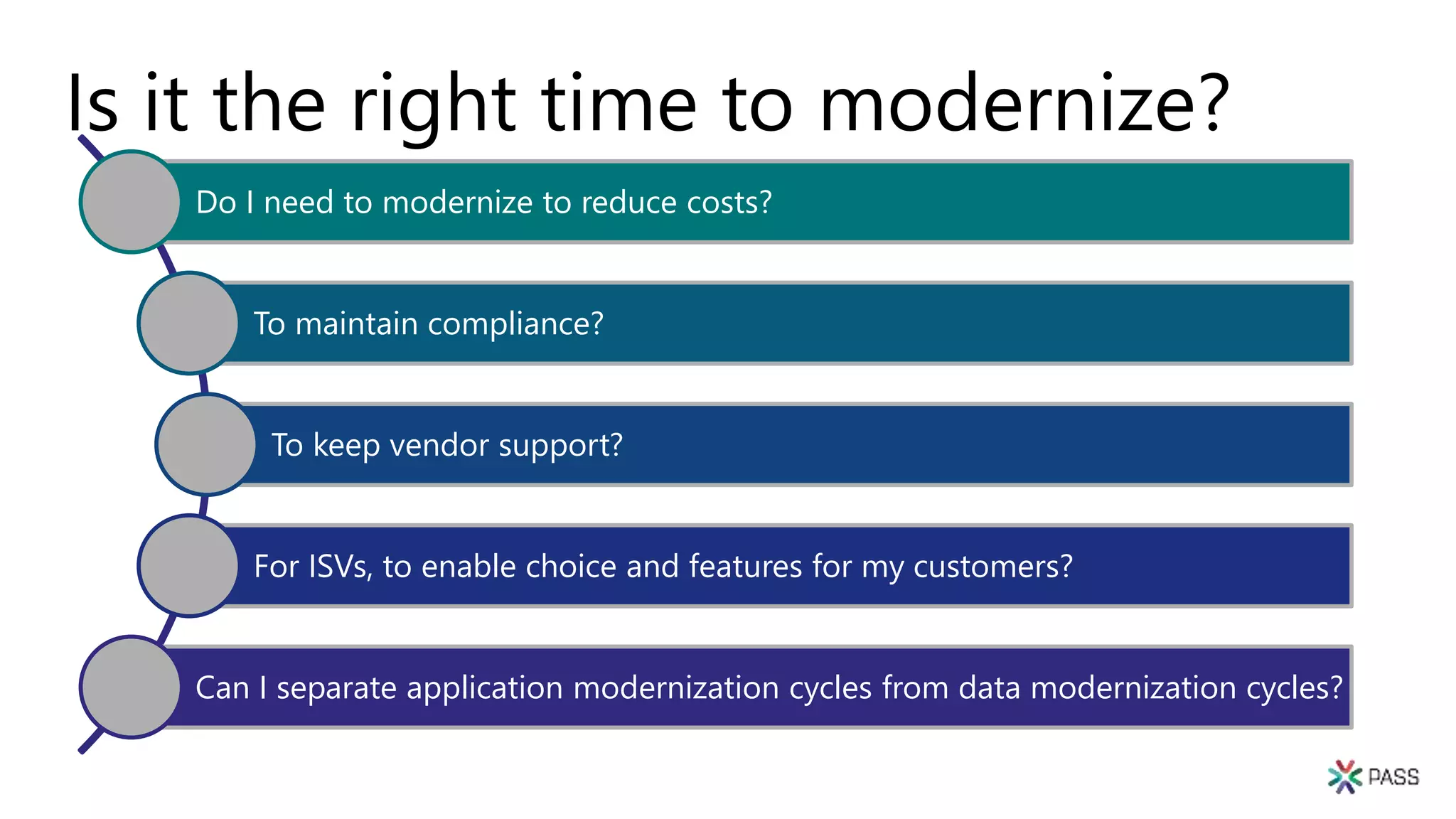
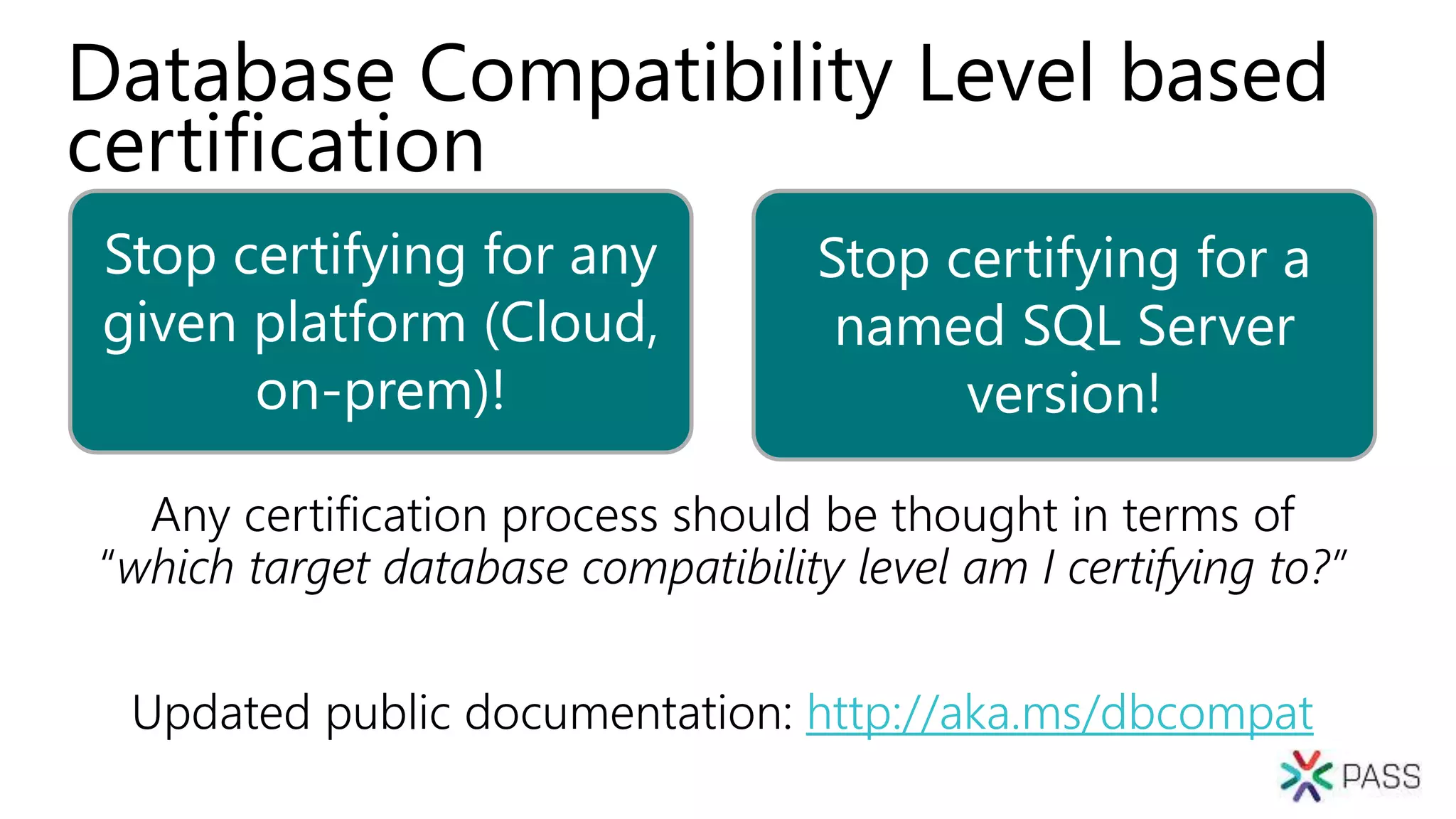
