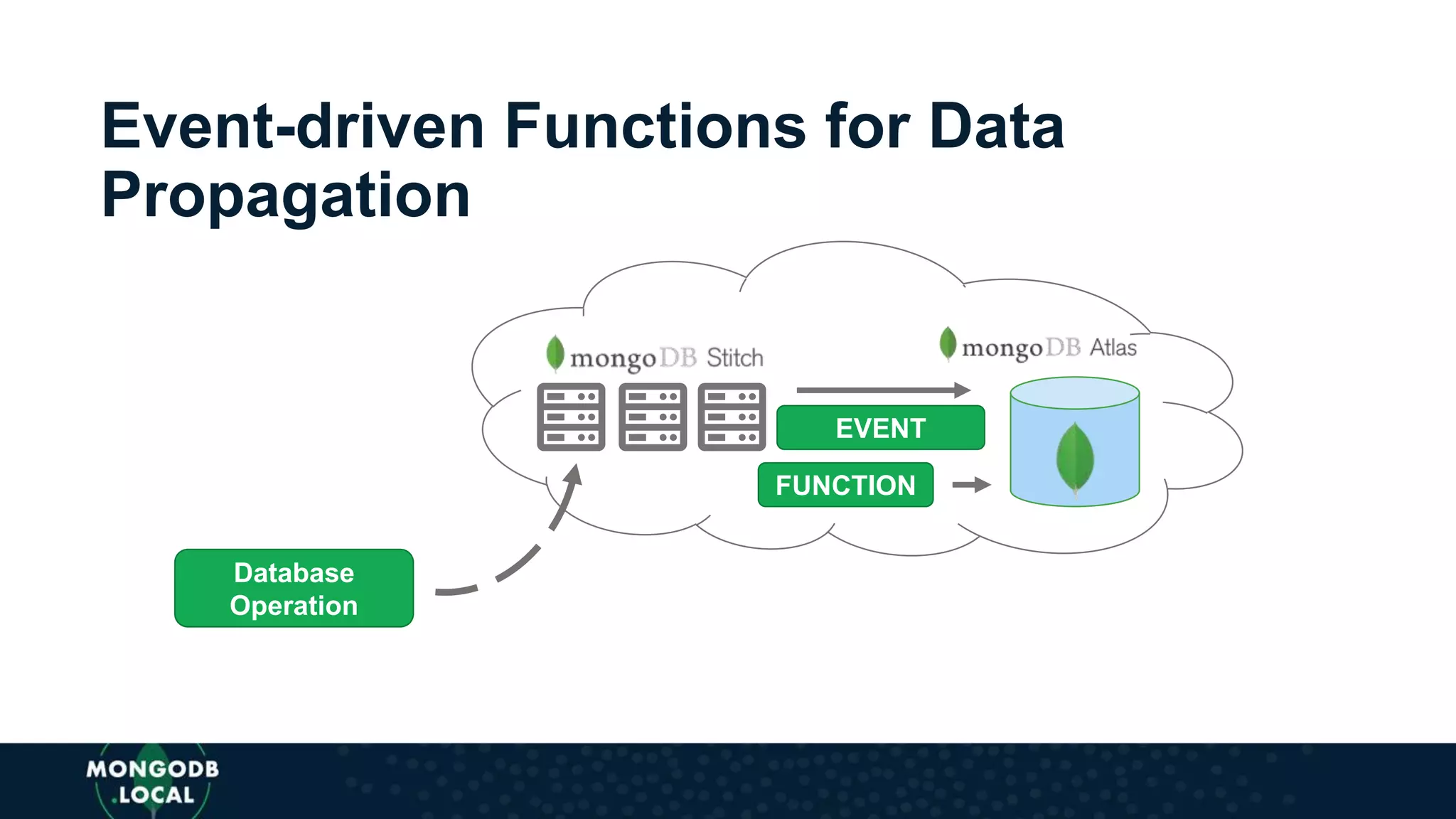
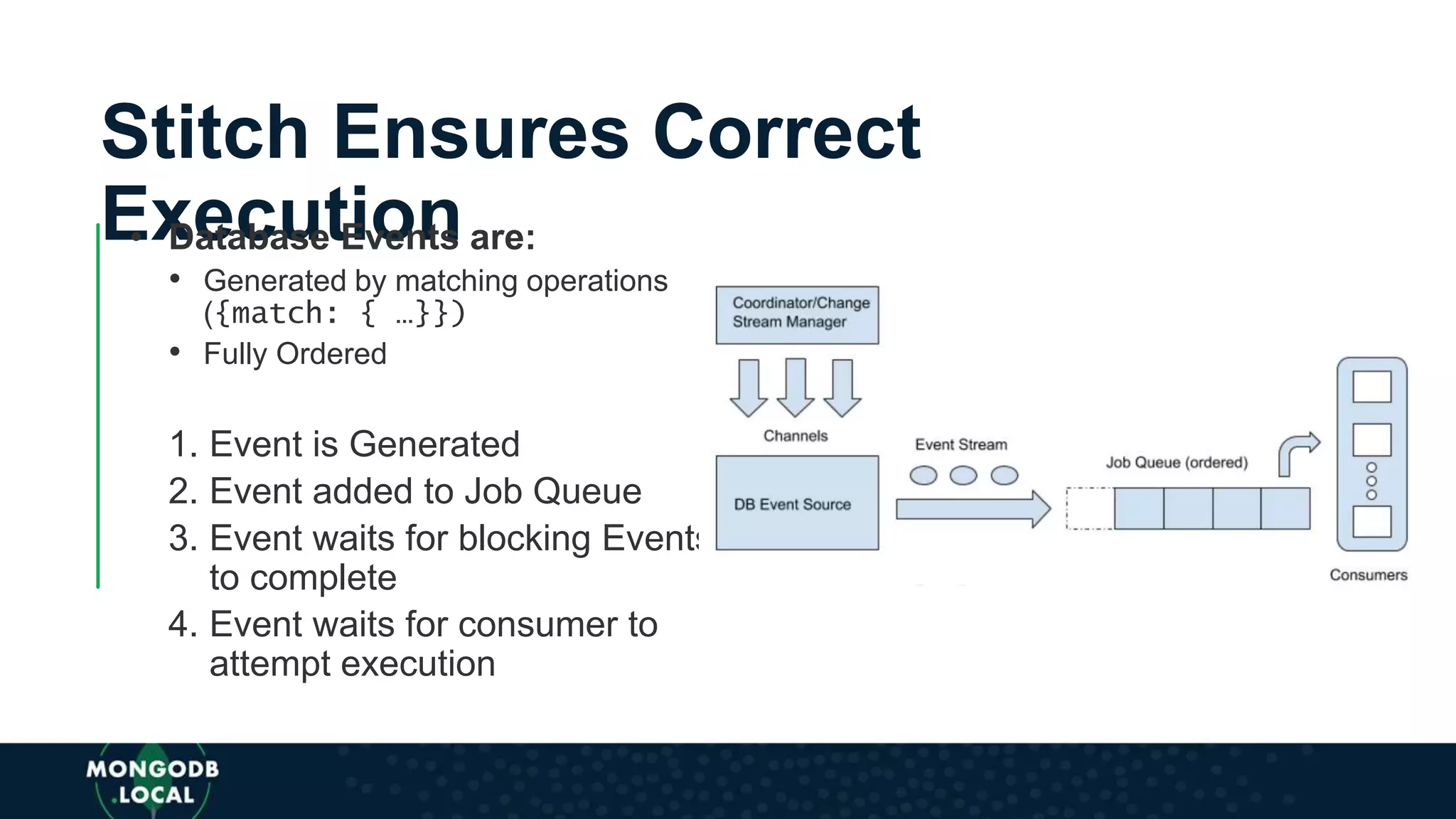
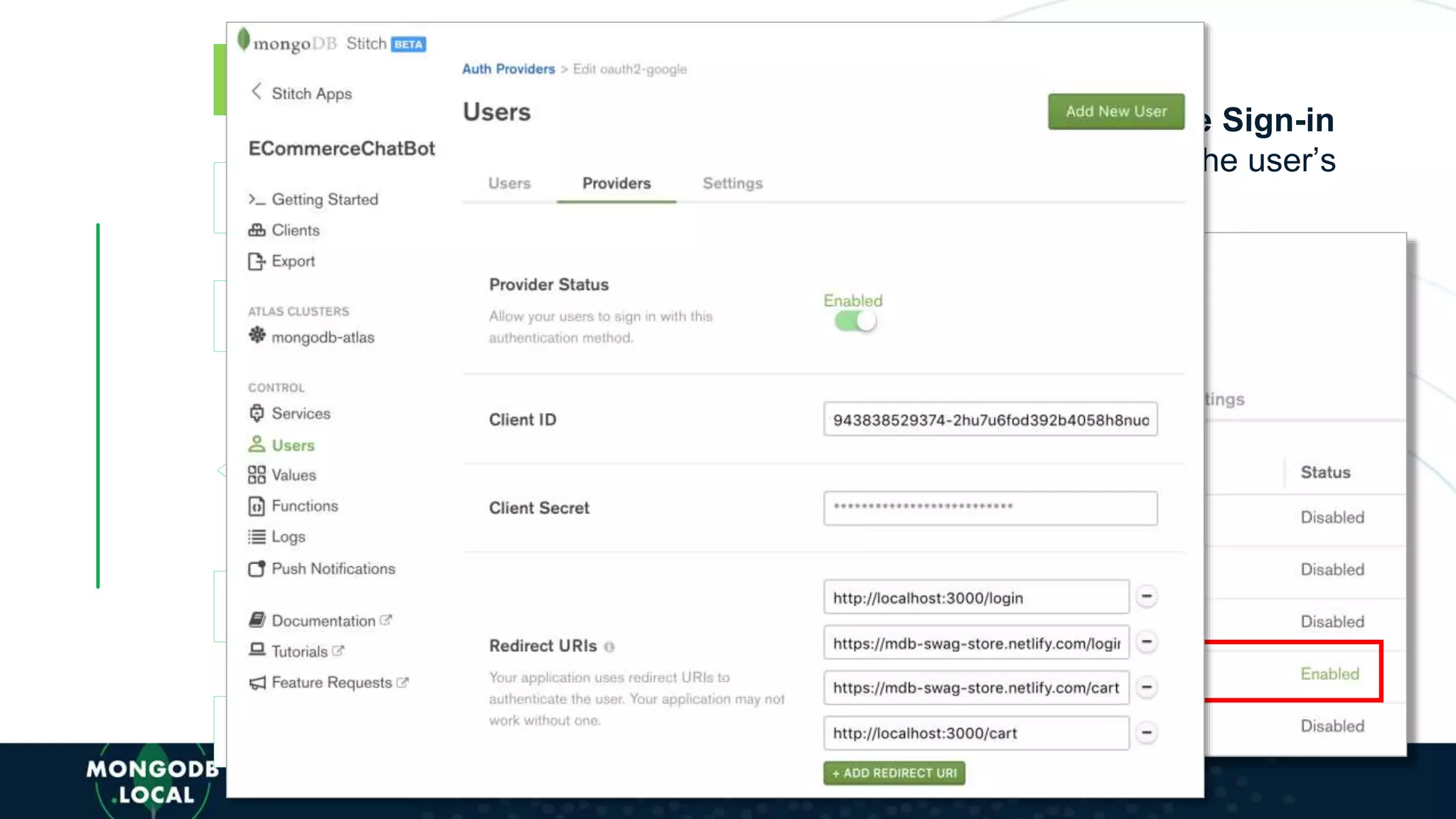
The document discusses the capabilities and evolution of MongoDB Stitch, focusing on its triggers, change streams, and integration with various services and databases. It emphasizes the ease of use, scalability, and efficiency of Stitch in application development, allowing