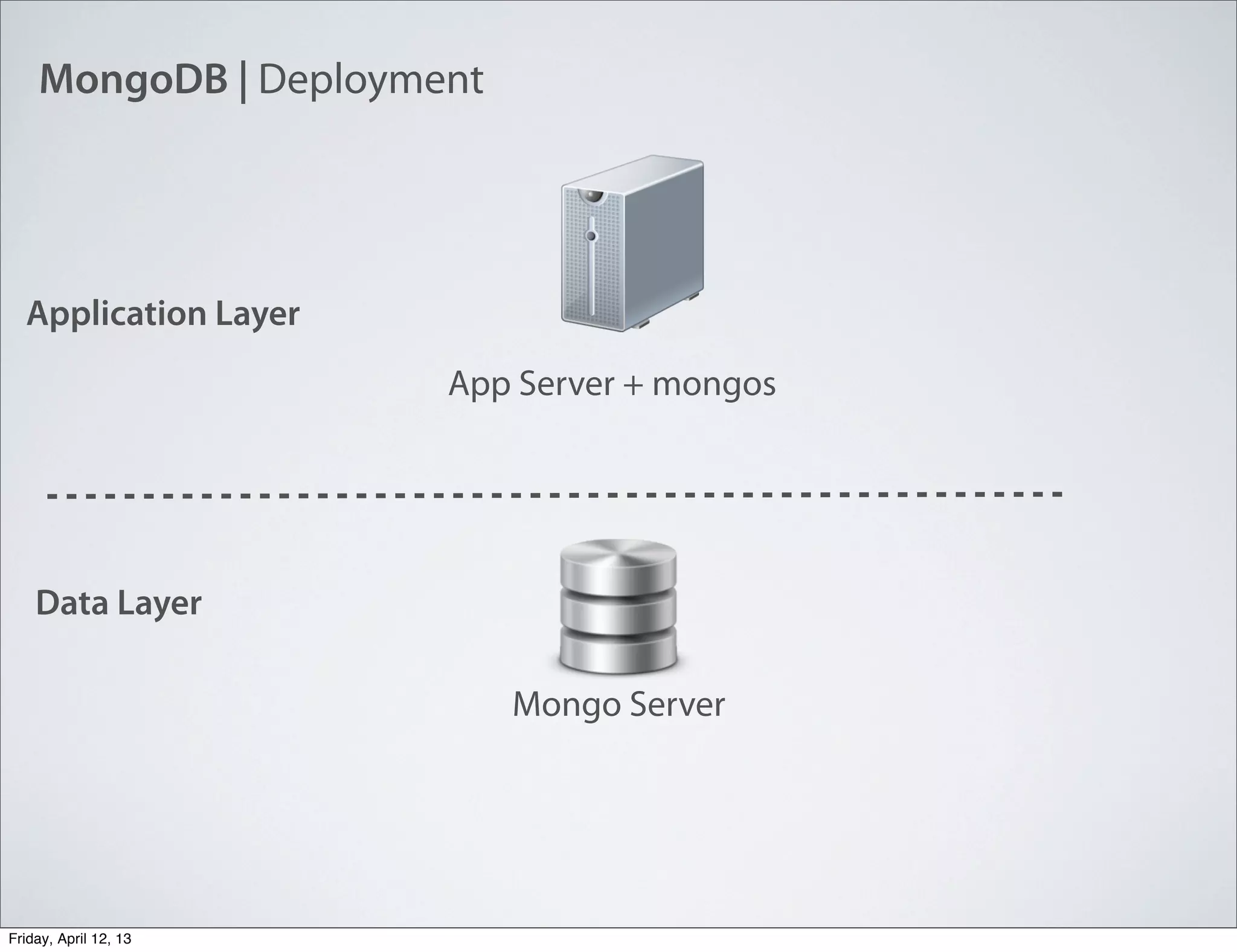
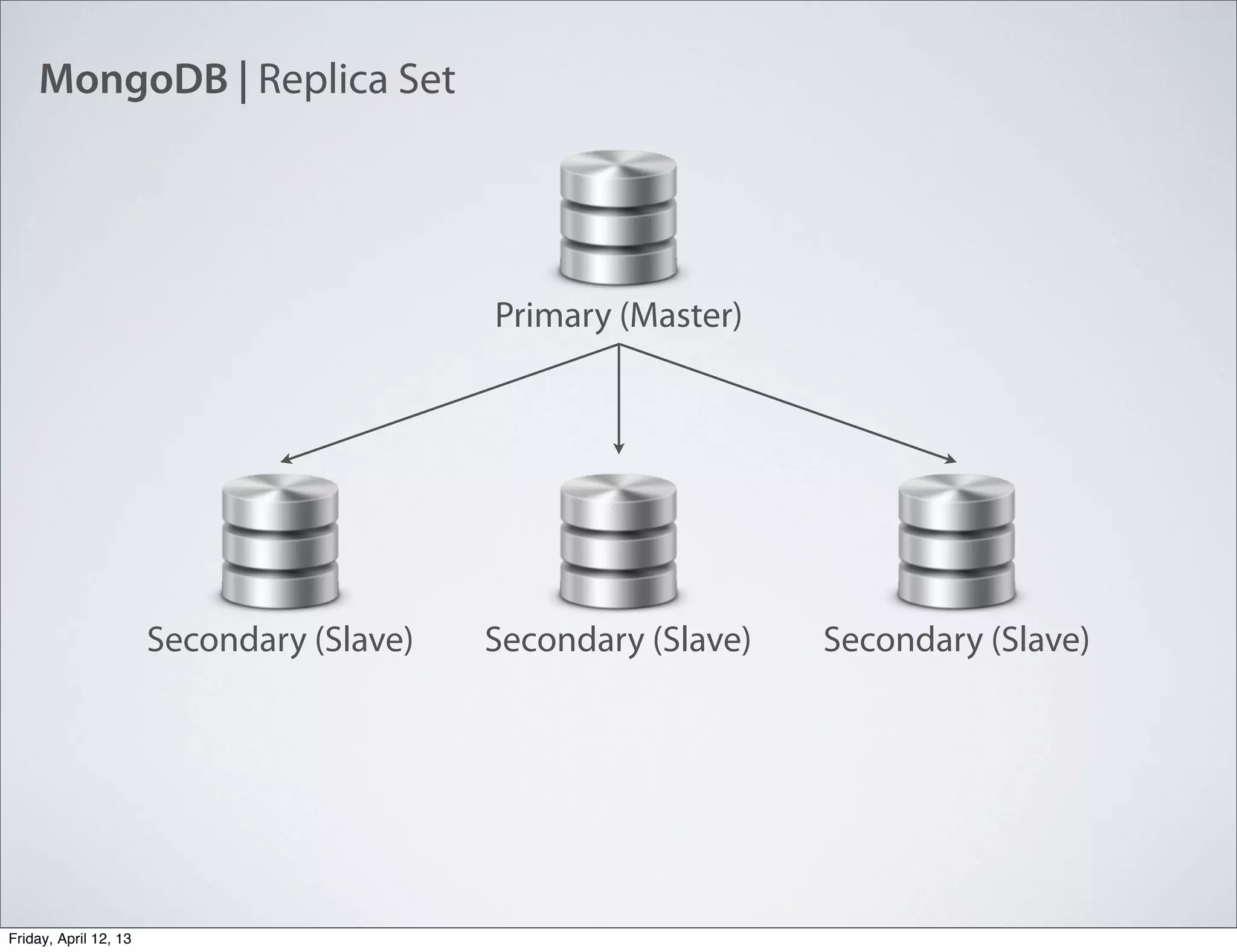
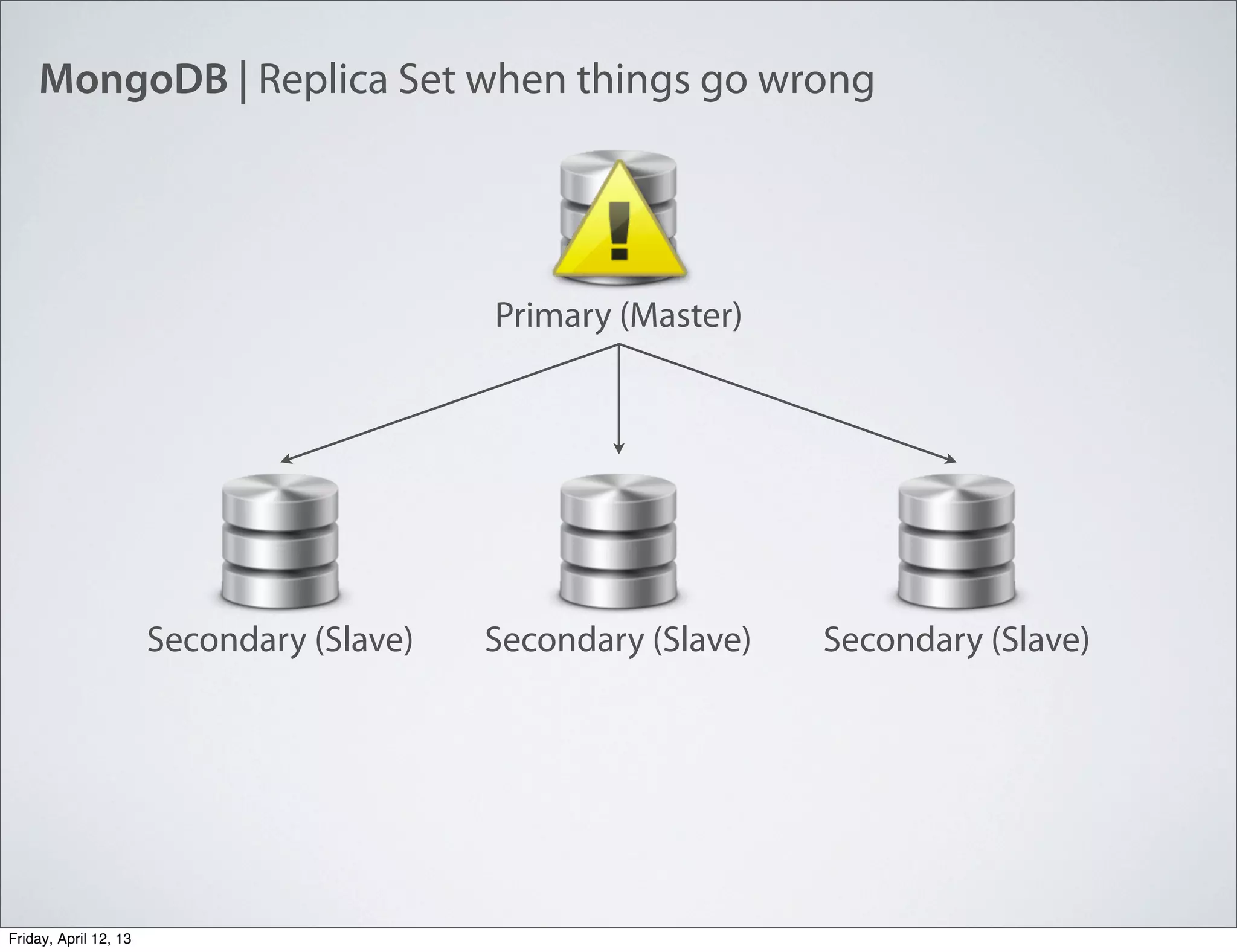