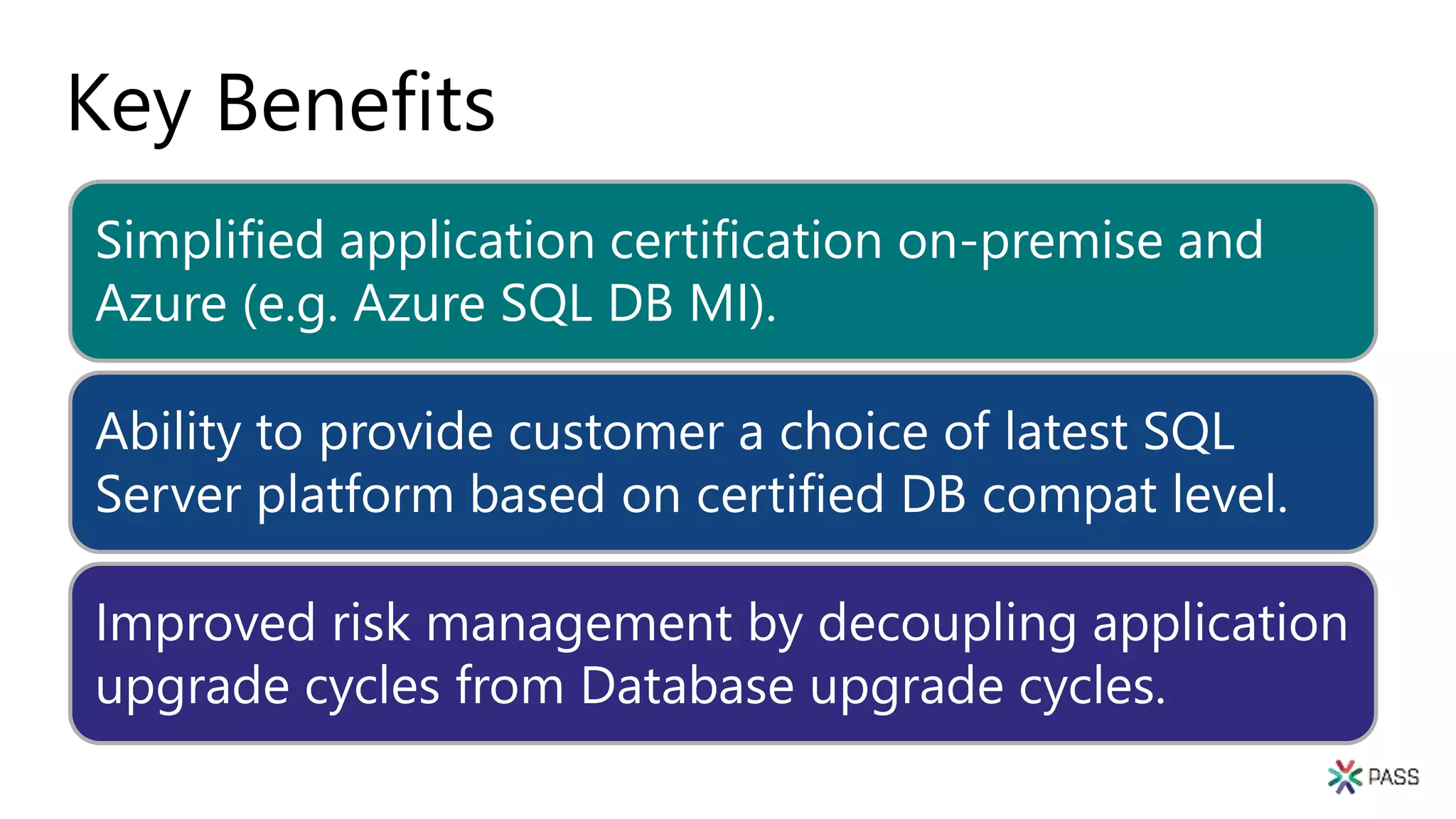
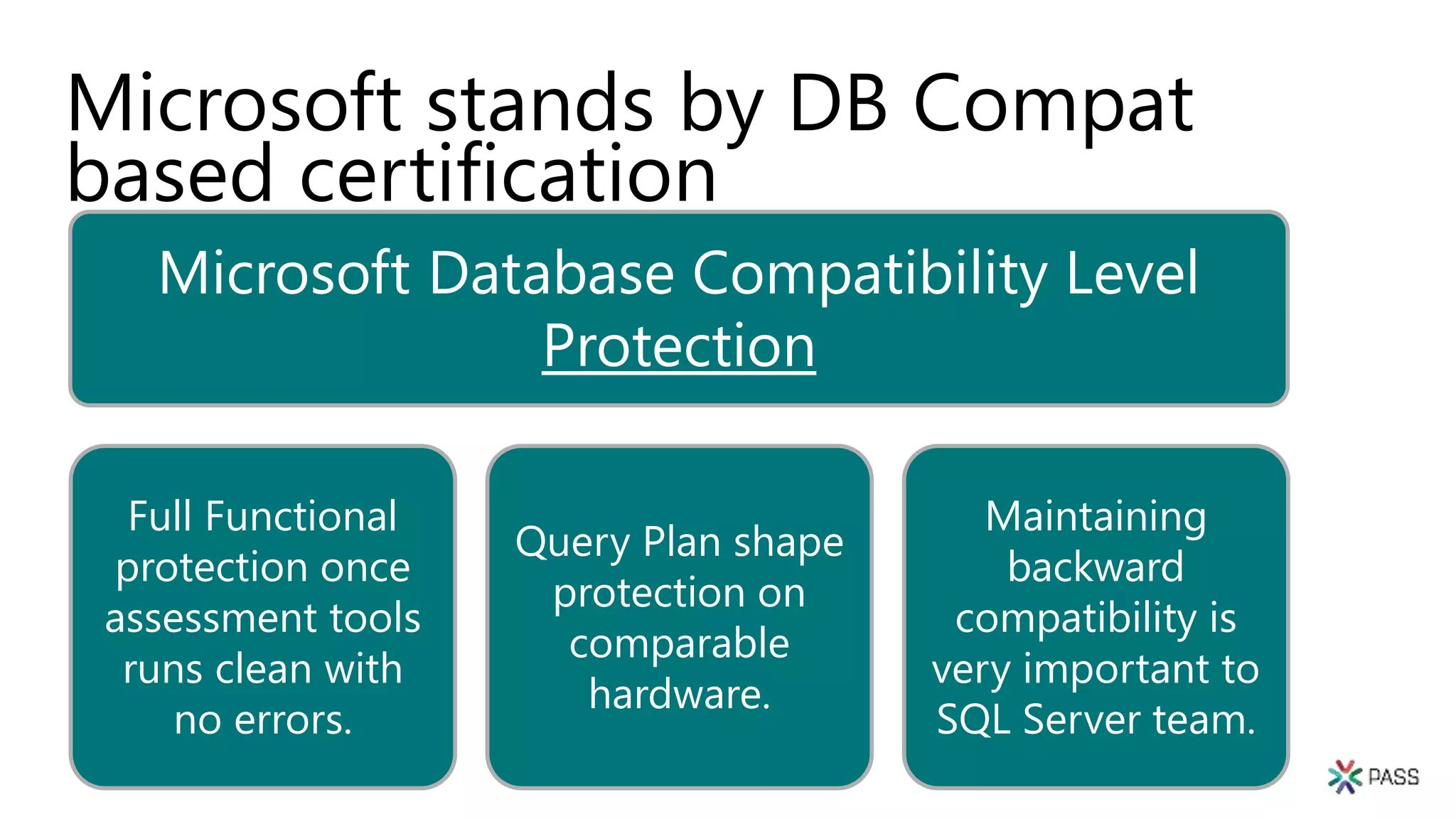