developers to concentrate on building applications rather than managing infrastructure. The document also covers event-driven functions and provides an overview of implementing a retail store application using Stitch features.















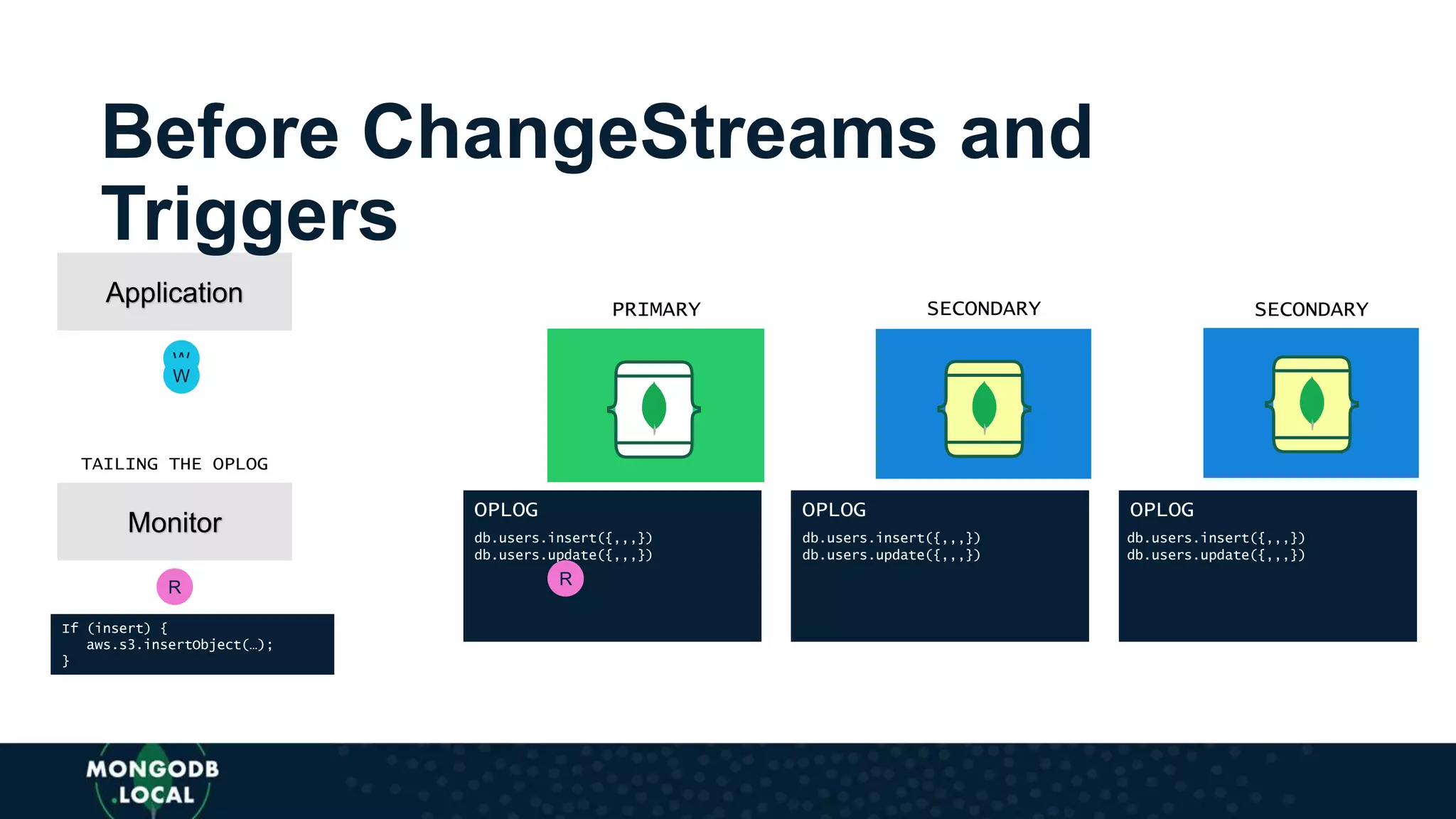
![Before Change Streams: Oplog
var MongoDB = require('mongodb');
oplogurl = 'mongodb+srv://mike:<PASSWORD>@dotlocaltalk-hhfkg.mongodb.net/test?retryWrites=true’;