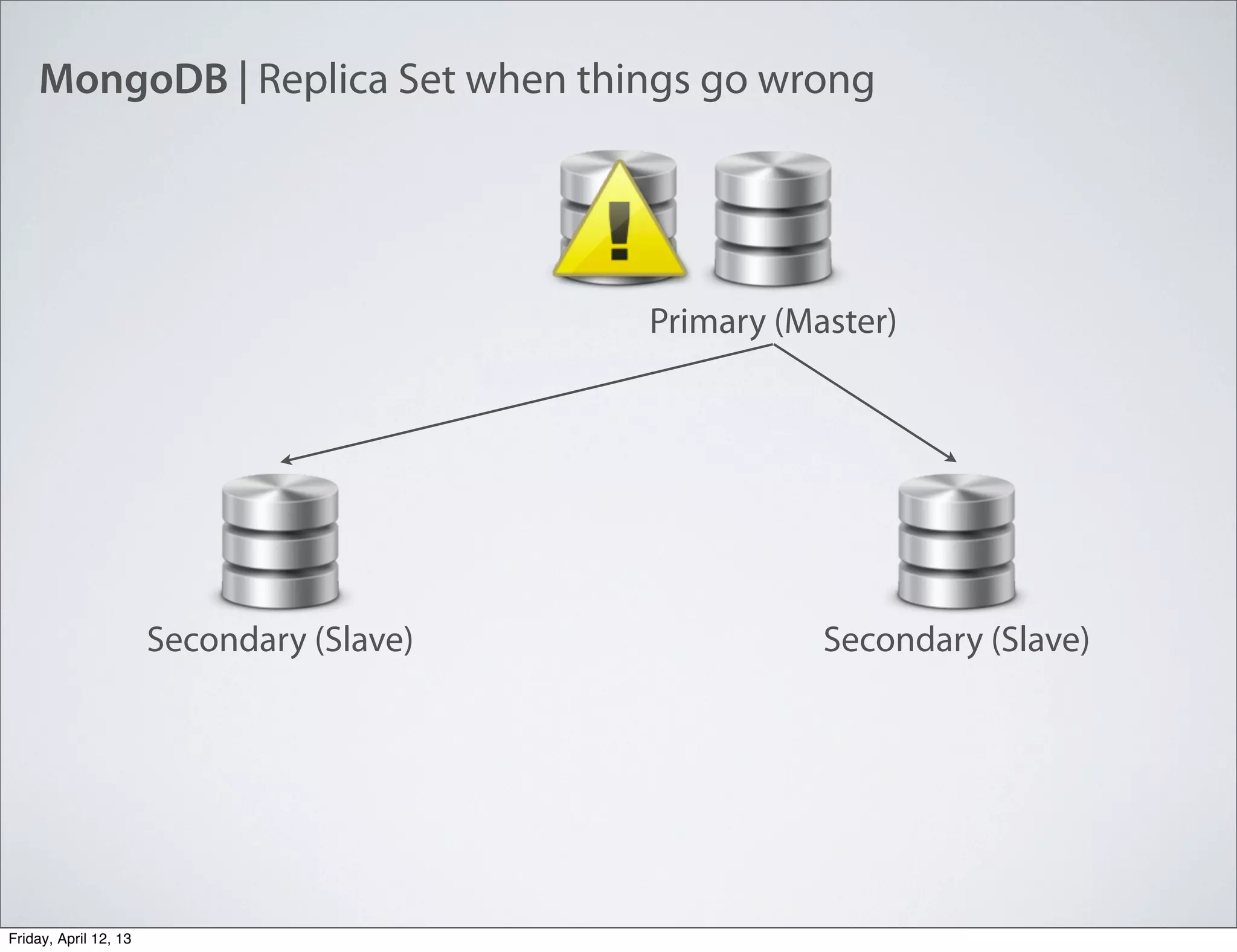
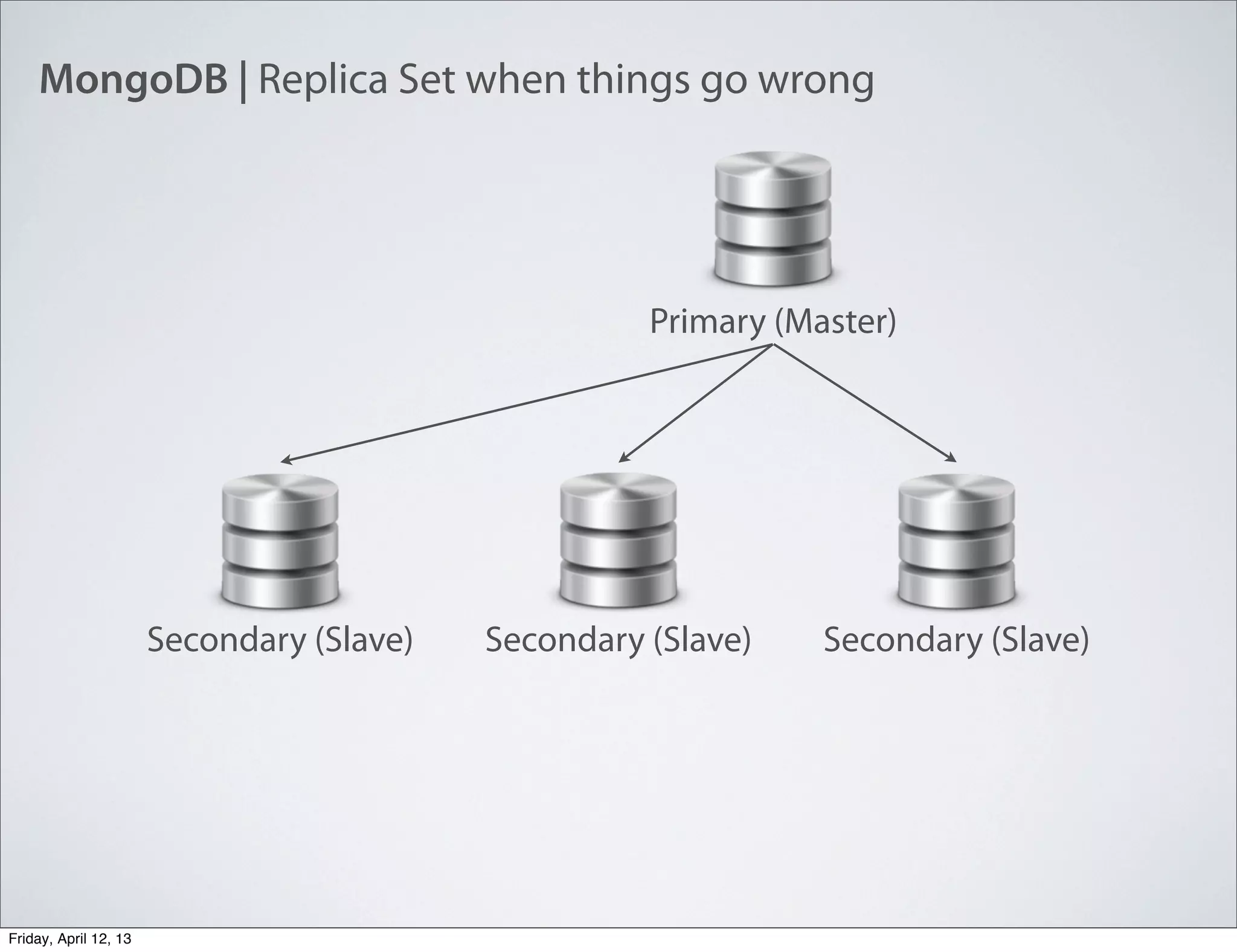
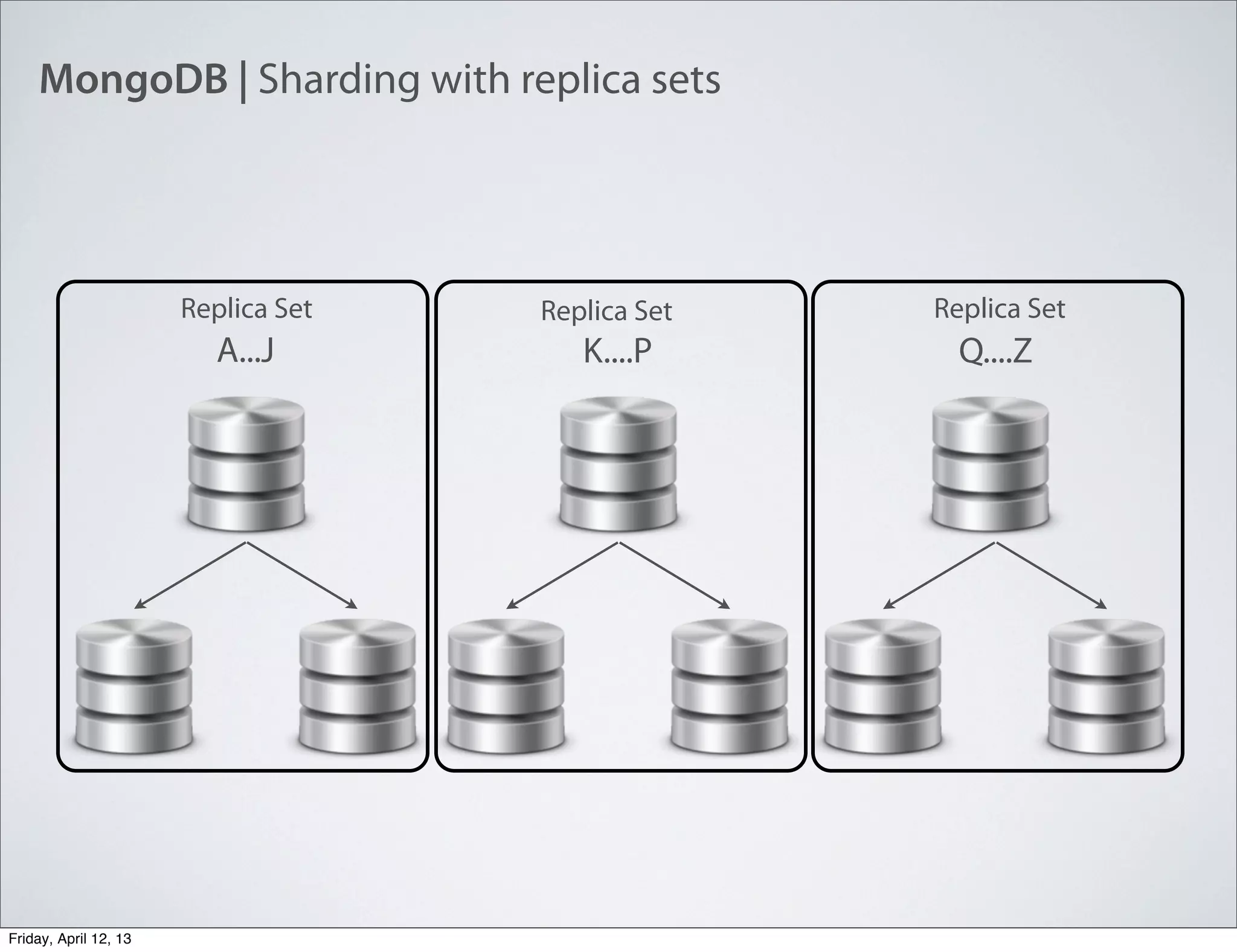
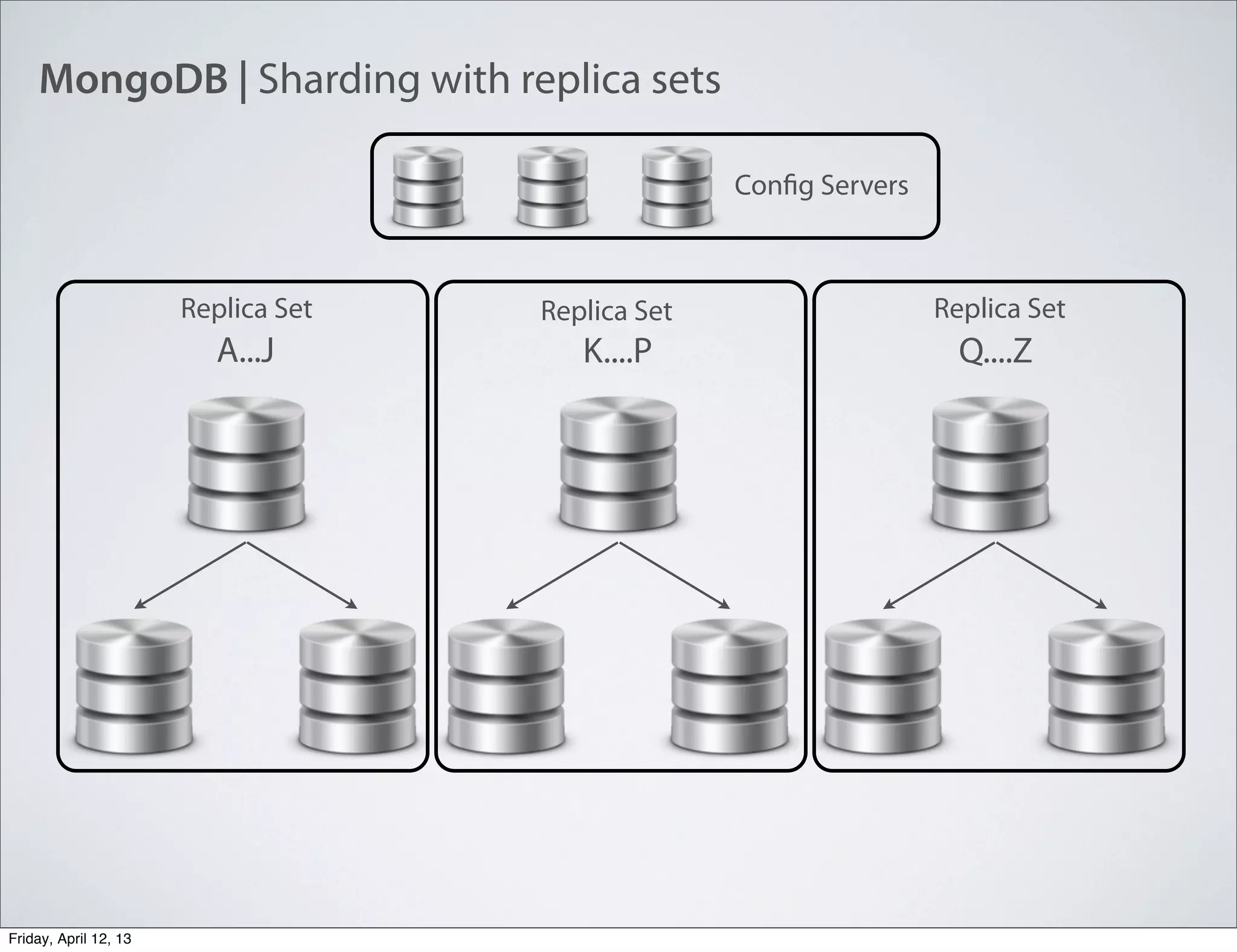
