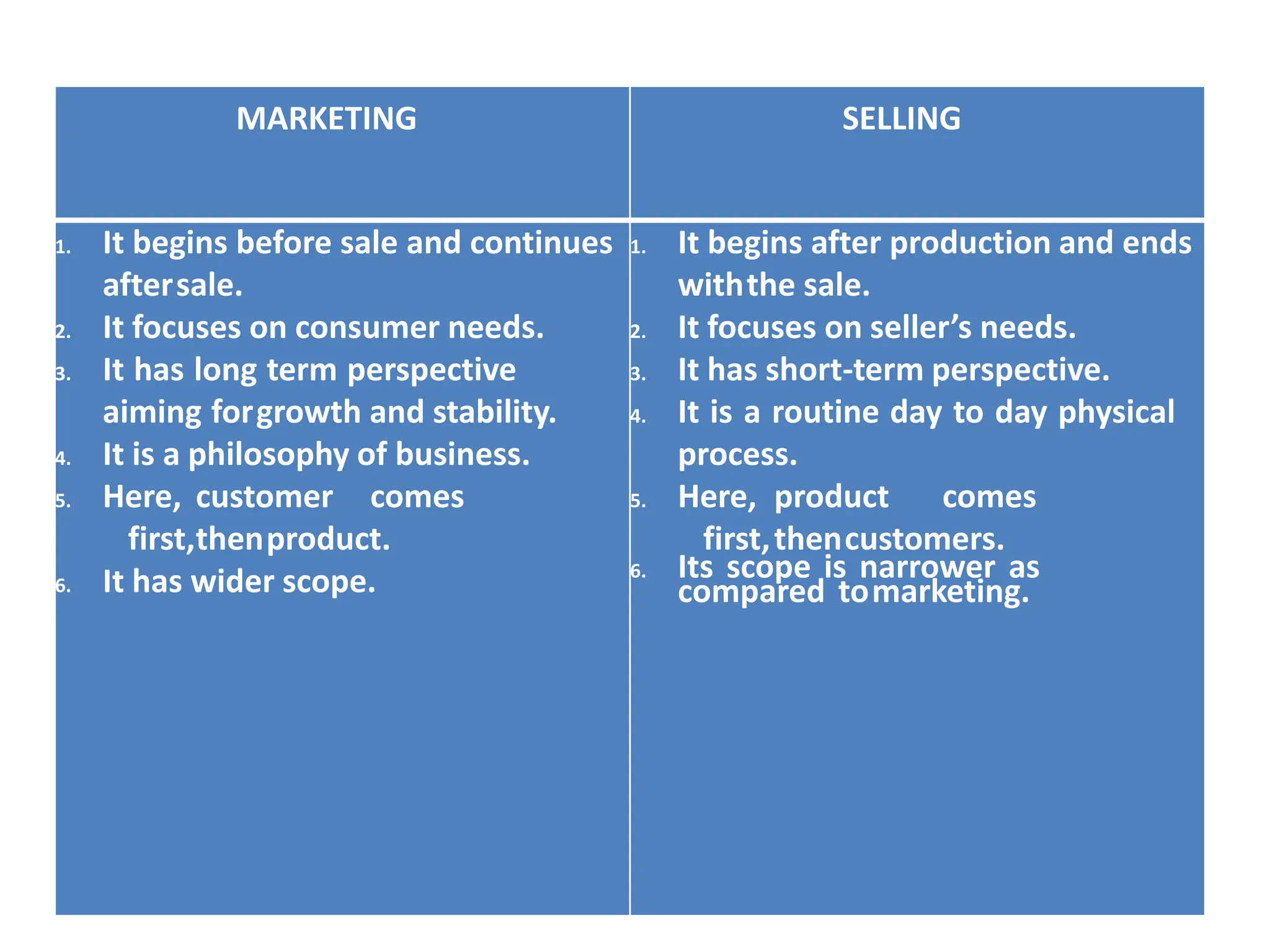
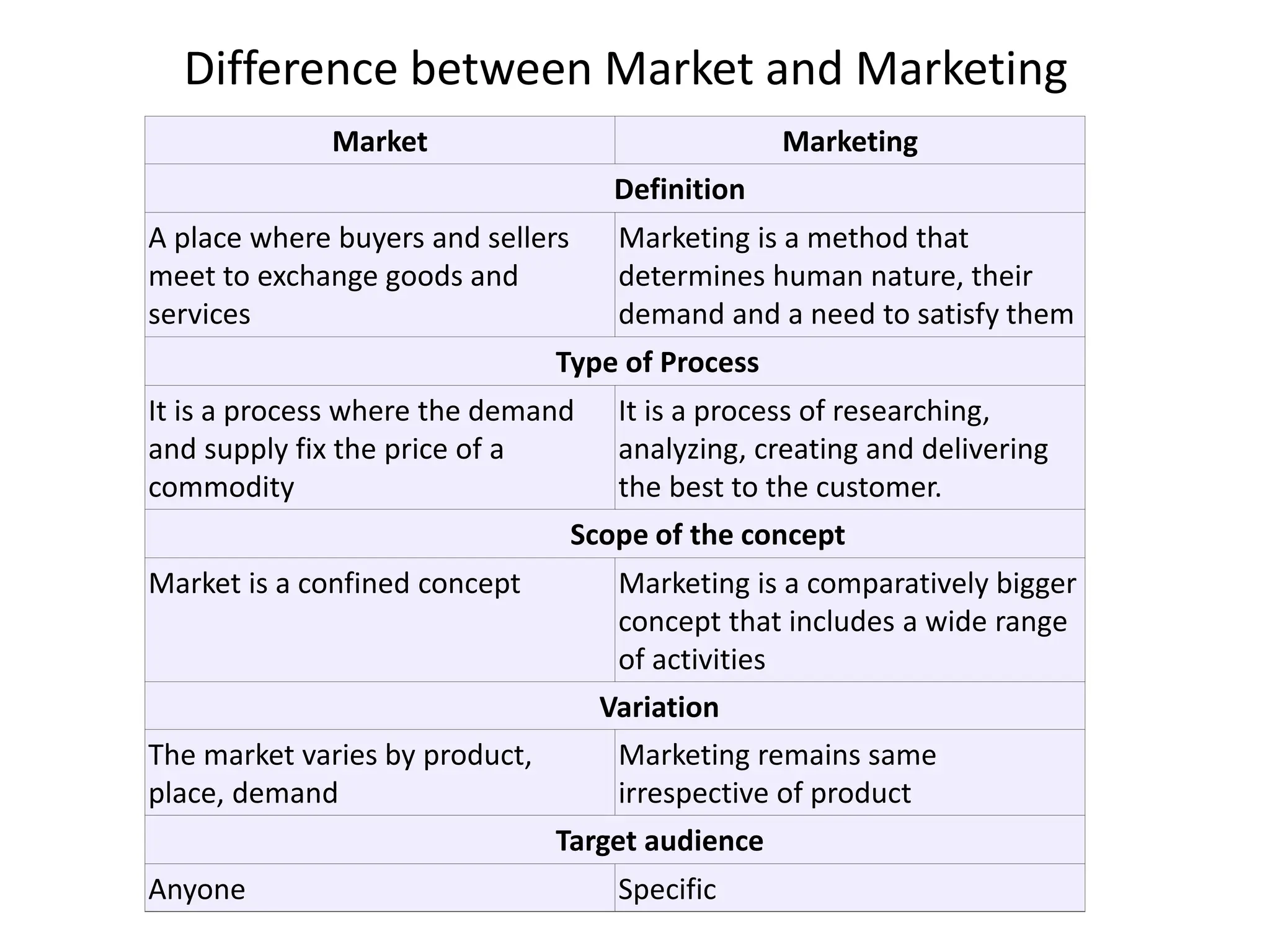
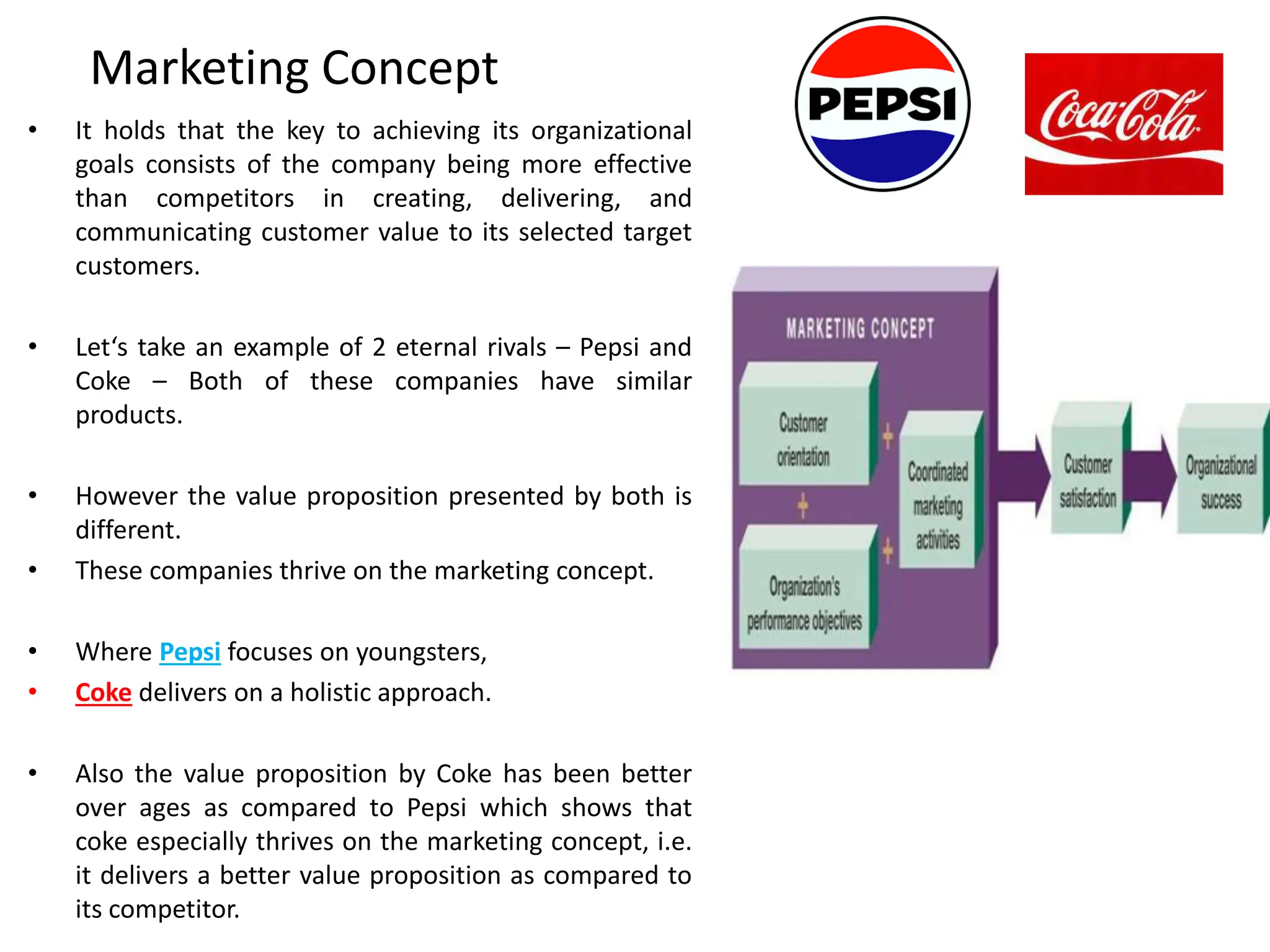
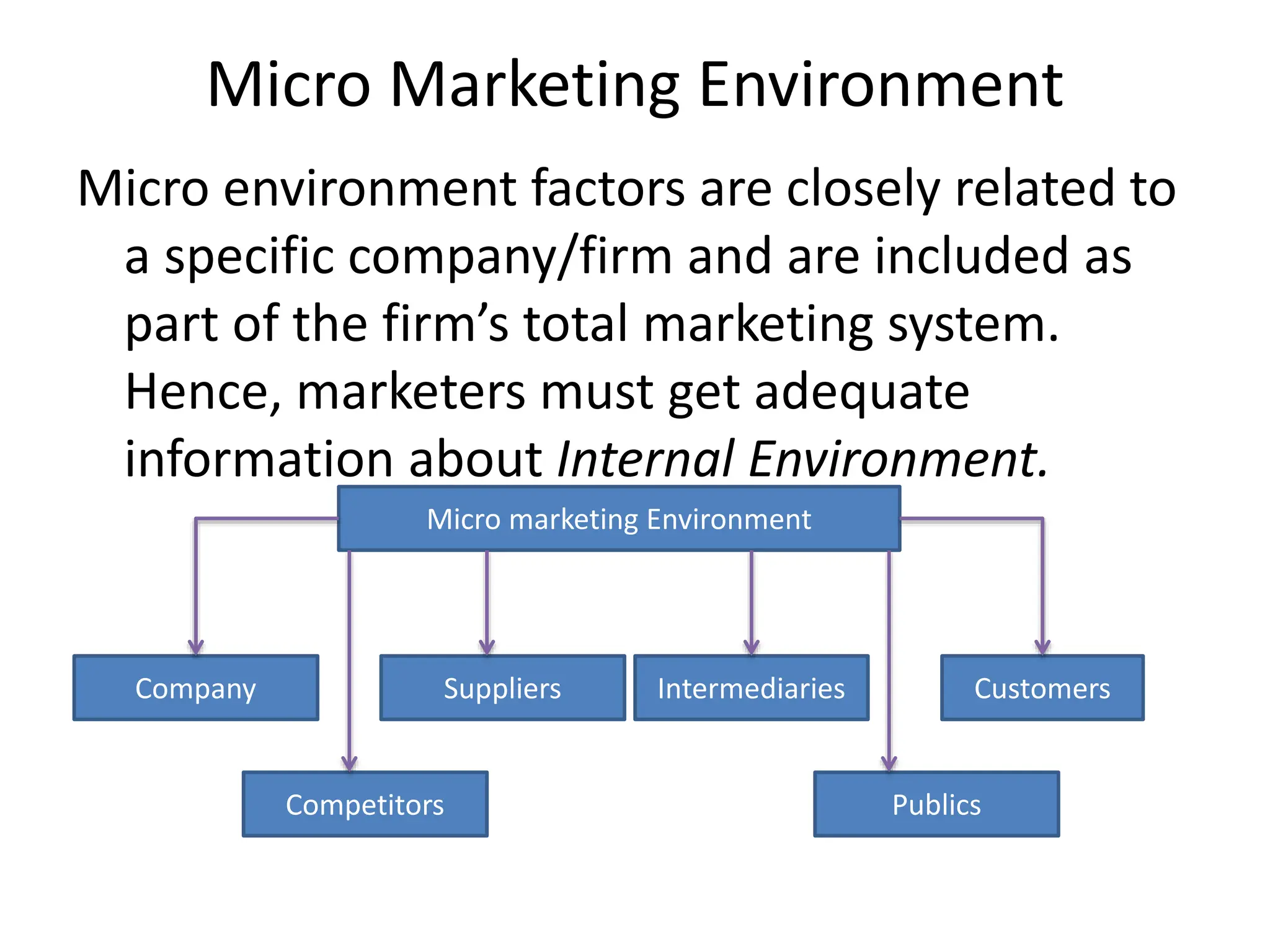
