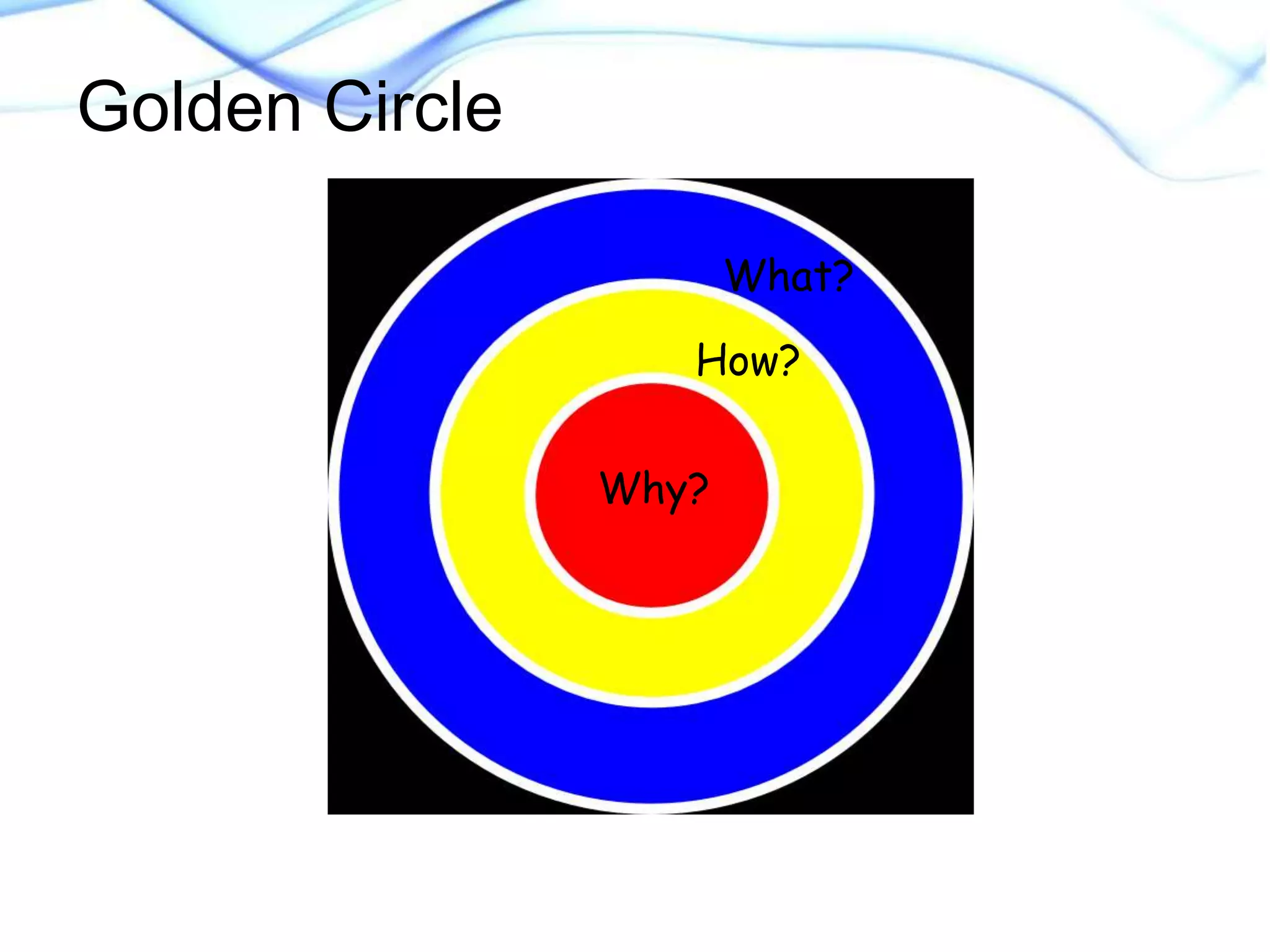
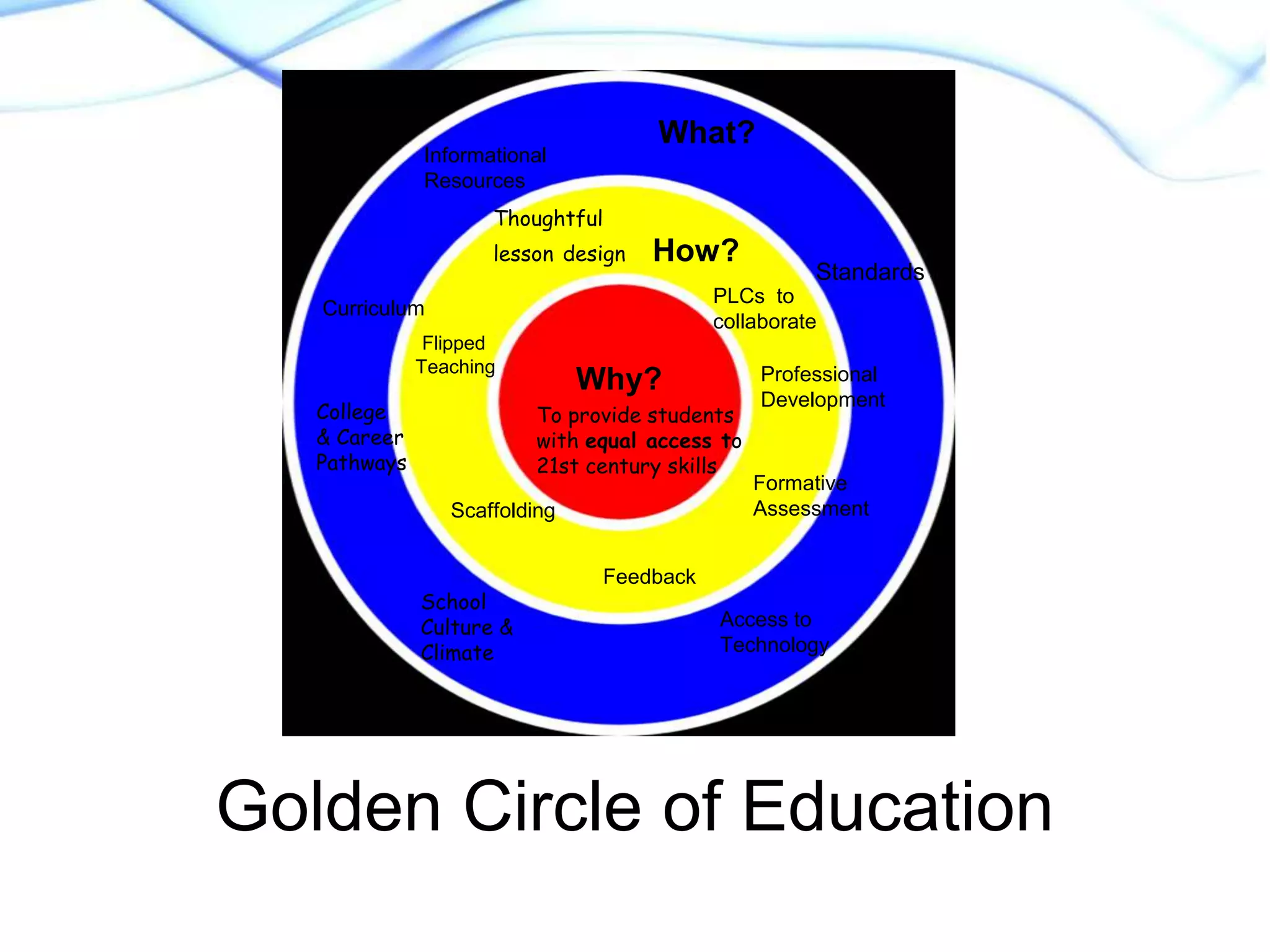
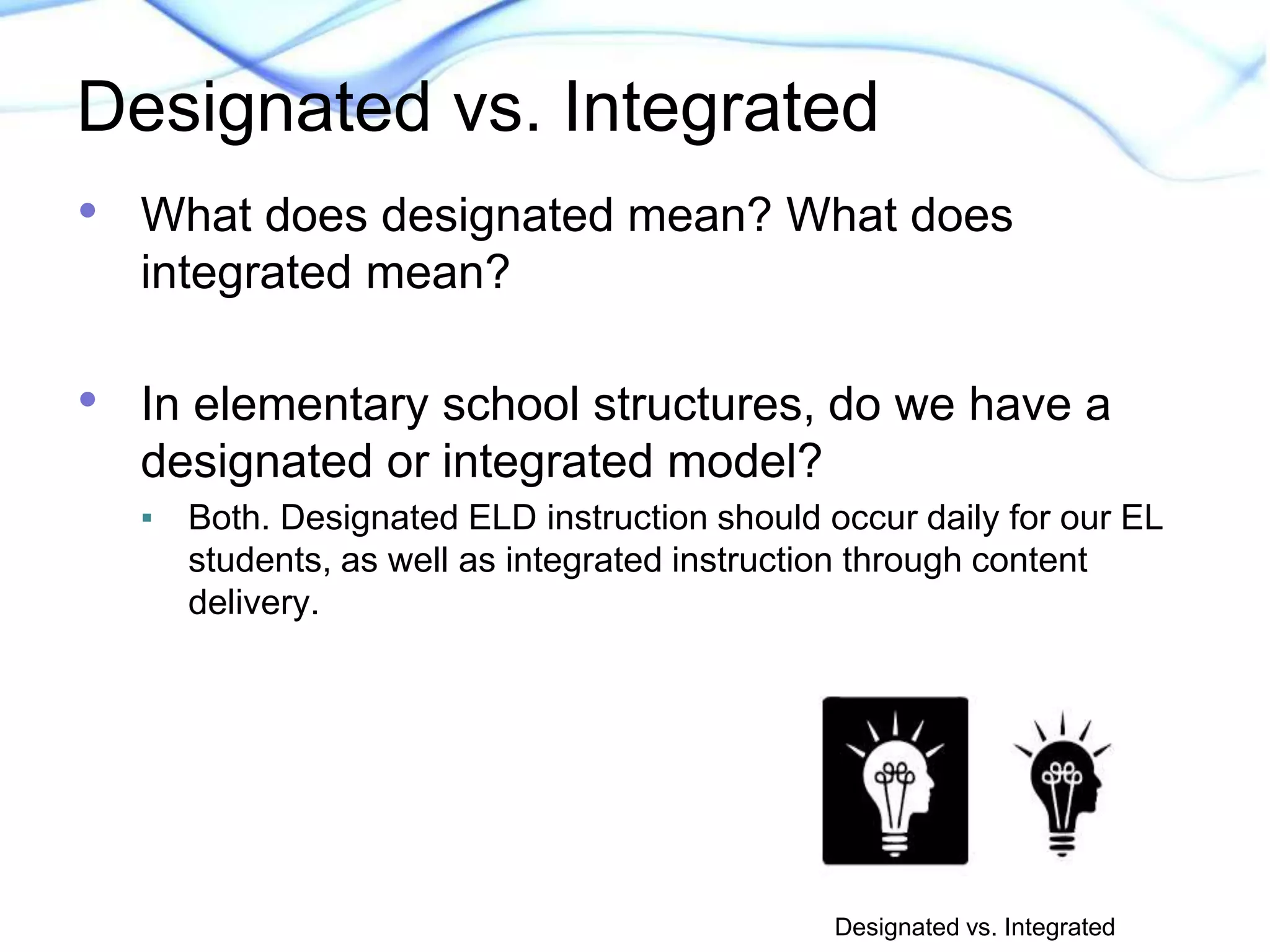
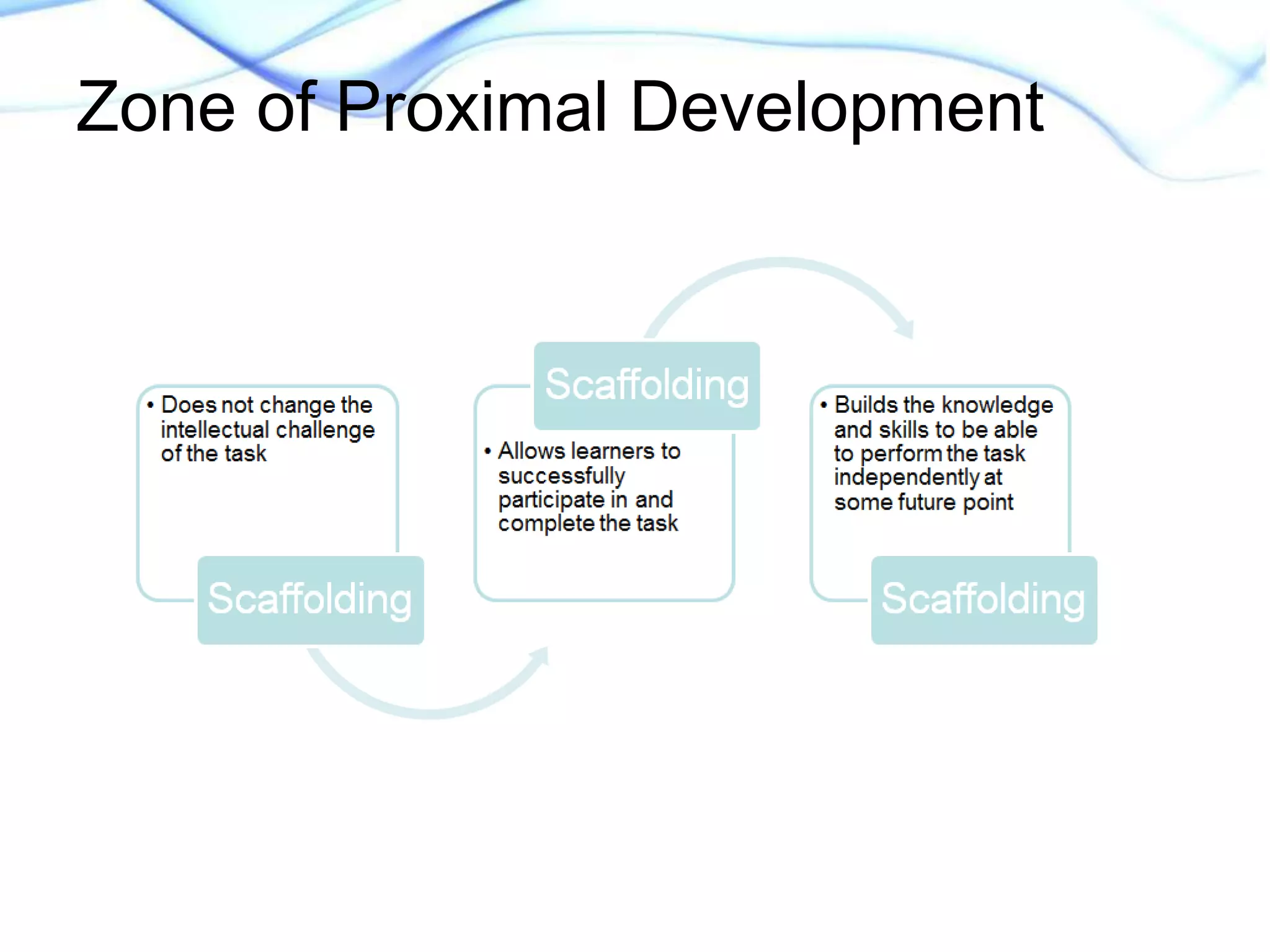