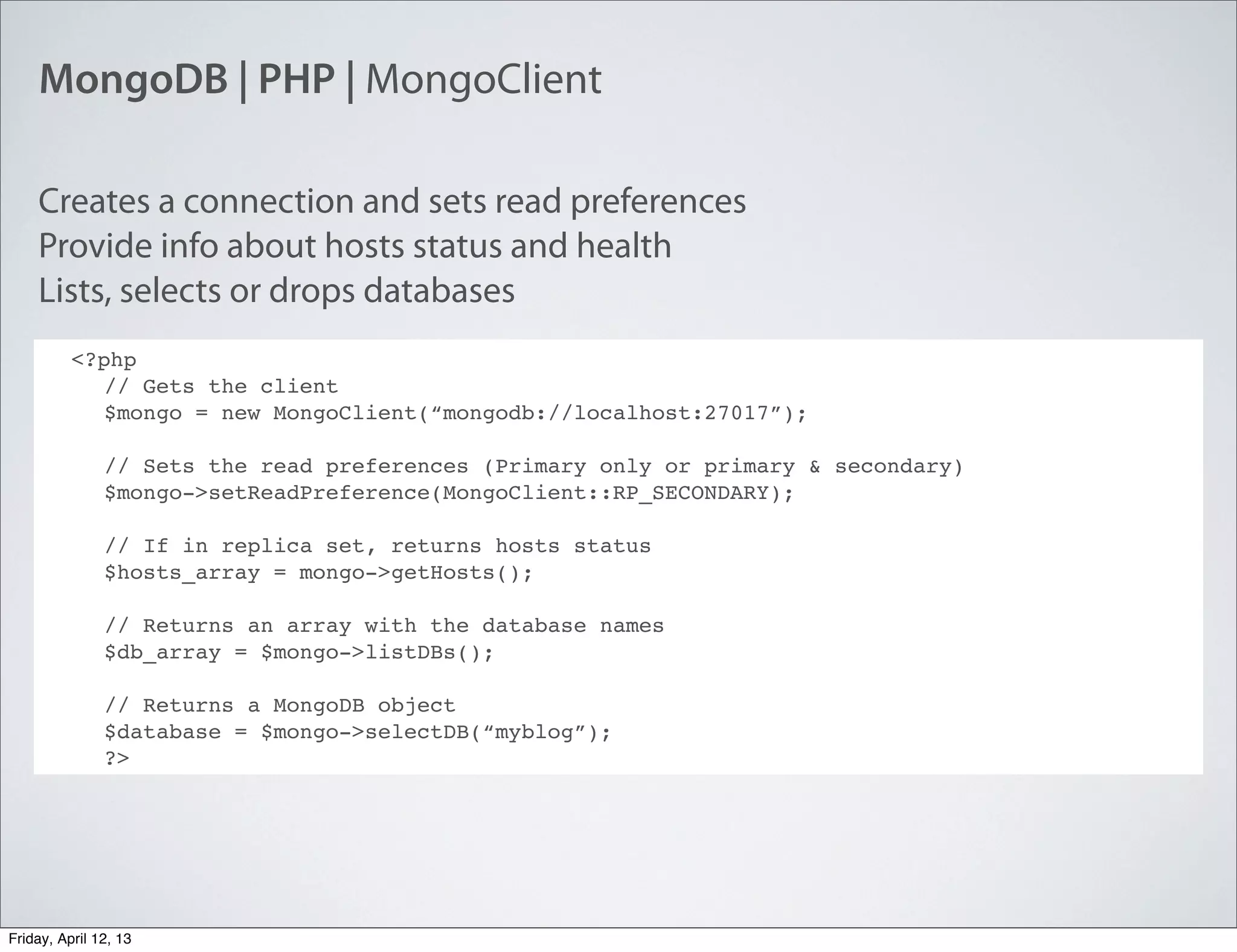
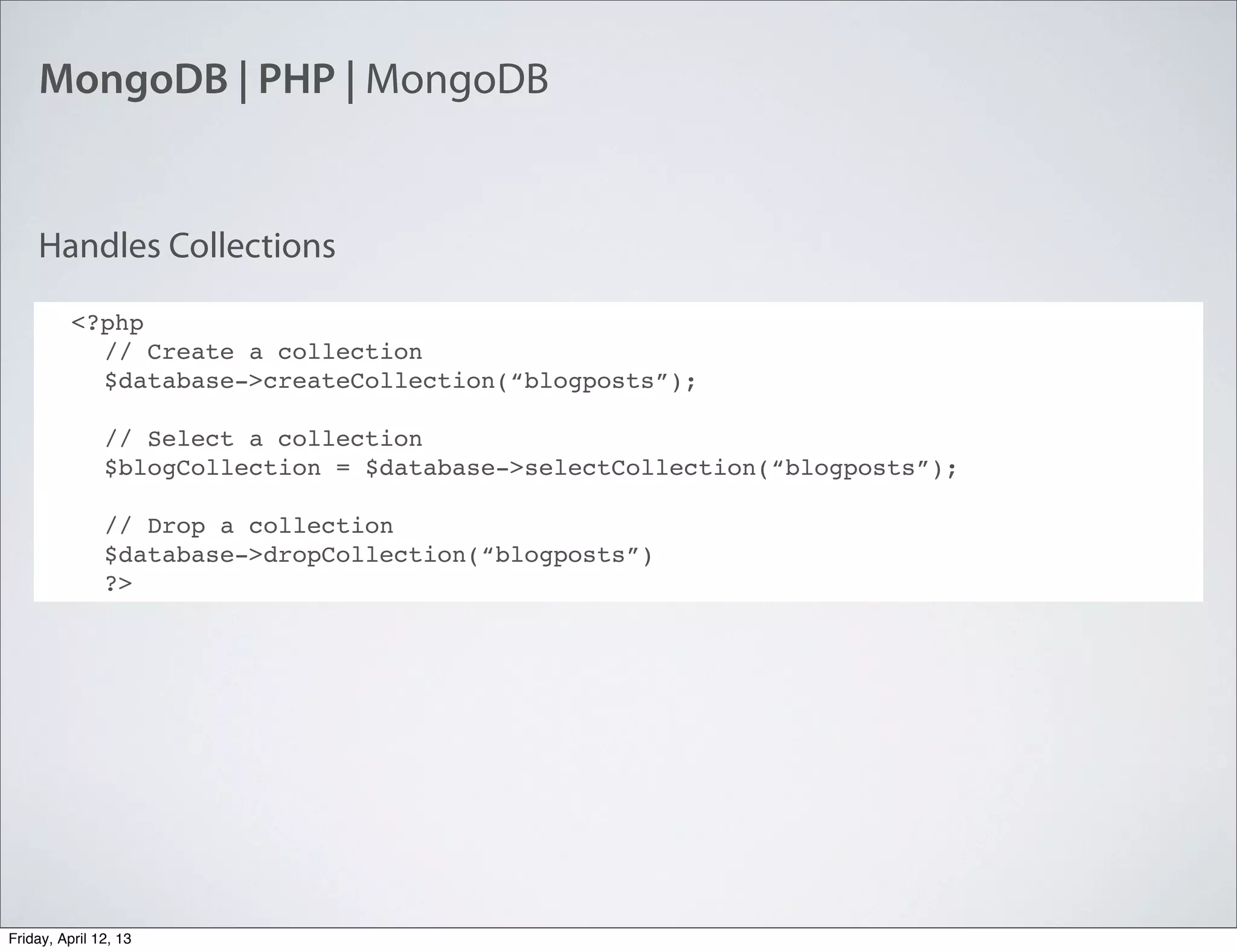
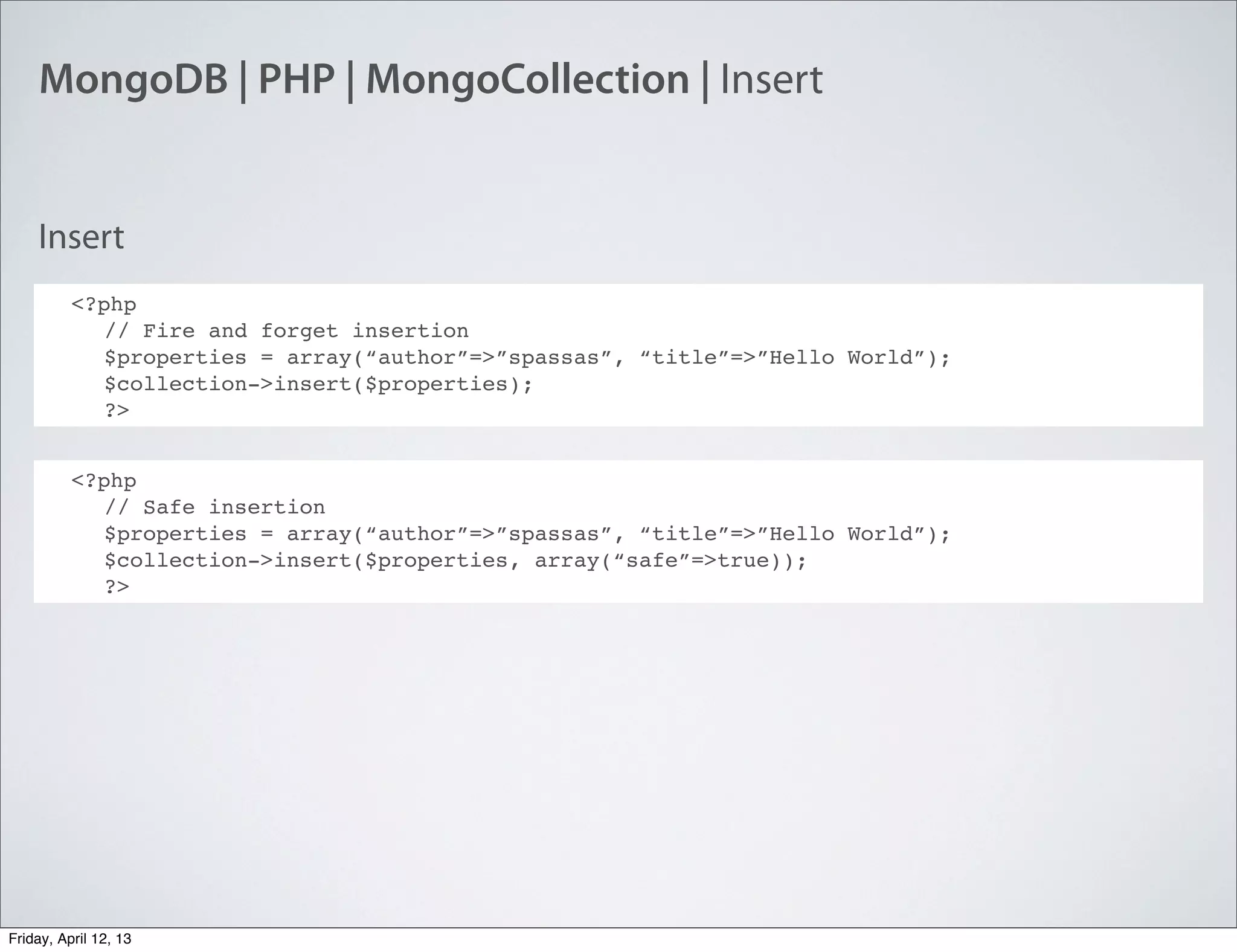