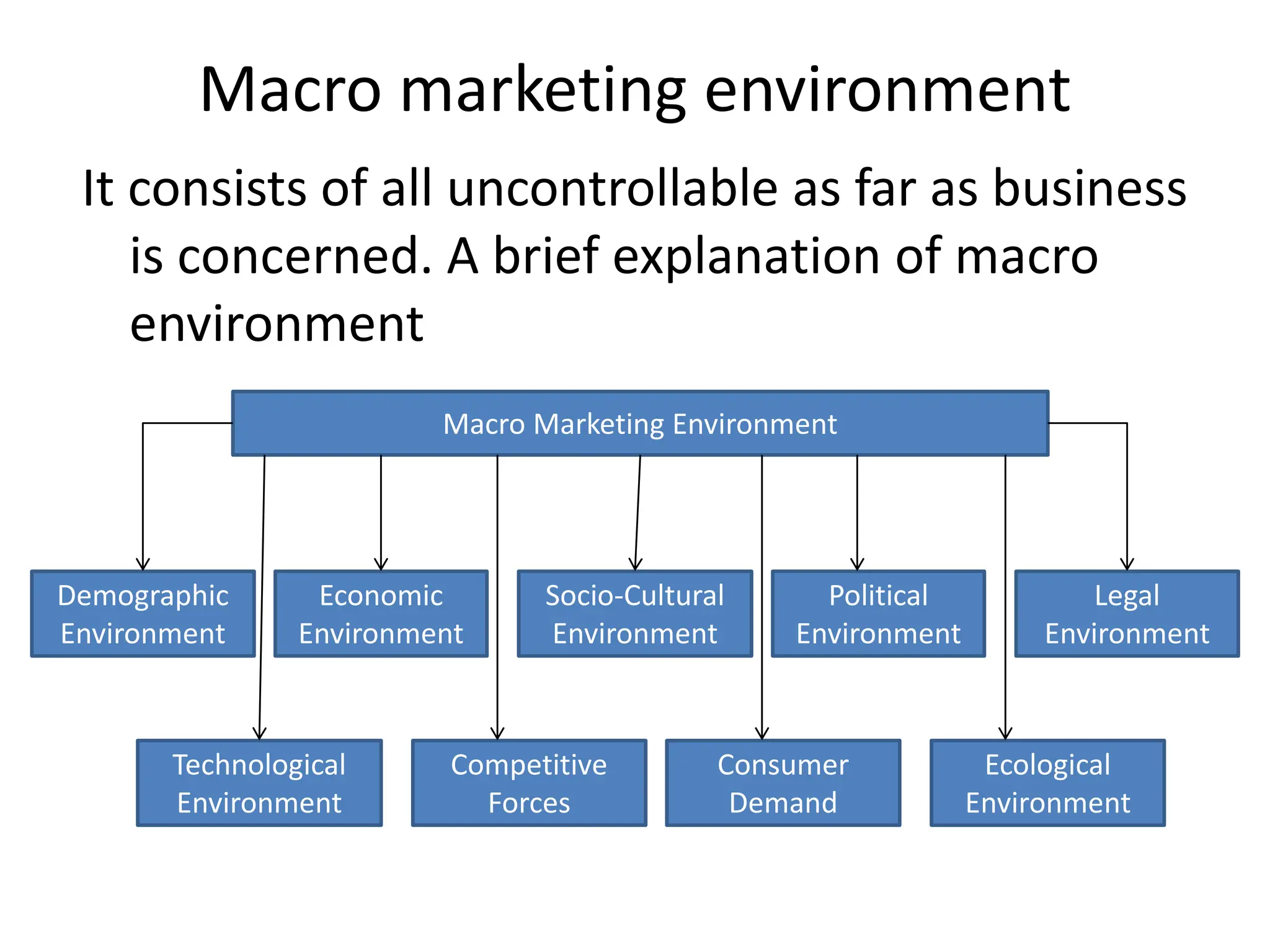
This document provides an overview of key marketing concepts and definitions. It begins by defining marketing and discussing the traditional and modern concepts of marketing. It then explains the differences between marketing and selling, and discusses the 4Ps of marketing - product, price, place, and promotion. The document also covers customer value and satisfaction, the evolution of marketing approaches over time, elements of the marketing concept like production and product concepts, and provides examples of companies that employ the marketing concept.