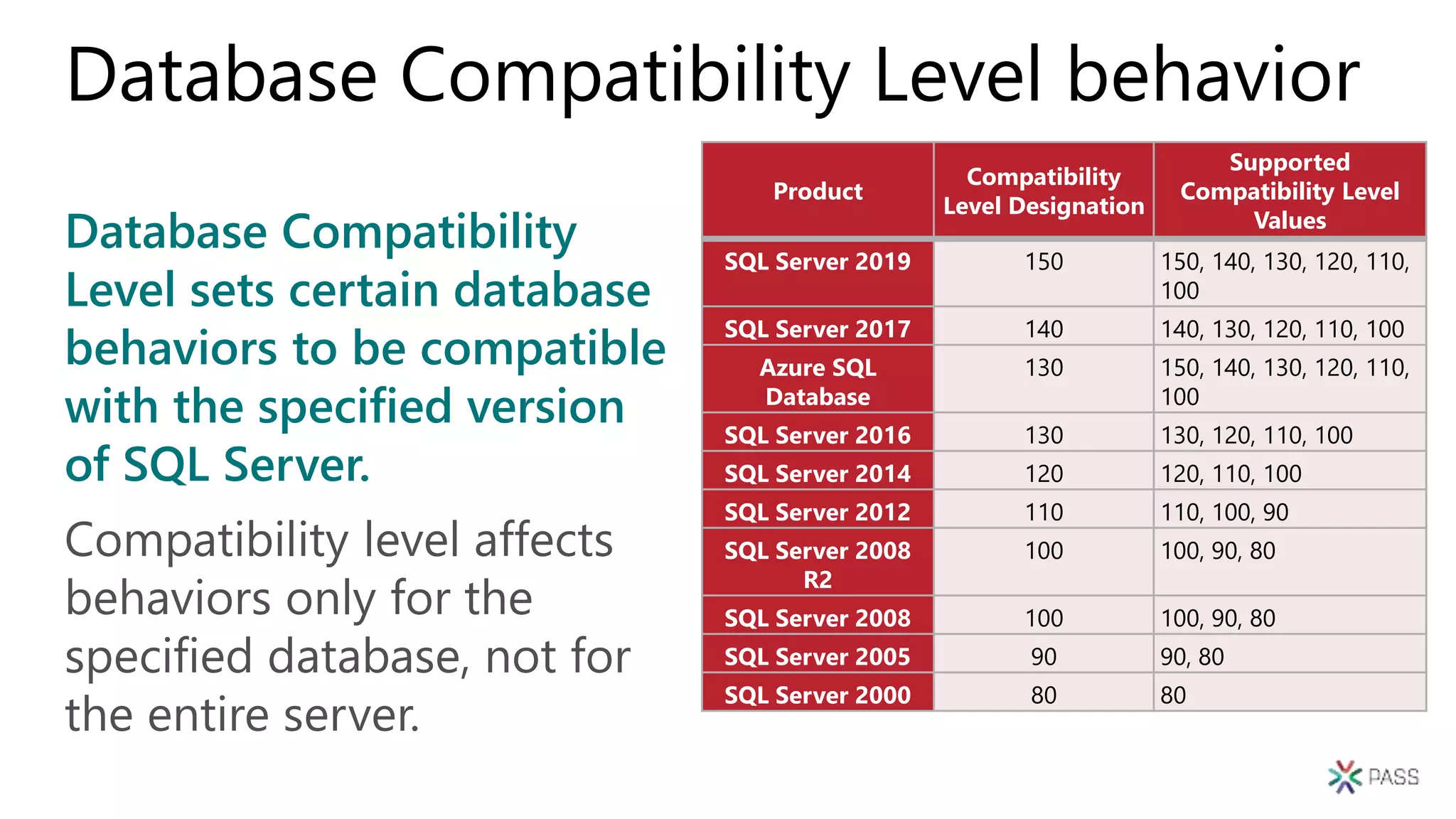
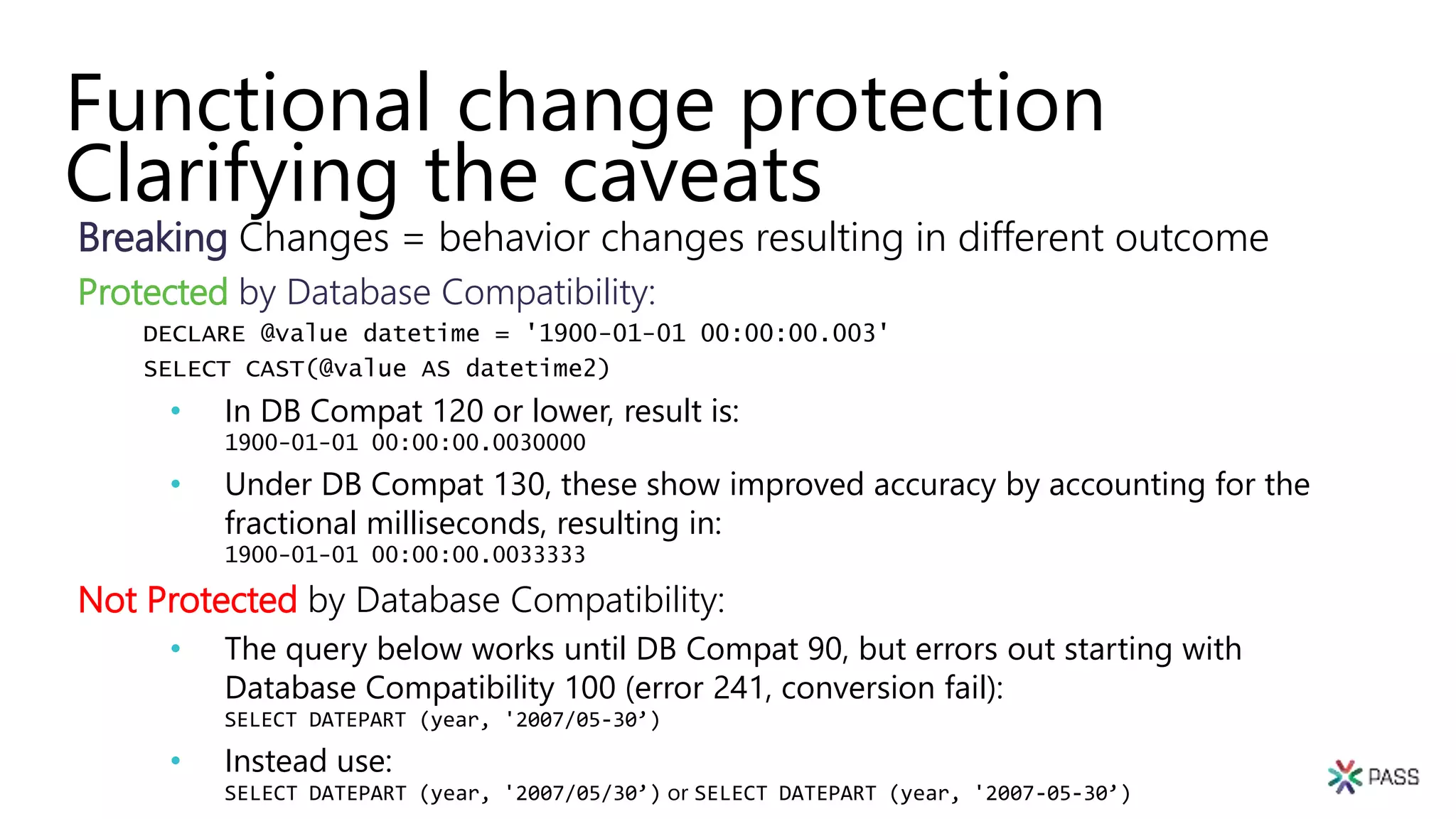
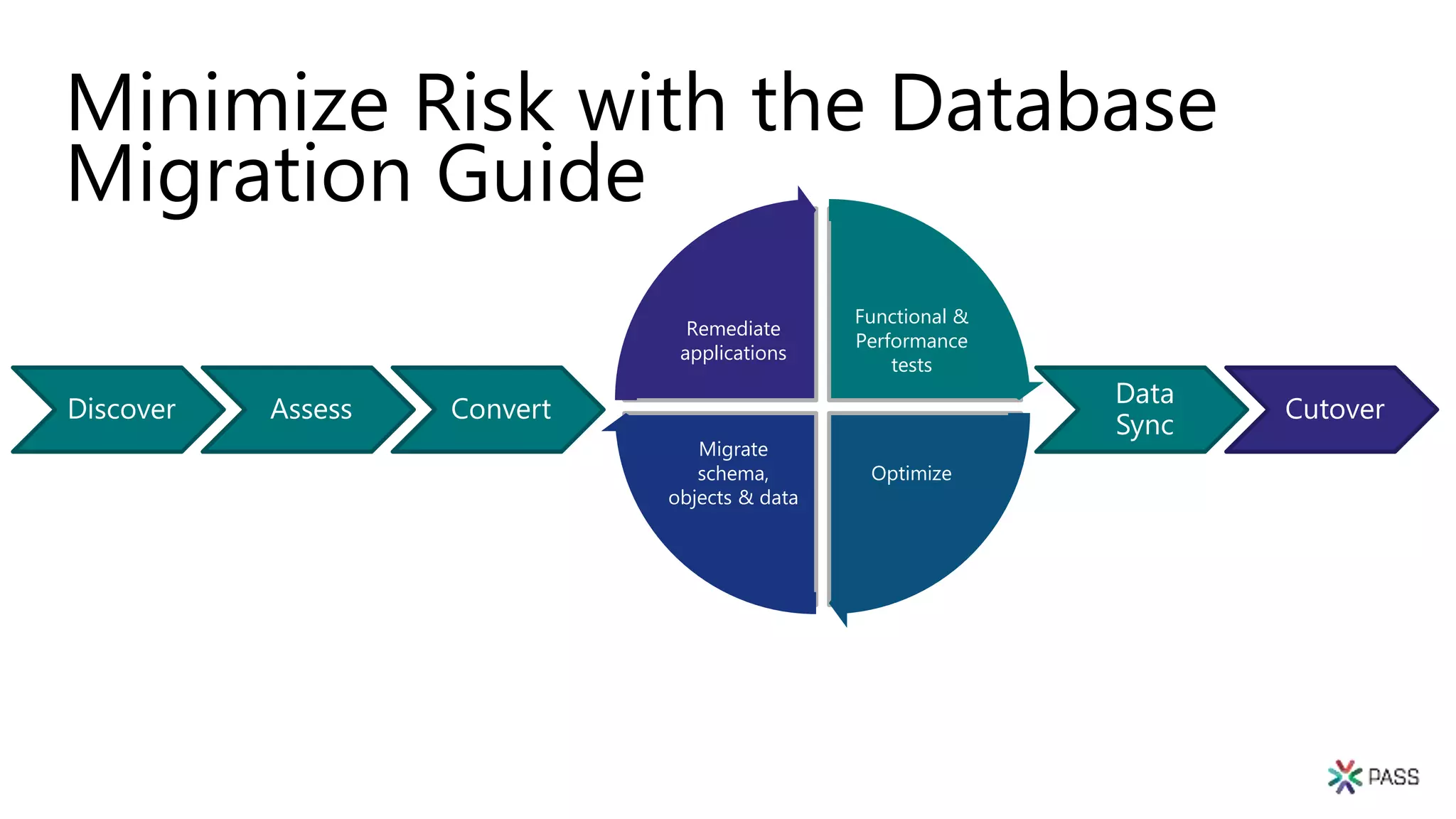