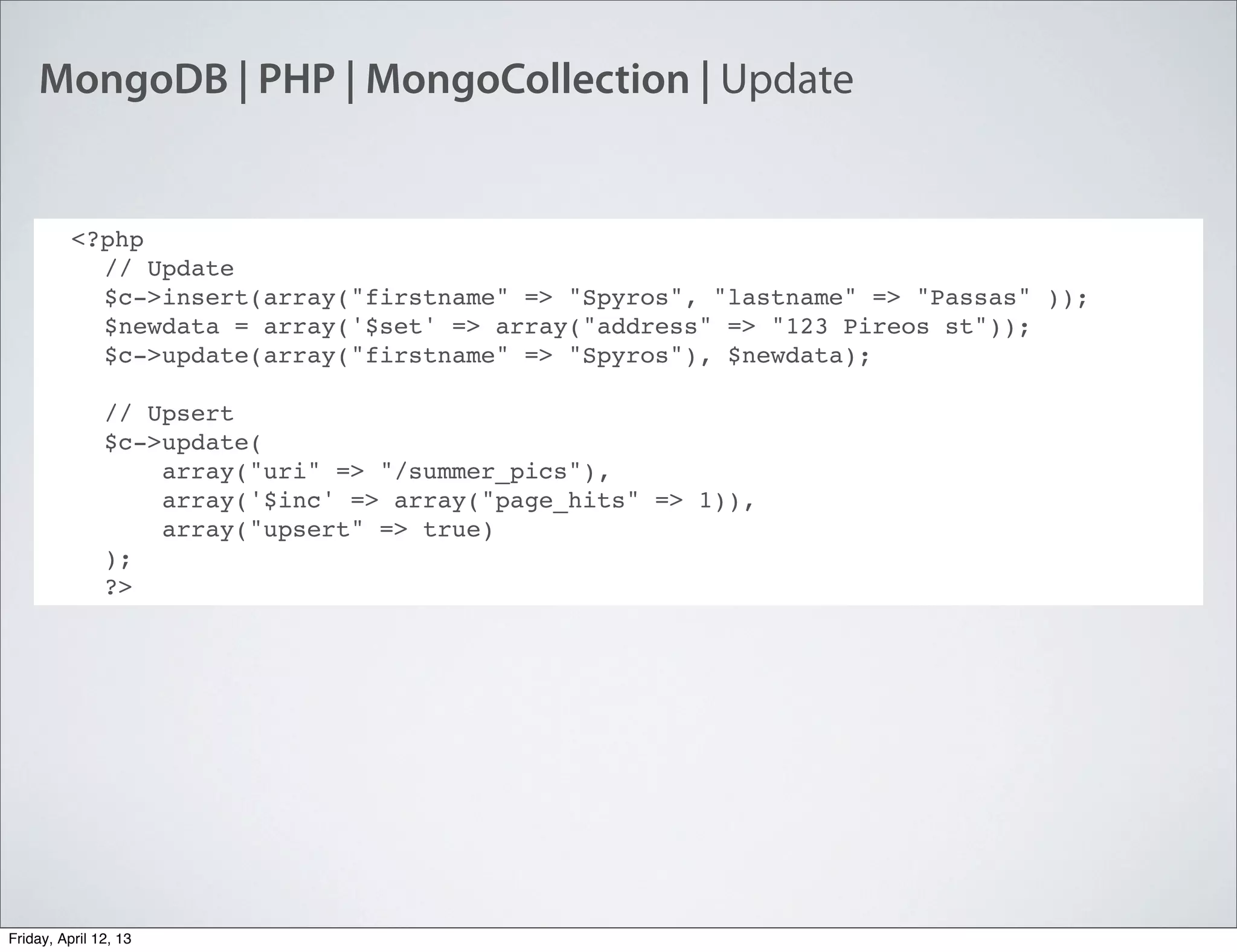
The document discusses NoSQL databases, specifically MongoDB, highlighting their benefits like flexibility, performance, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional SQL databases. It covers key concepts such as data models, indexing, and deployment strategies, while also addressing potential drawbacks like limited reporting and security features. Additionally, it provides code examples for using MongoDB with PHP, showcasing how to manage collections and perform CRUD operations.