MongoDB.MongoClient.connect(oplogurl, function(err, db) {
db.collection("oplog.rs", function(err, oplog) {
oplog.find({}, {
ts: 1
}).sort({
$natural: -1
}).limit(1).toArray(function(err, data) {
lastOplogTime = data[0].ts;
if (lastOplogTime) {
queryForTime = {
$gt: lastOplogTime
};
} else {
tstamp = new MongoDB.Timestamp(0, Math.floor(new Date().getTime() / 1000))
queryForTime = {
$gt: tstamp
};
}
cursor = oplog.find({
ts: queryForTime
}, {
tailable: true,
awaitdata: true,
oplogReplay: true,
numberOfRetries: -1
});
stream = cursor.stream();
stream.on('data', function(oplogdoc) {
console.log(oplogdoc);
});
});
});
})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/355-theater4-stitch-triggers-092018-short-generictemplate-181002150239/75/MongoDB-local-Austin-2018-Ch-Ch-Ch-Ch-Changes-Taking-Your-MongoDB-Stitch-Application-to-the-Next-Level-With-Triggers-25-2048.jpg)

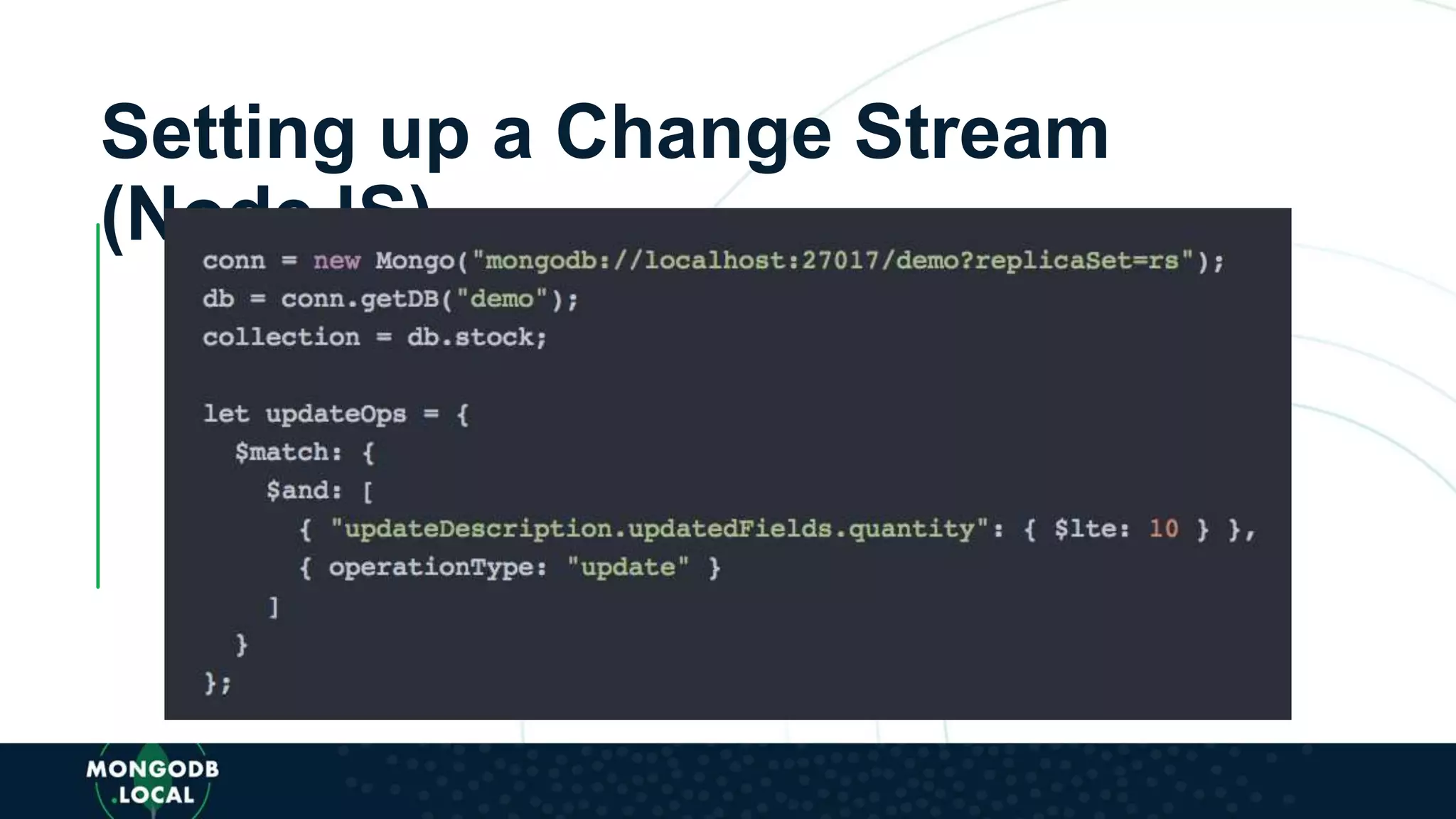





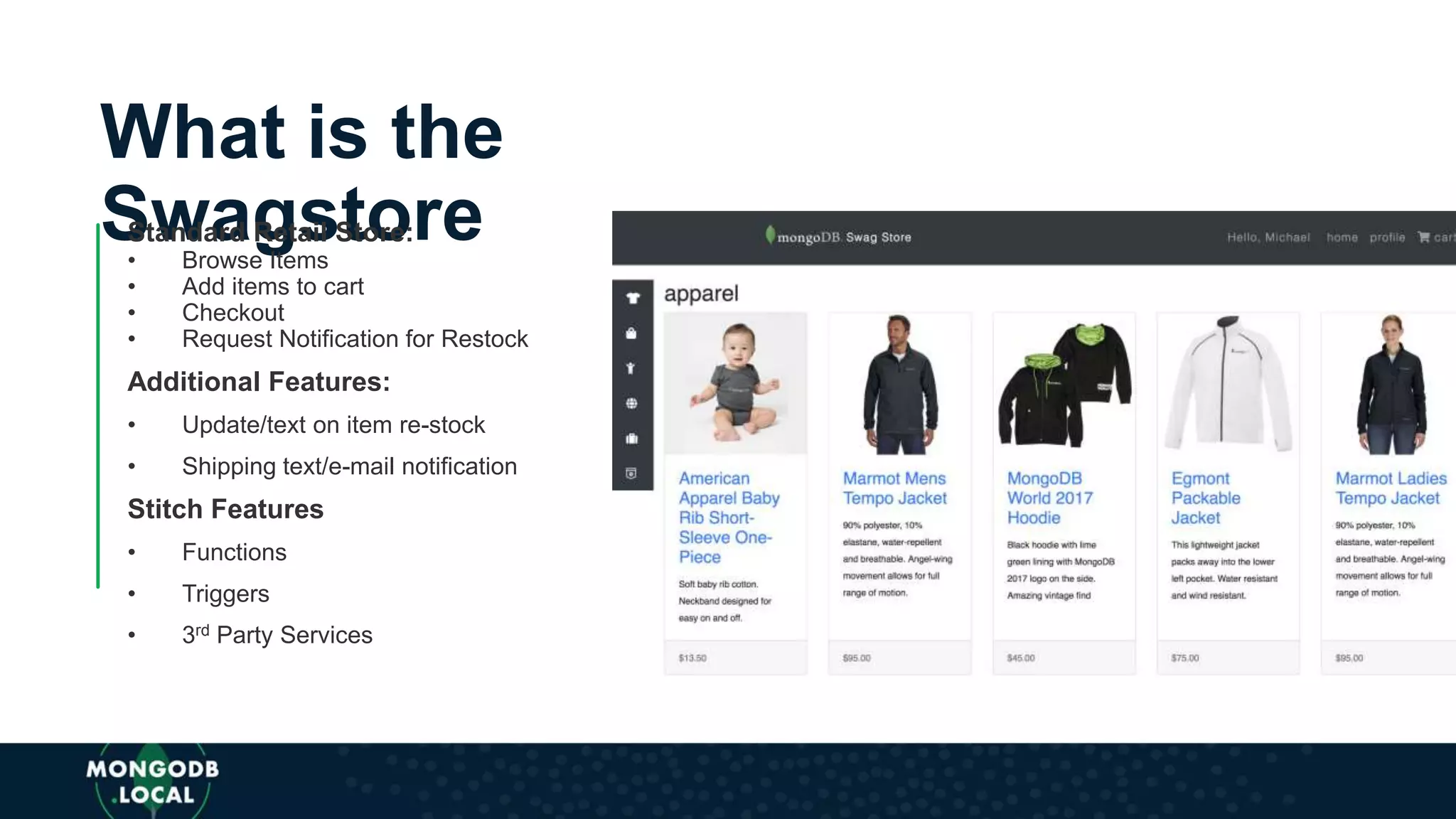
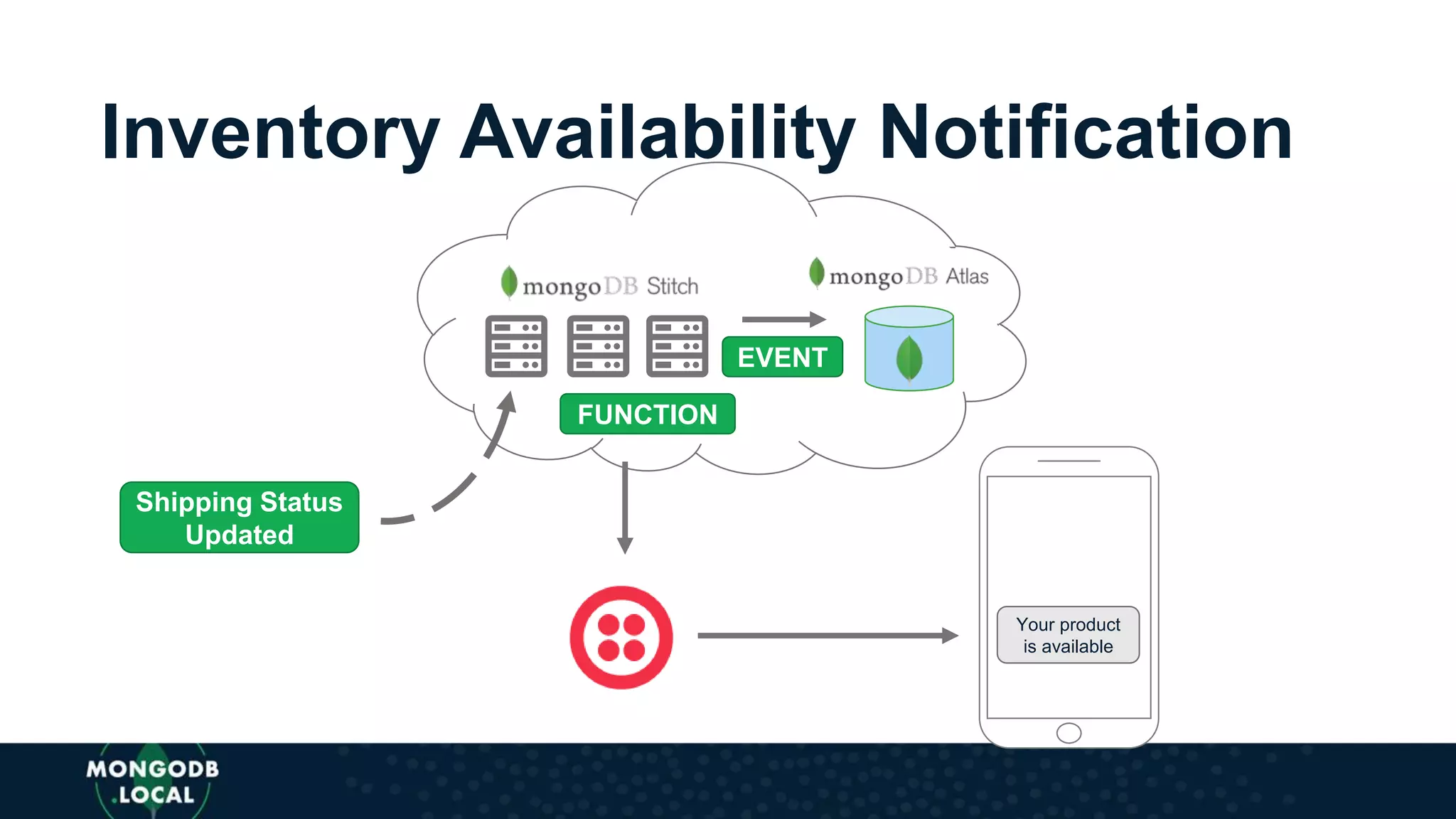


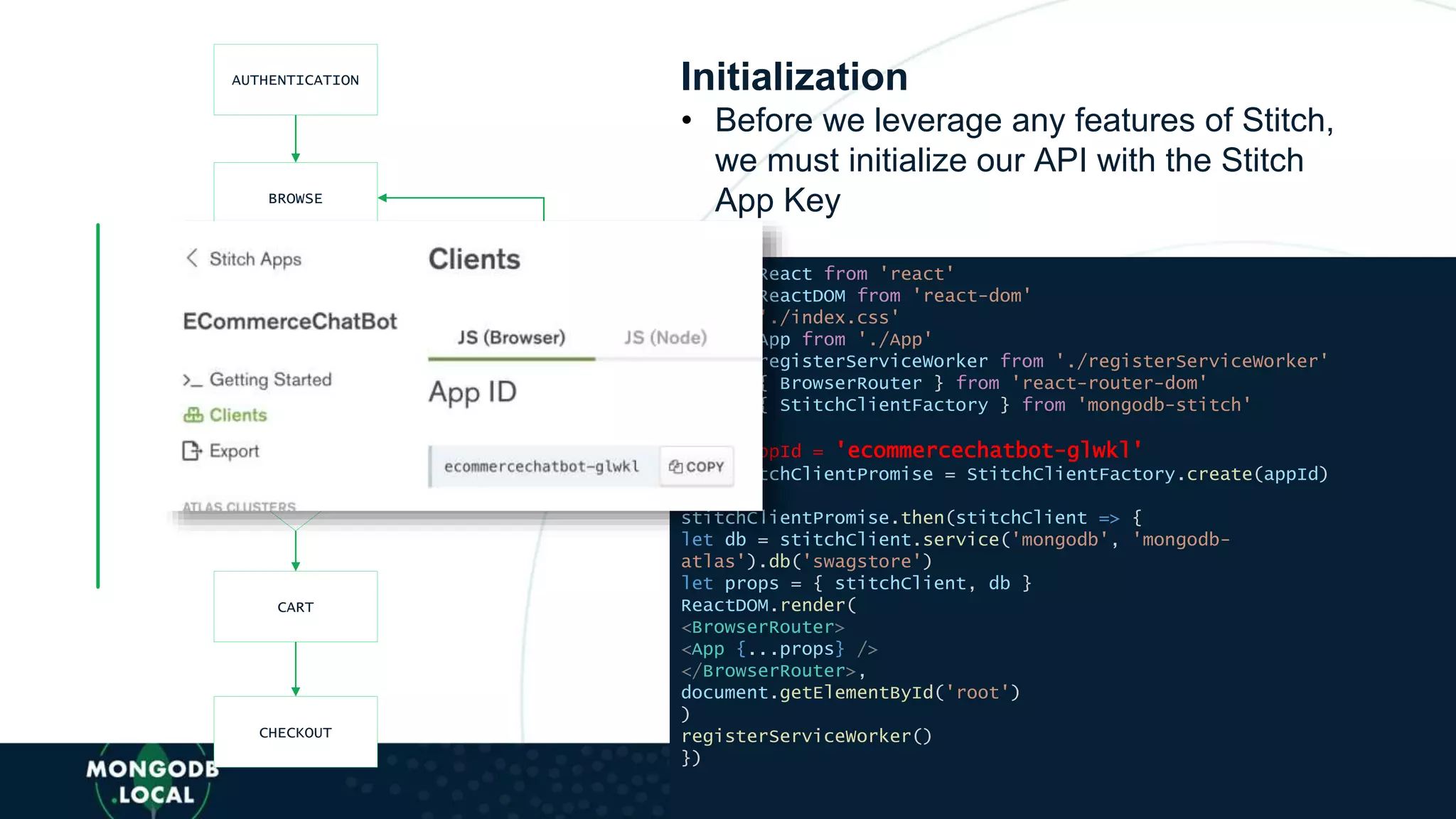
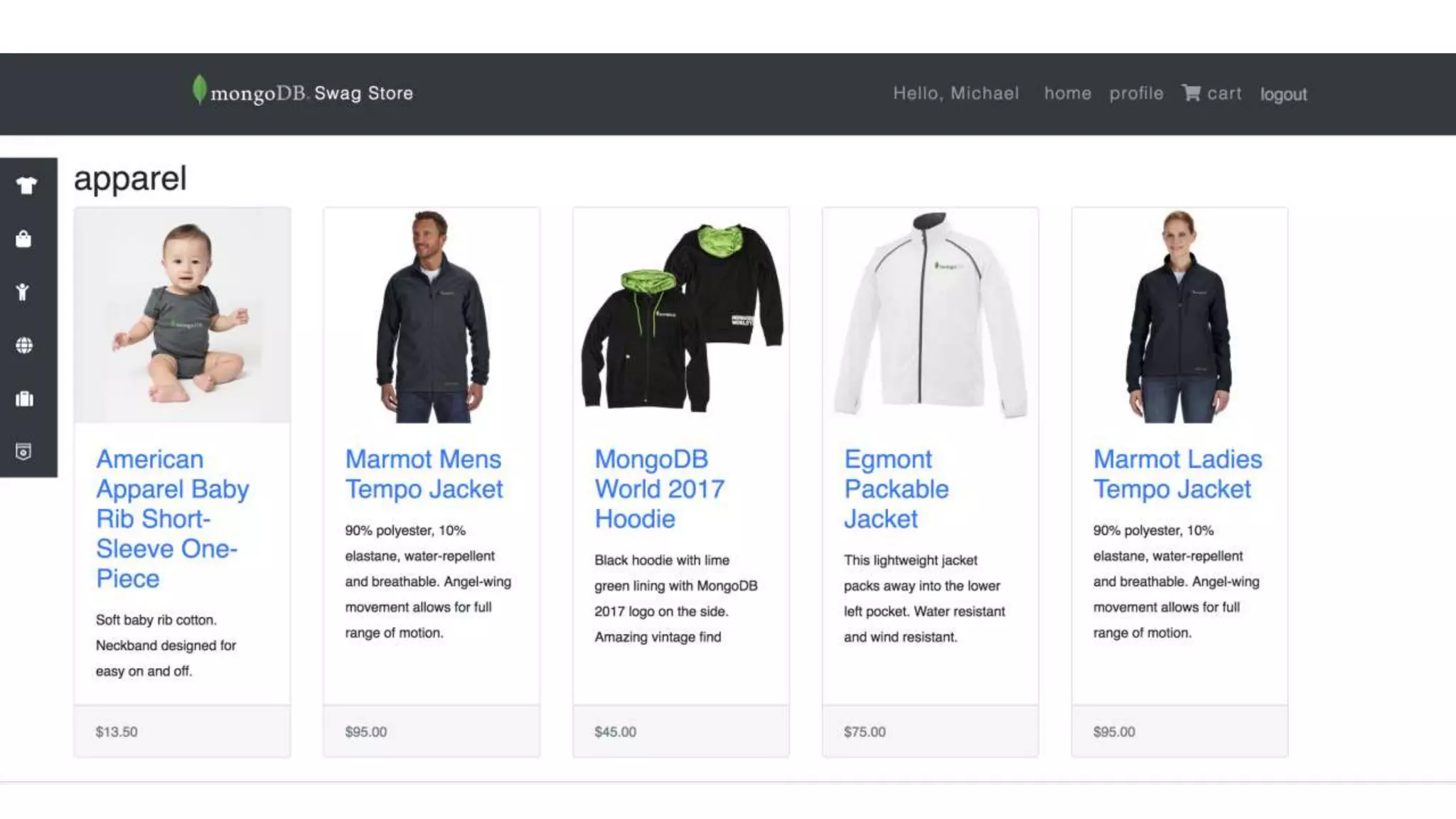
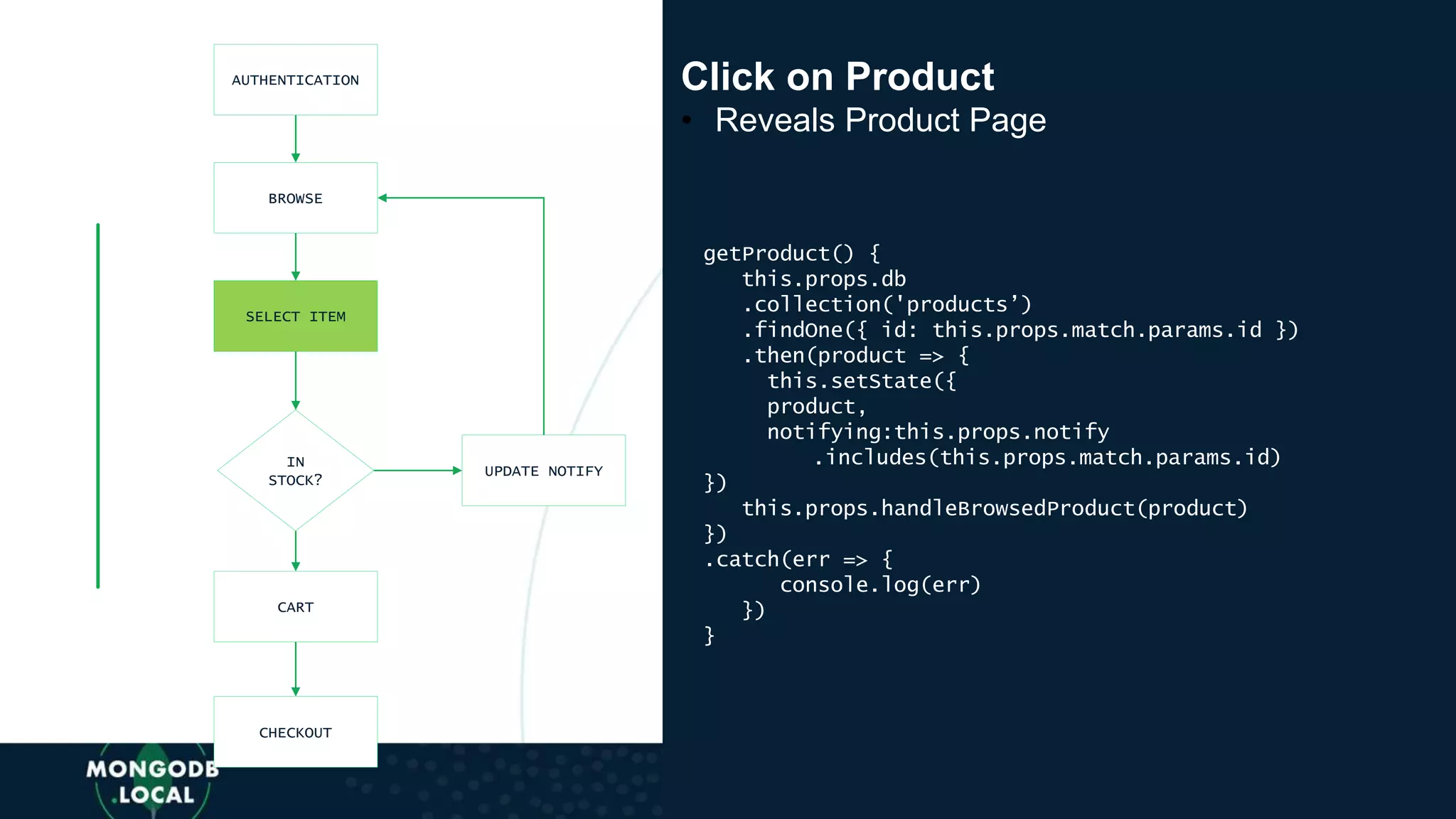