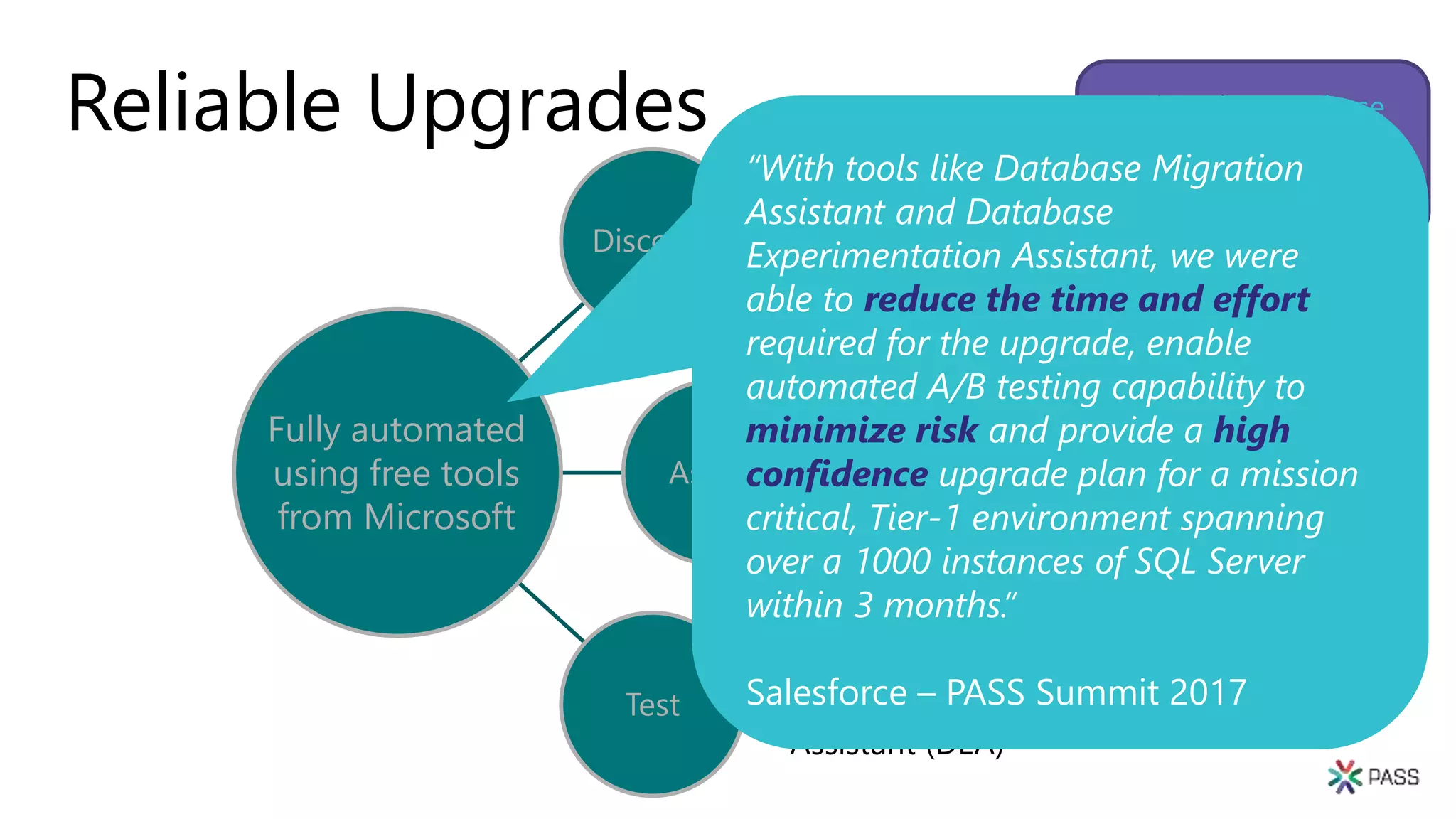
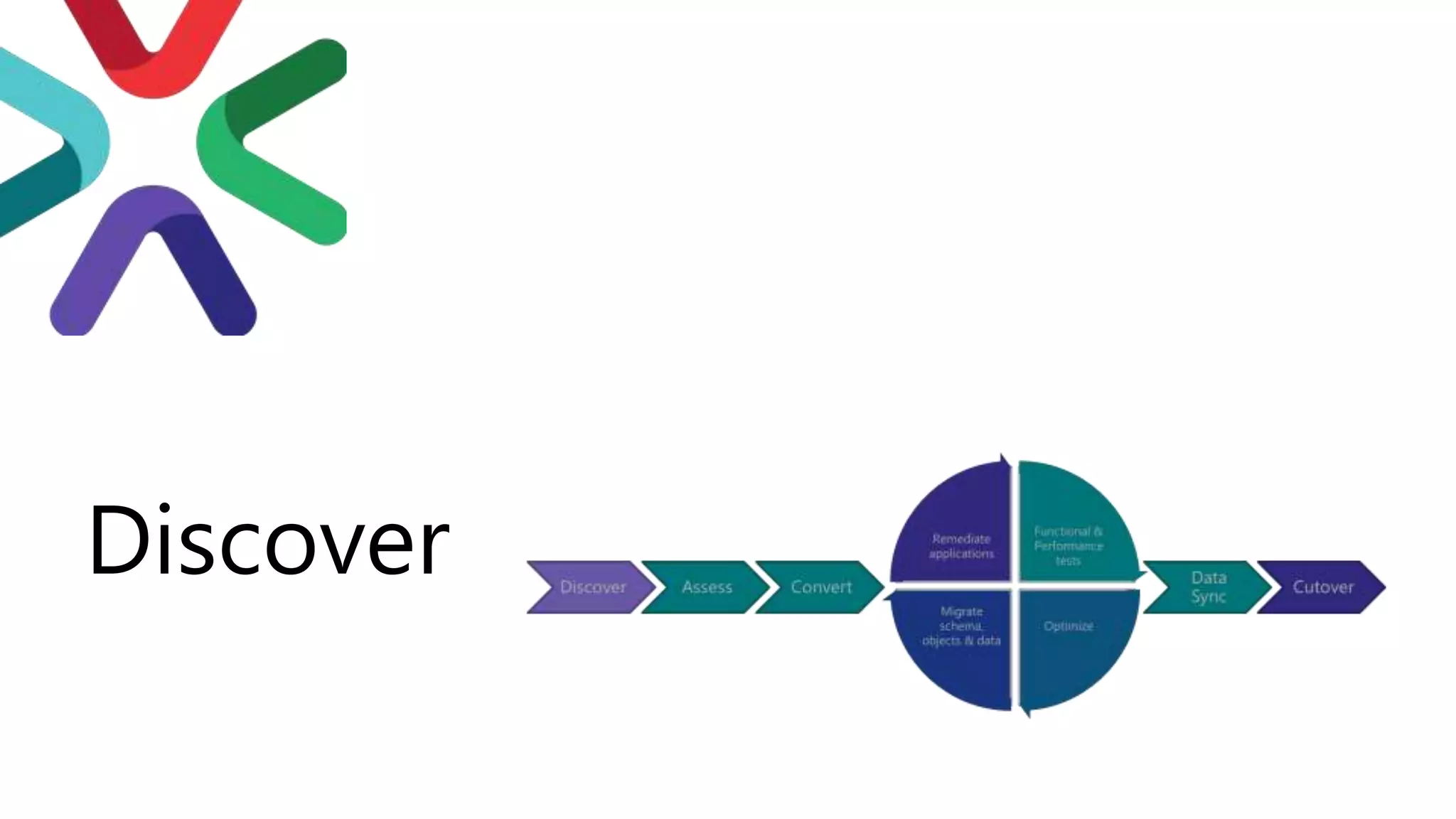