![MongoDB | What can a value be?
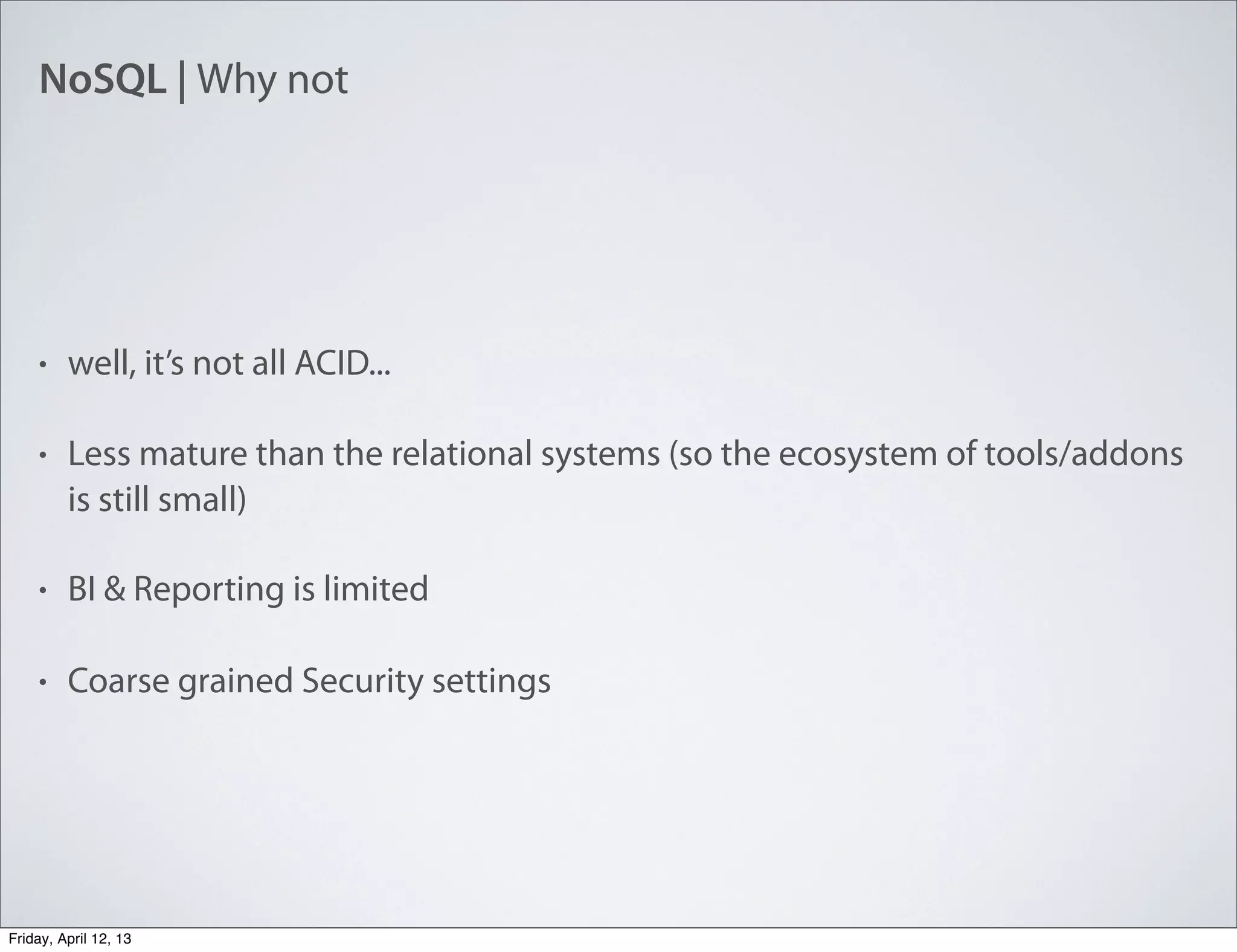
• Keys are always strings (without . and $)
• Value can be
• String
• Number
• Date
• Array
• Document
{“name” : “Spyros Passas”}
{“age” : 30}
{“birthday” : Date(“1982-12-12”}
{“interests” : [“Programming”, “NoSQL”]}
{“address” : {
“street” : “123 Pireus st.”,
“city” : “Athens”,
“zip_code” : 17121
}
}
Friday, April 12, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbphpshakennotstirredjoomlafrappe-130415131913-phpapp01/75/Mongo-db-php_shaken_not_stirred_joomlafrappe-8-2048.jpg)
![MongoDB | Example of a document
{
“_id” : ObjectId(“47cc67093475061e3d95369d”),
“name” : “Spyros Passas”,
“birthday” : Date(“1982-12-12”),
“age” : 30,
“interests” : [“Programming”, “NoSQL”],
“address” : {
“street” : “123 Pireus st.”,
“city” : “Athens”,
“zip_code” : 17121
}
“_id” : ObjectId(“47cc67093475061e3d95369d”)
ObjectId is a special type
Friday, April 12, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbphpshakennotstirredjoomlafrappe-130415131913-phpapp01/75/Mongo-db-php_shaken_not_stirred_joomlafrappe-9-2048.jpg)