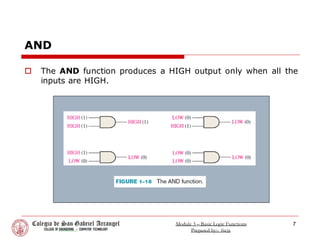
This document introduces basic logic functions including NOT, AND, and OR. It discusses how George Boole developed Boolean algebra to represent logic statements with symbols. The three basic logic functions are represented by distinctive symbols and implemented with digital circuits. NOT inverts the input logic level, AND outputs HIGH only when all inputs are HIGH, and OR outputs HIGH when one or more inputs are HIGH.