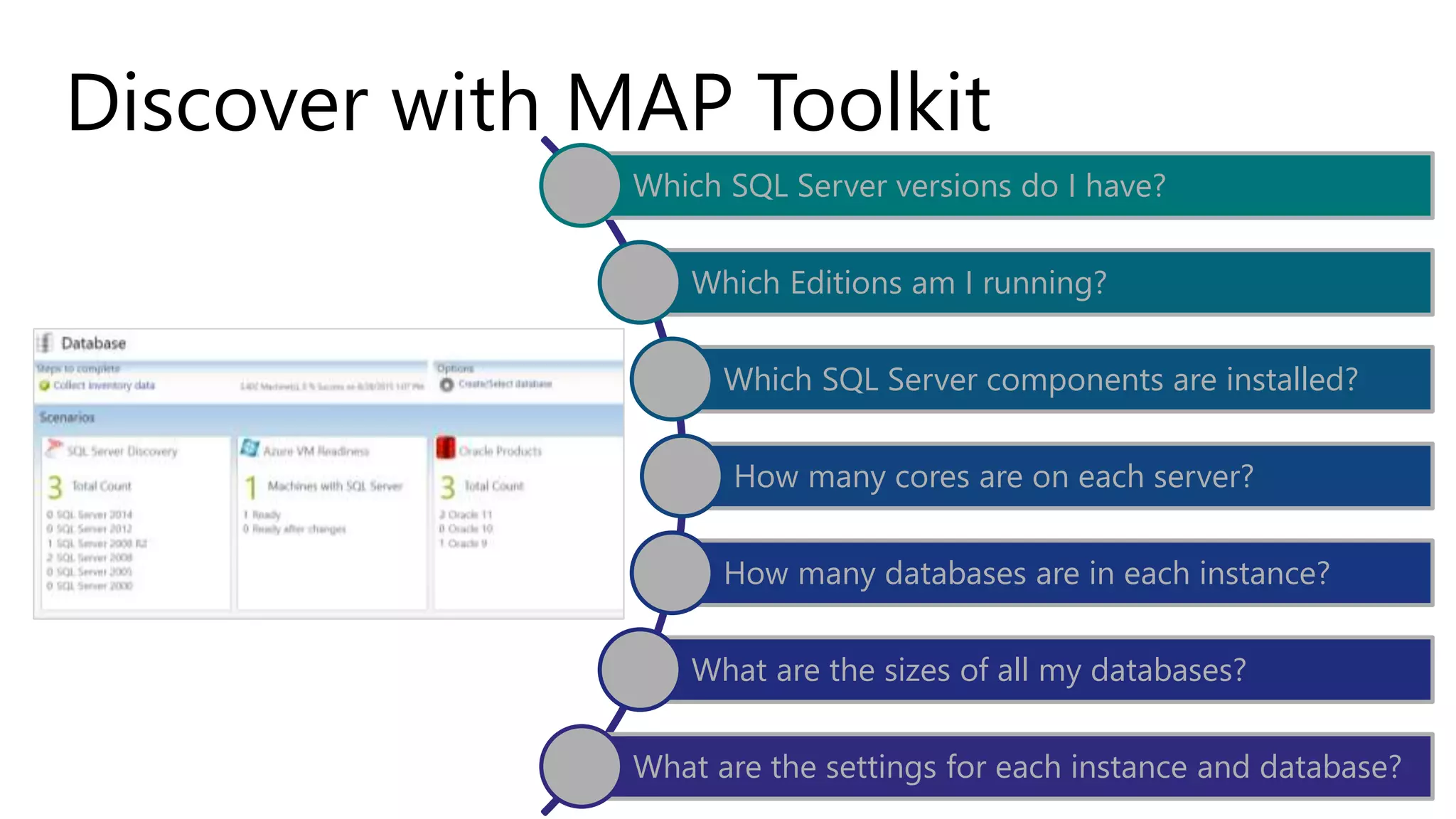
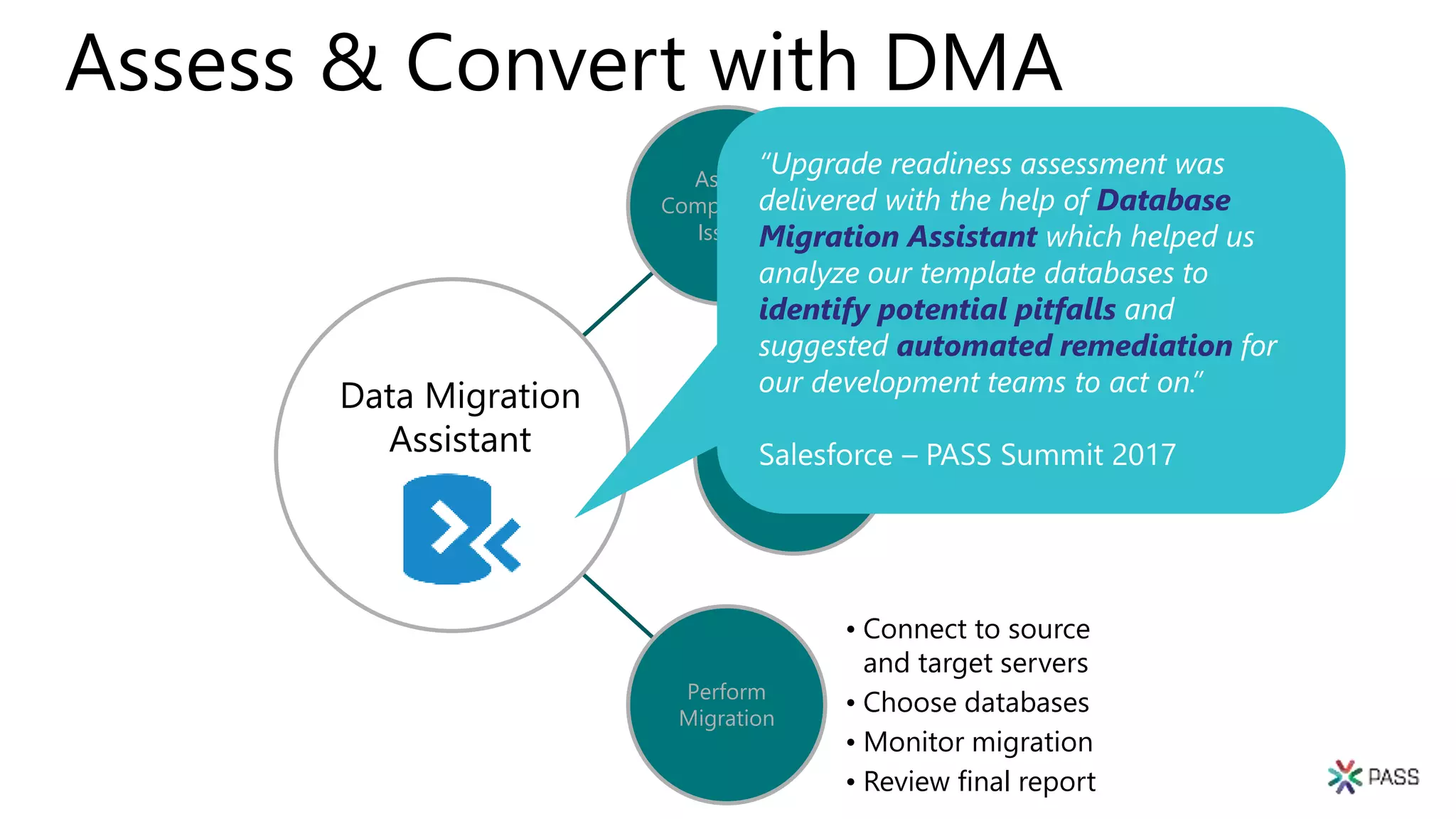