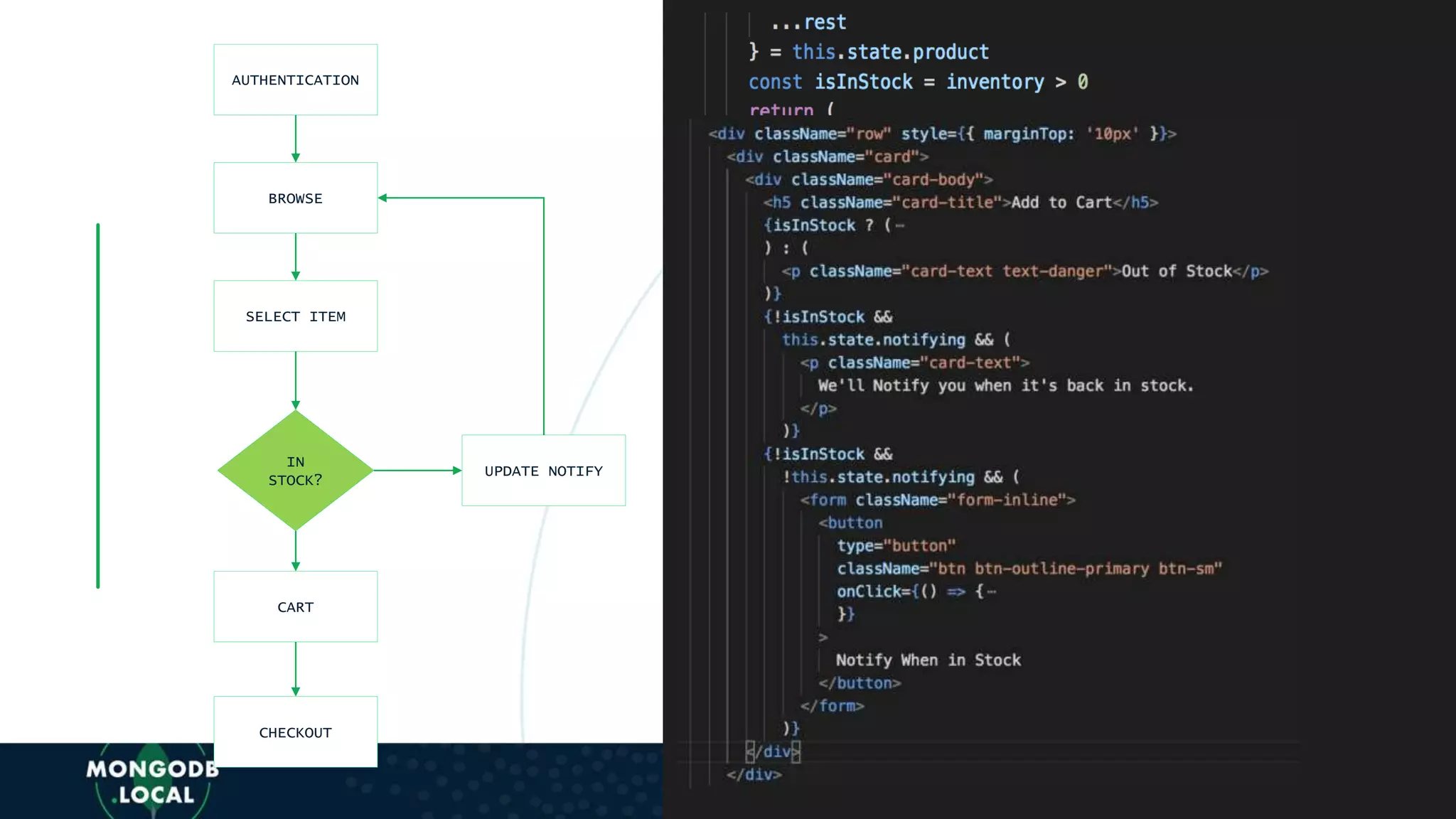
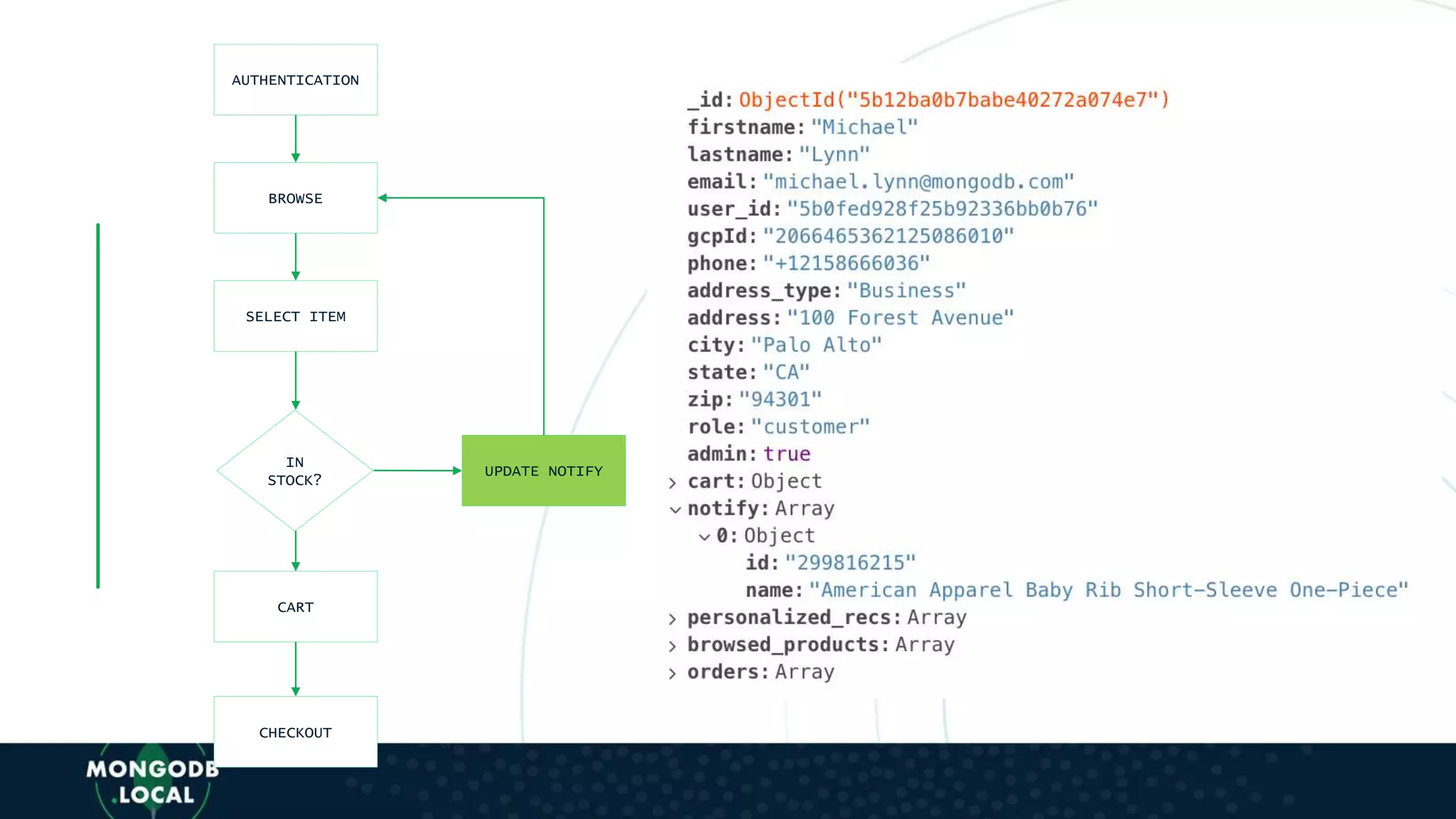
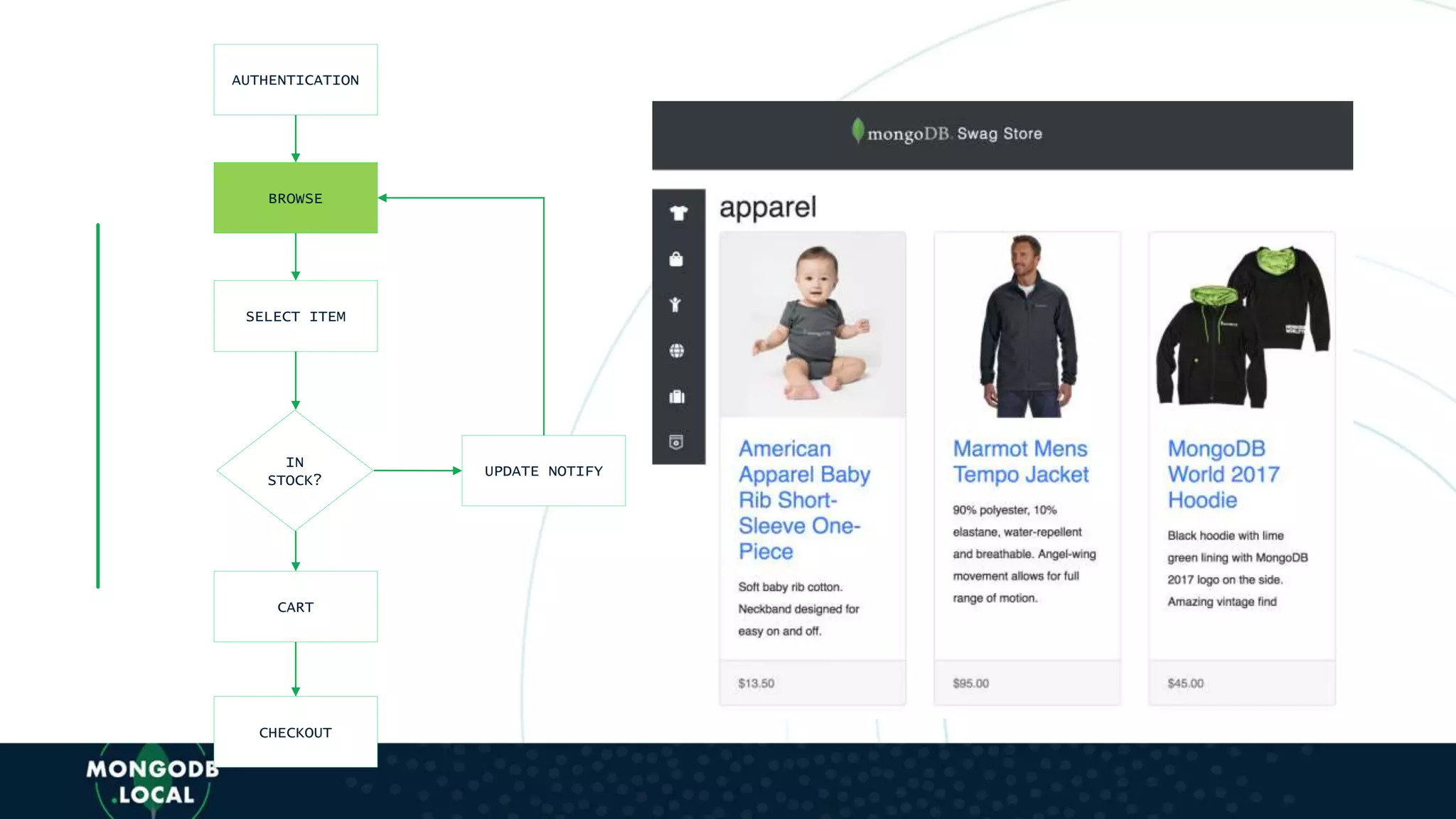
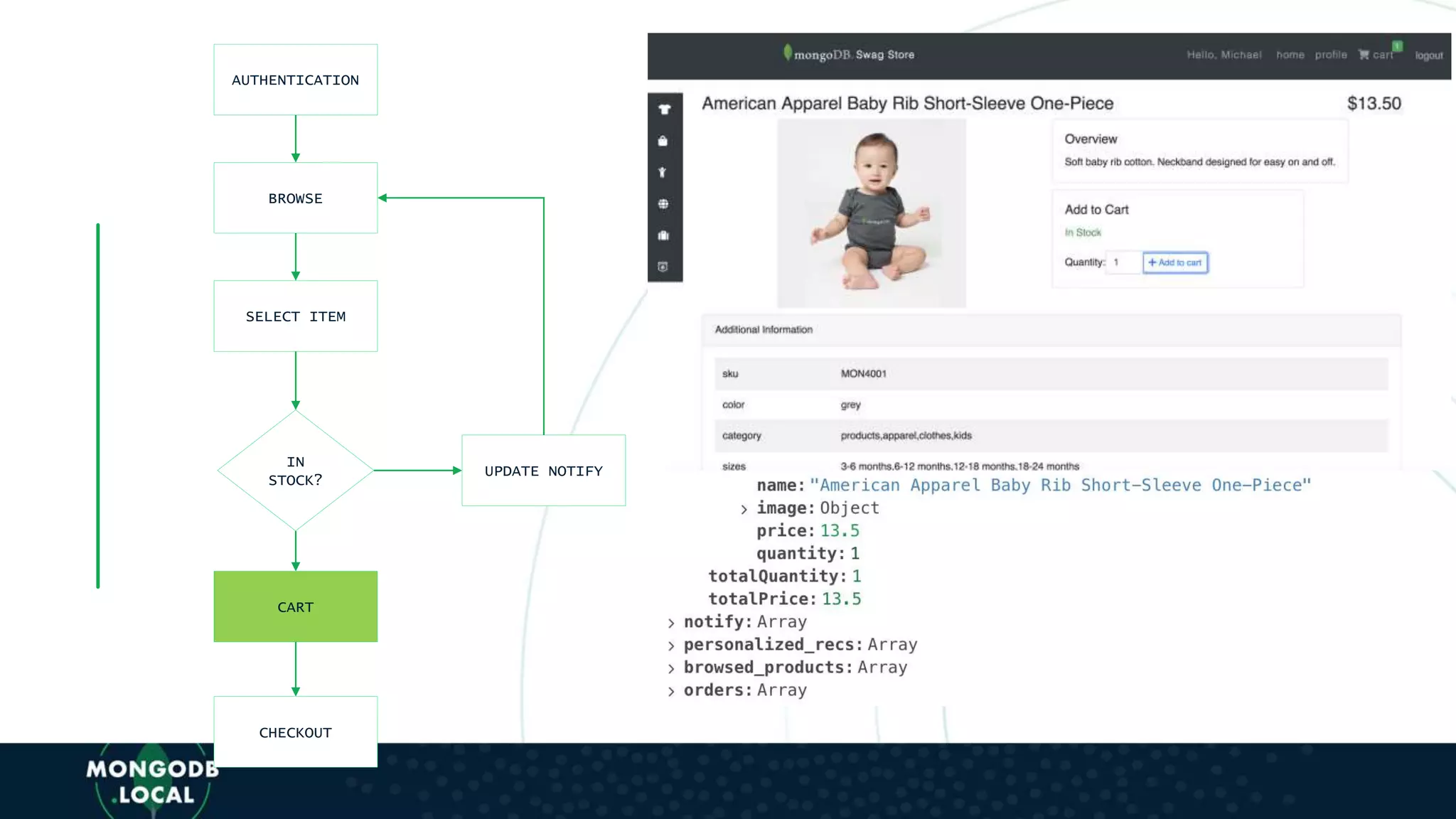
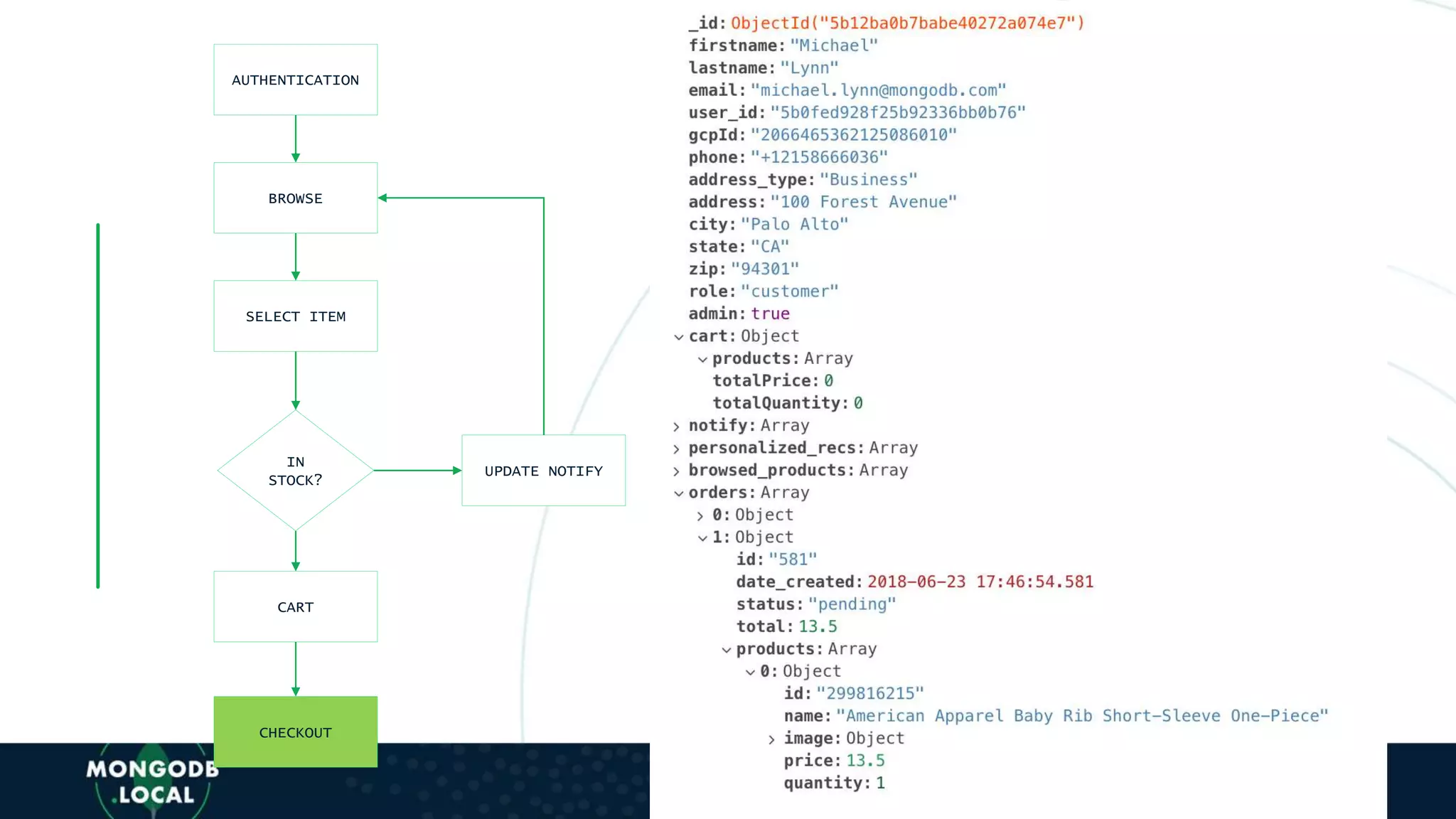
![AUTHENTICATION
BROWSE
SELECT ITEM
IN
STOCK?
CART
CHECKOUT
UPDATE NOTIFY
Browse
• Leverage SDK db.collection() to access
SWAG-STORE database and products
collection
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { ProductDeck } from '../components/Products'
class ProductsPage extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
products: []
}
}
getProducts() {
this.props.db
.collection('products’)
.find({ category: this.props.match.params.category })
.execute()
.then(products => {
this.setState({ products })
})
.catch(err => {
console.log(err)
})
}
componentDidMount() {
this.getProducts()
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
if (this.props.match.params.category !== prevProps.match.params.category) {](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/355-theater4-stitch-triggers-092018-short-generictemplate-181002150239/75/MongoDB-local-Austin-2018-Ch-Ch-Ch-Ch-Changes-Taking-Your-MongoDB-Stitch-Application-to-the-Next-Level-With-Triggers-50-2048.jpg)