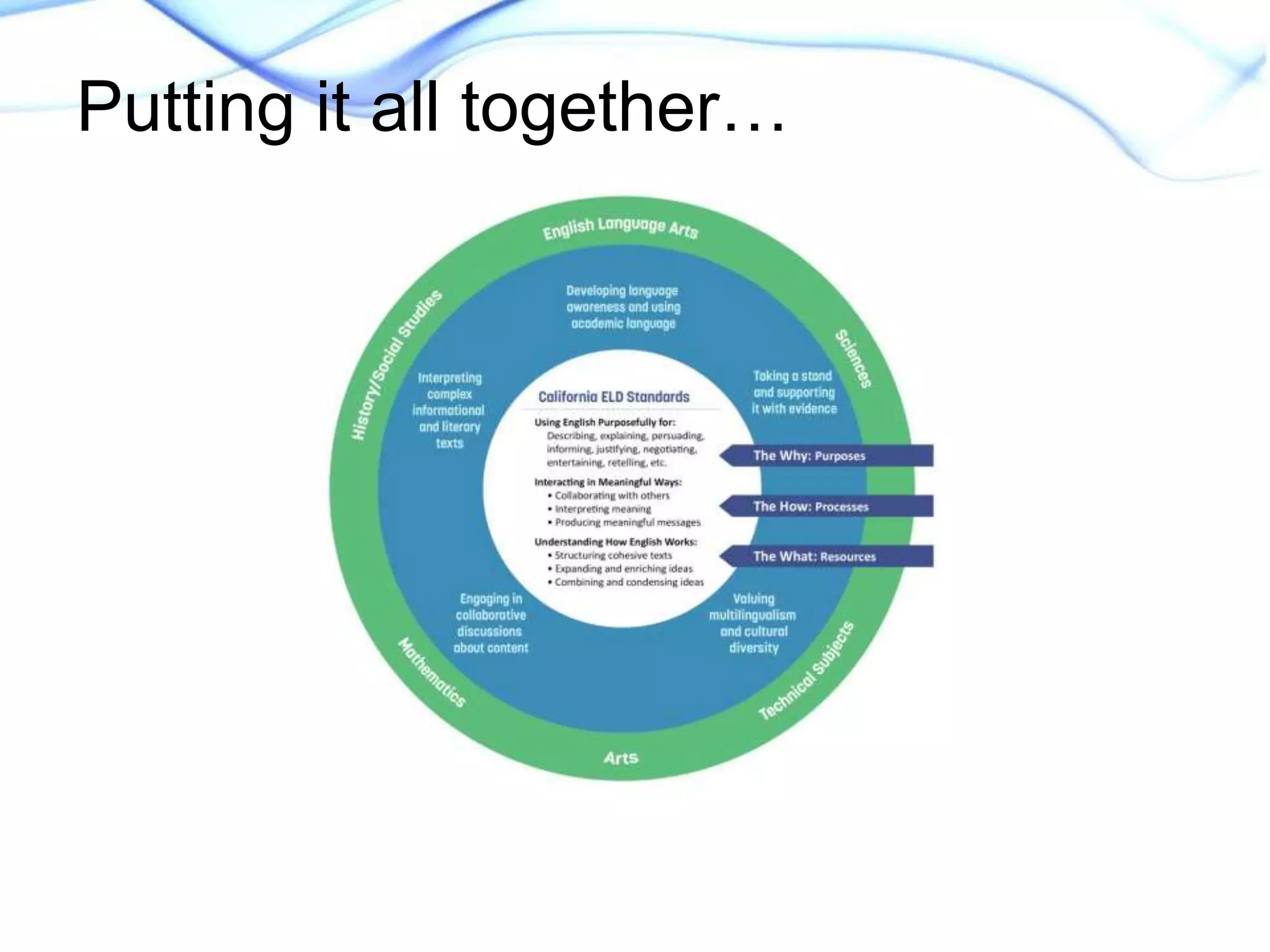
This document discusses strategies for supporting academic language acquisition in the classroom. It begins by outlining the objectives of developing an understanding of designated and integrated instruction models. It then contrasts designated vs integrated instruction and provides examples of each. The document also discusses scaffolding, differentiation, and modification strategies and provides examples. It emphasizes the importance of explicitly teaching academic vocabulary and using strategies like visuals, partner work, and modeling thinking to support English language learners.