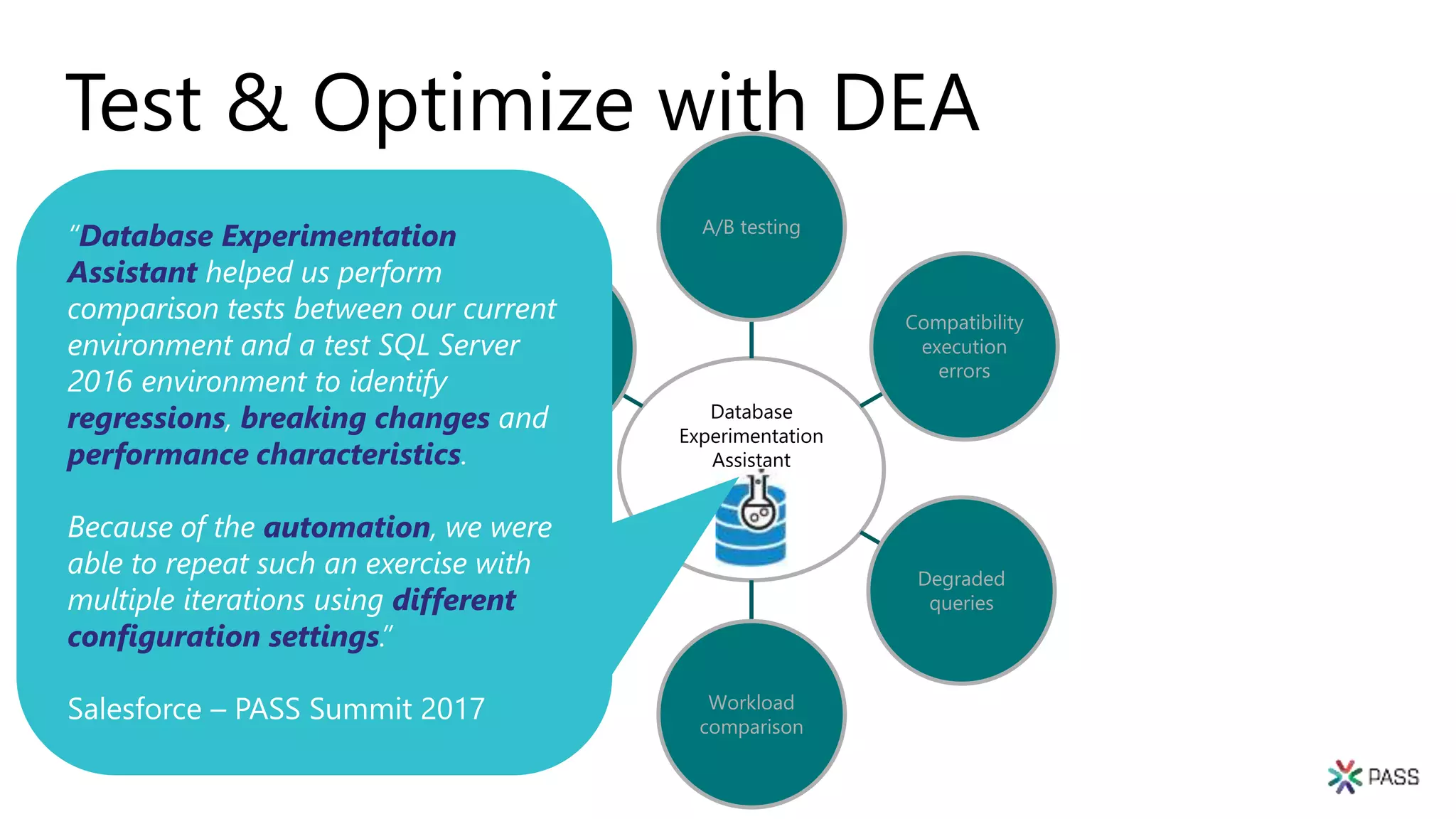
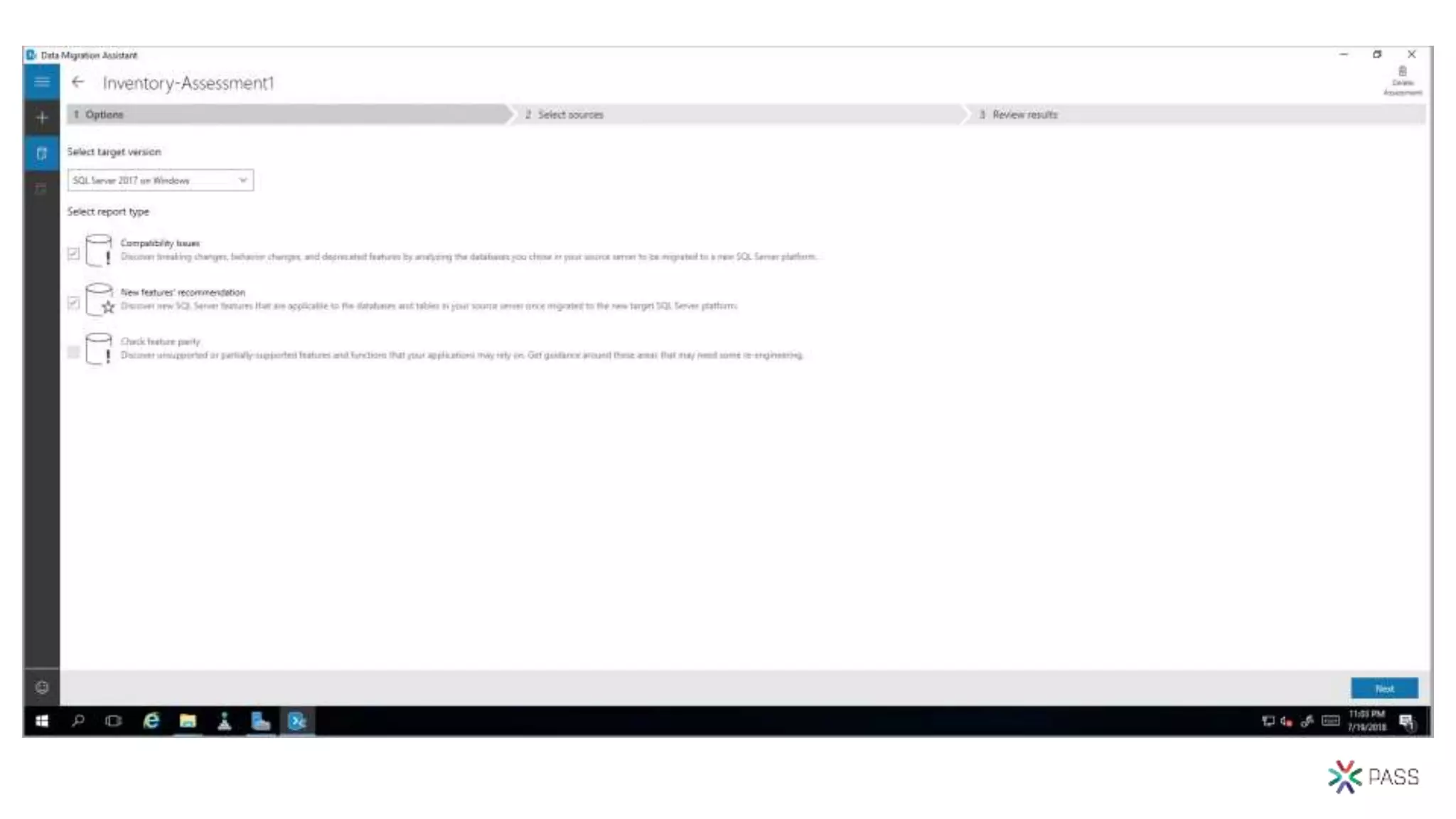
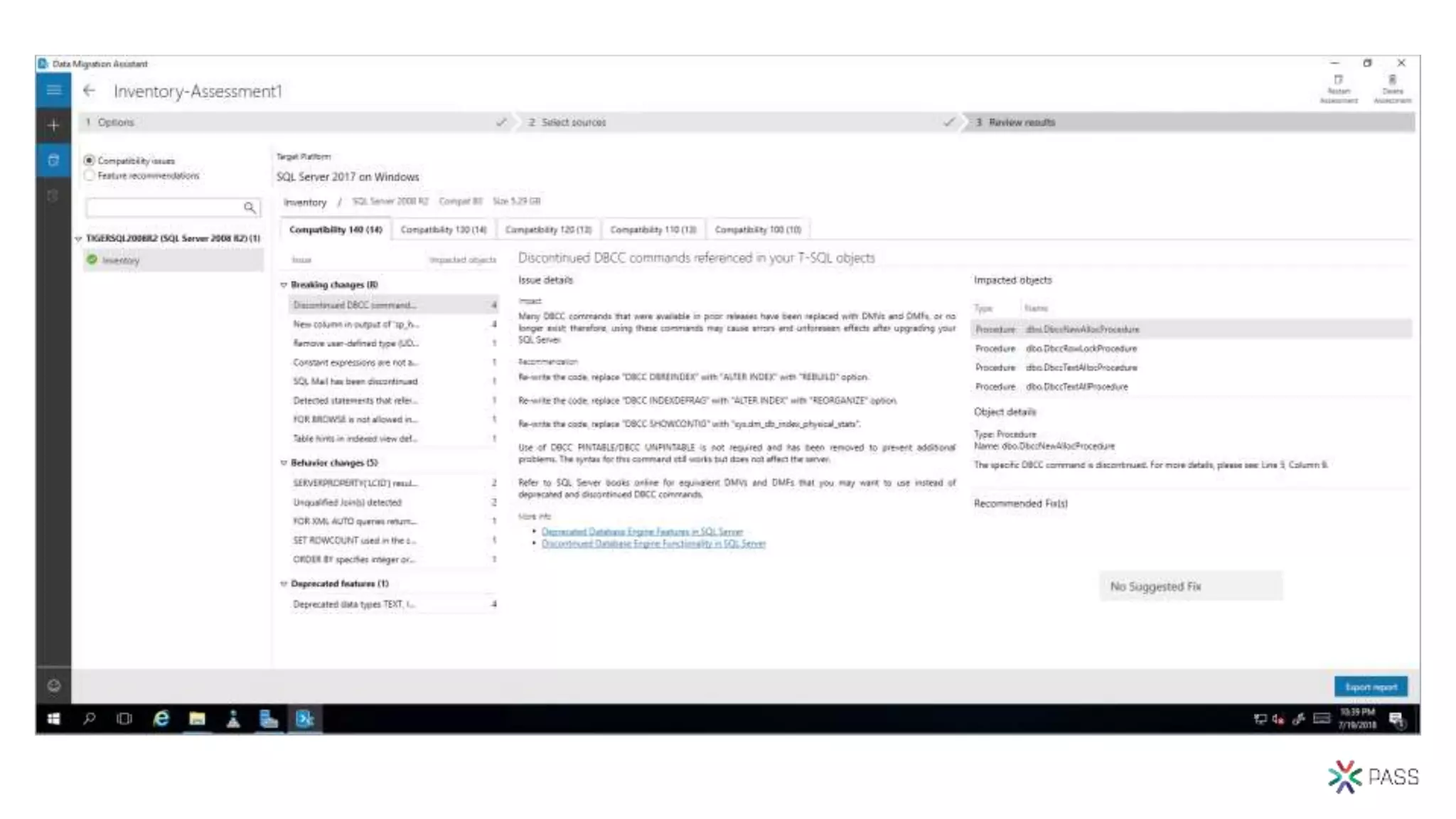
