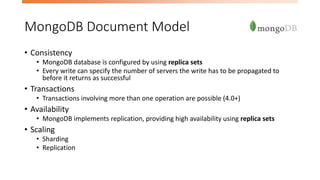
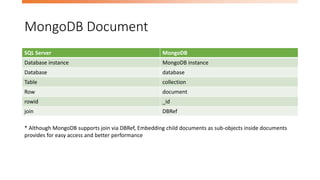
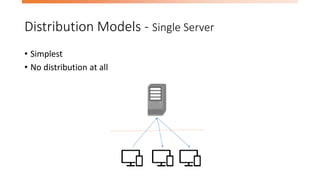
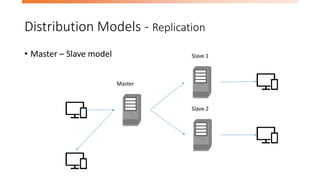
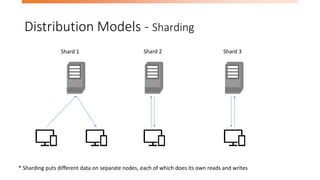
The document discusses the limitations of relational databases (RDBMS) in handling big data, highlighting issues like rigid schemas and performance challenges. It introduces NoSQL as a solution, specifically focusing on MongoDB's document model, sharding, and replication for improved scalability and availability. The document includes a demo of basic CRUD operations in MongoDB and presents various use cases for its application.





![Impedance Mismatch
• Relational Model
• Tables, Columns, Rows, Relations
• We are developers
• OOP, Polymorphism, Inheritance
• Objects are not uniform
• Work around
• Mapping layer, ORMs
Id Name
1 Comp A
2 Comp B
Id Name
02 Cairo
03 Alexandria
CompanyId CityId
1 02
2 03
1 03
// application code
class Company { int Id; string Name; City[] Cities; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-gettingstarted-200406132530/85/MongoDB-Getting-Started-11-320.jpg)


![Impedance Mismatch - Solution
• No Relational Model
• Tables, Columns, Rows, Relations
// application code
class Company { int Id; string Name; City[] Cities; }
// mongo document for Company
{
id: 1,
name: “Comp A”,
cities: [ “Cairo”, ”Alexandria” ]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodb-gettingstarted-200406132530/85/MongoDB-Getting-Started-14-320.jpg)