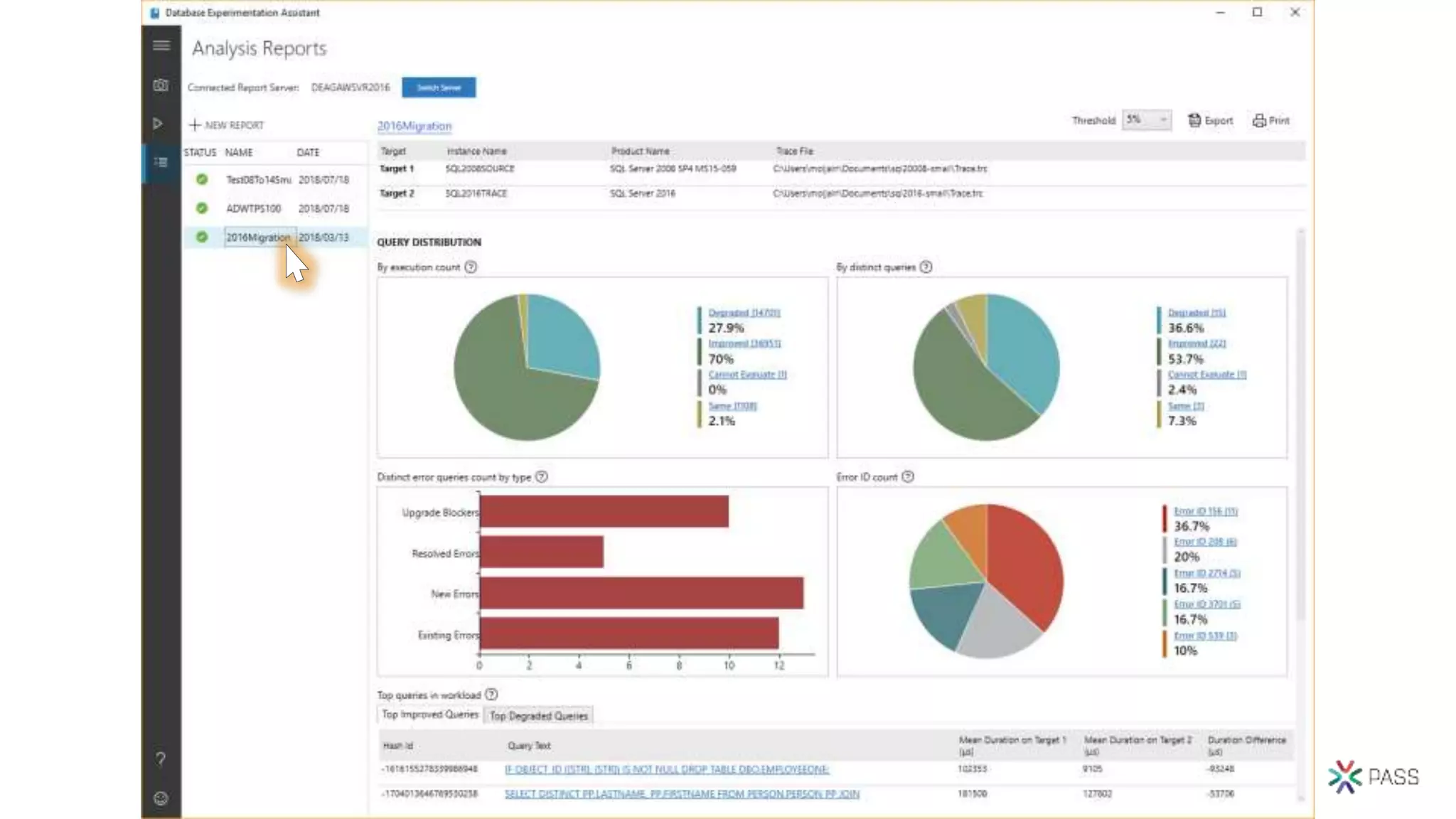
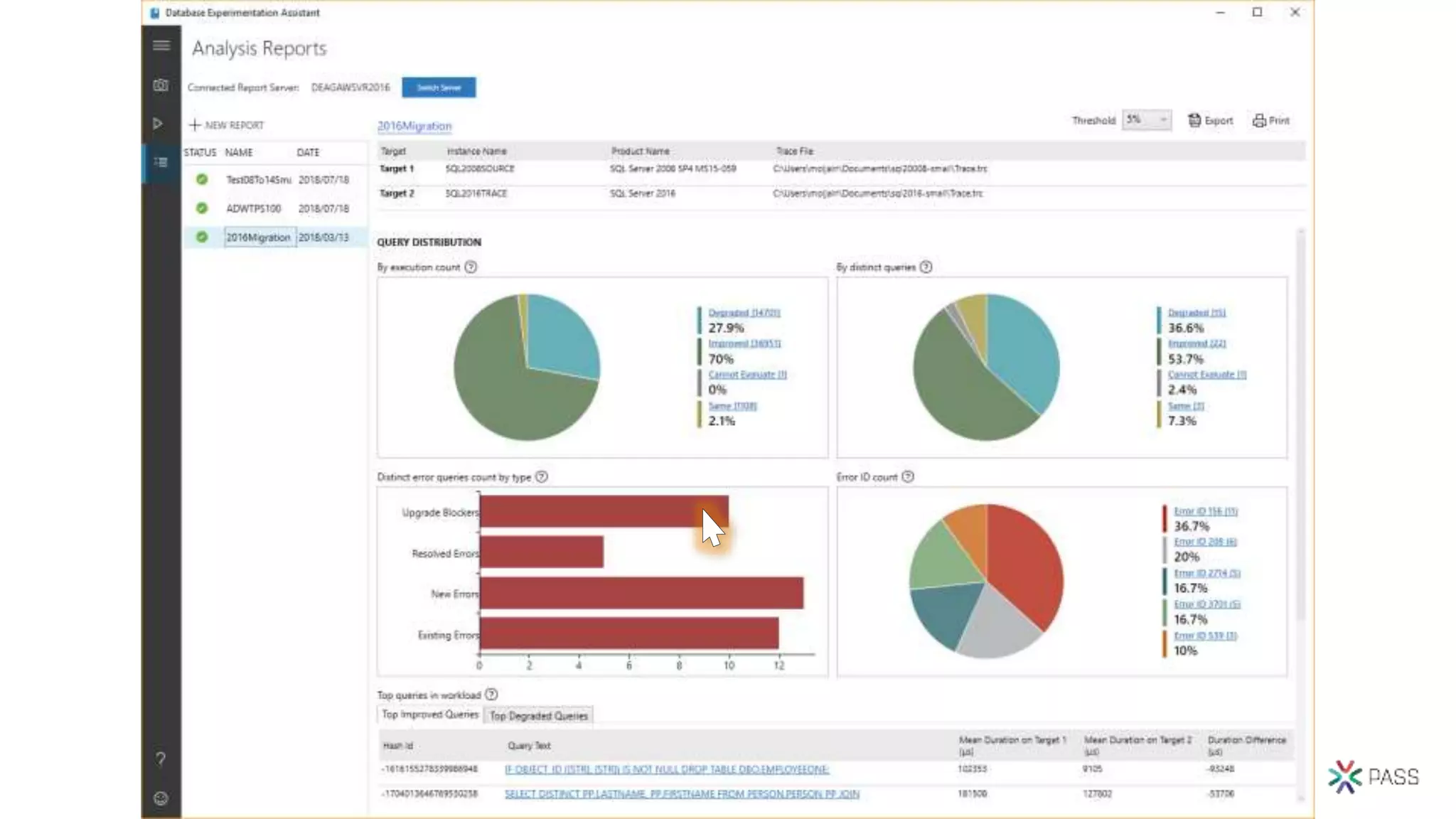
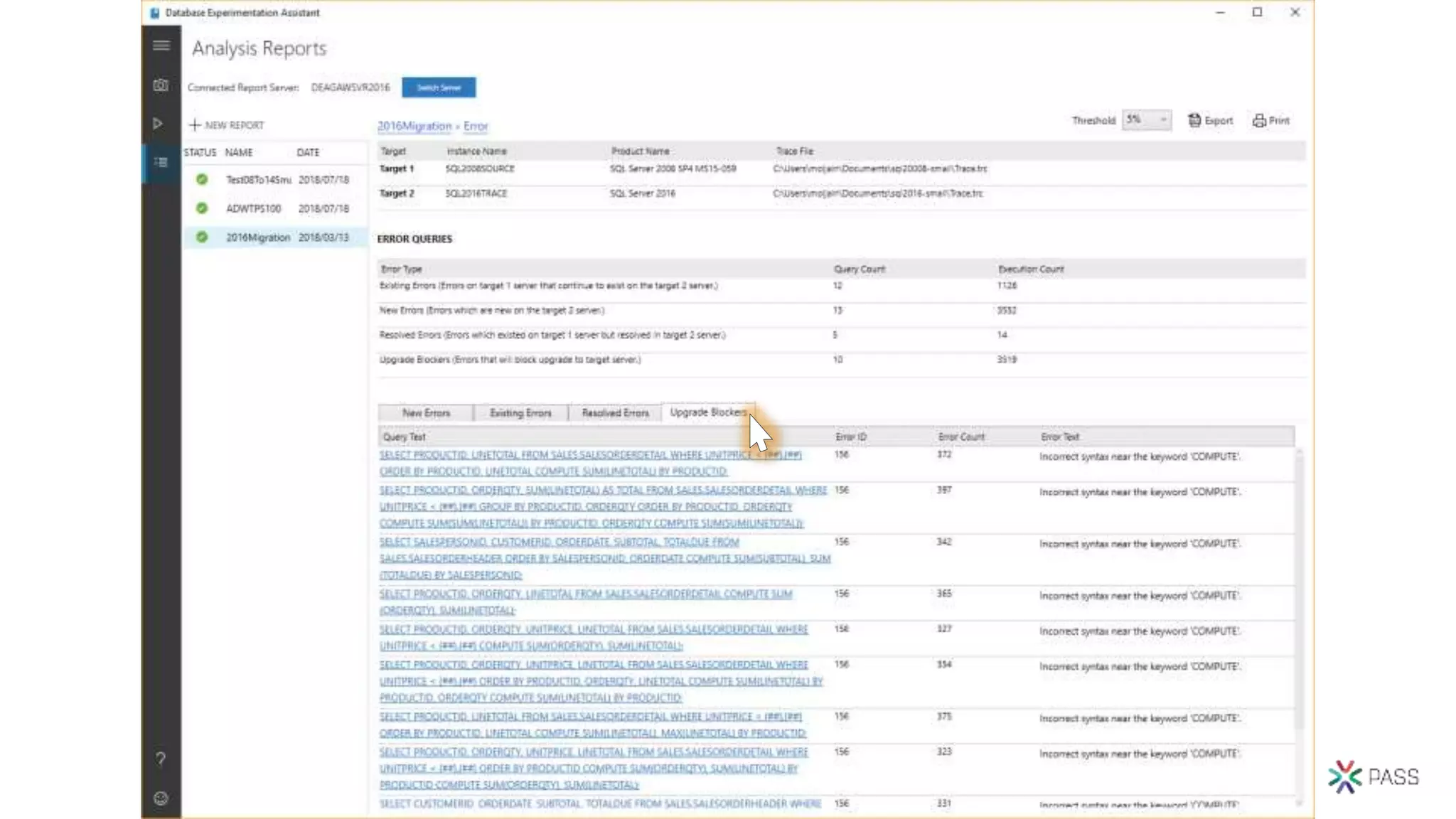
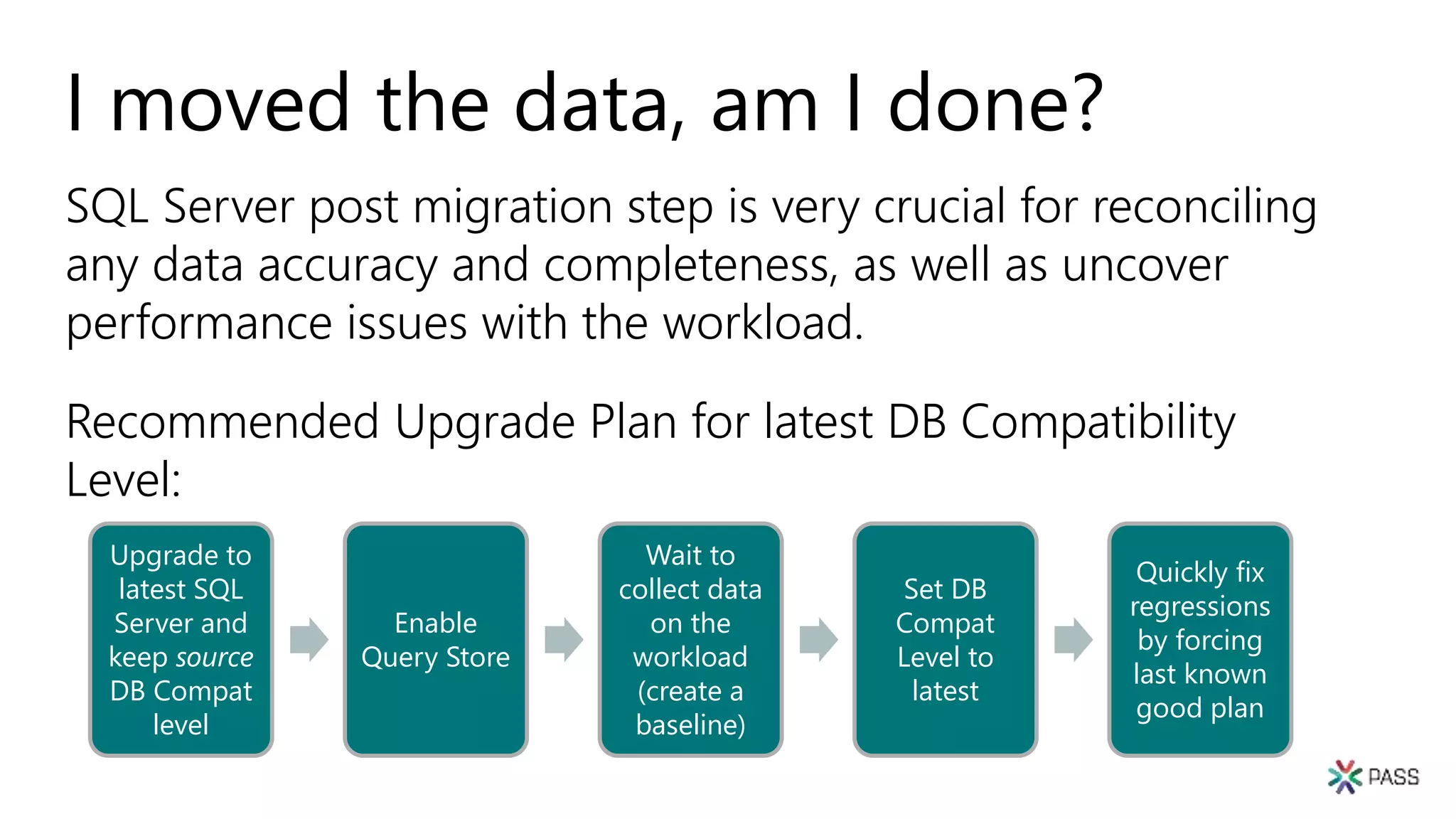
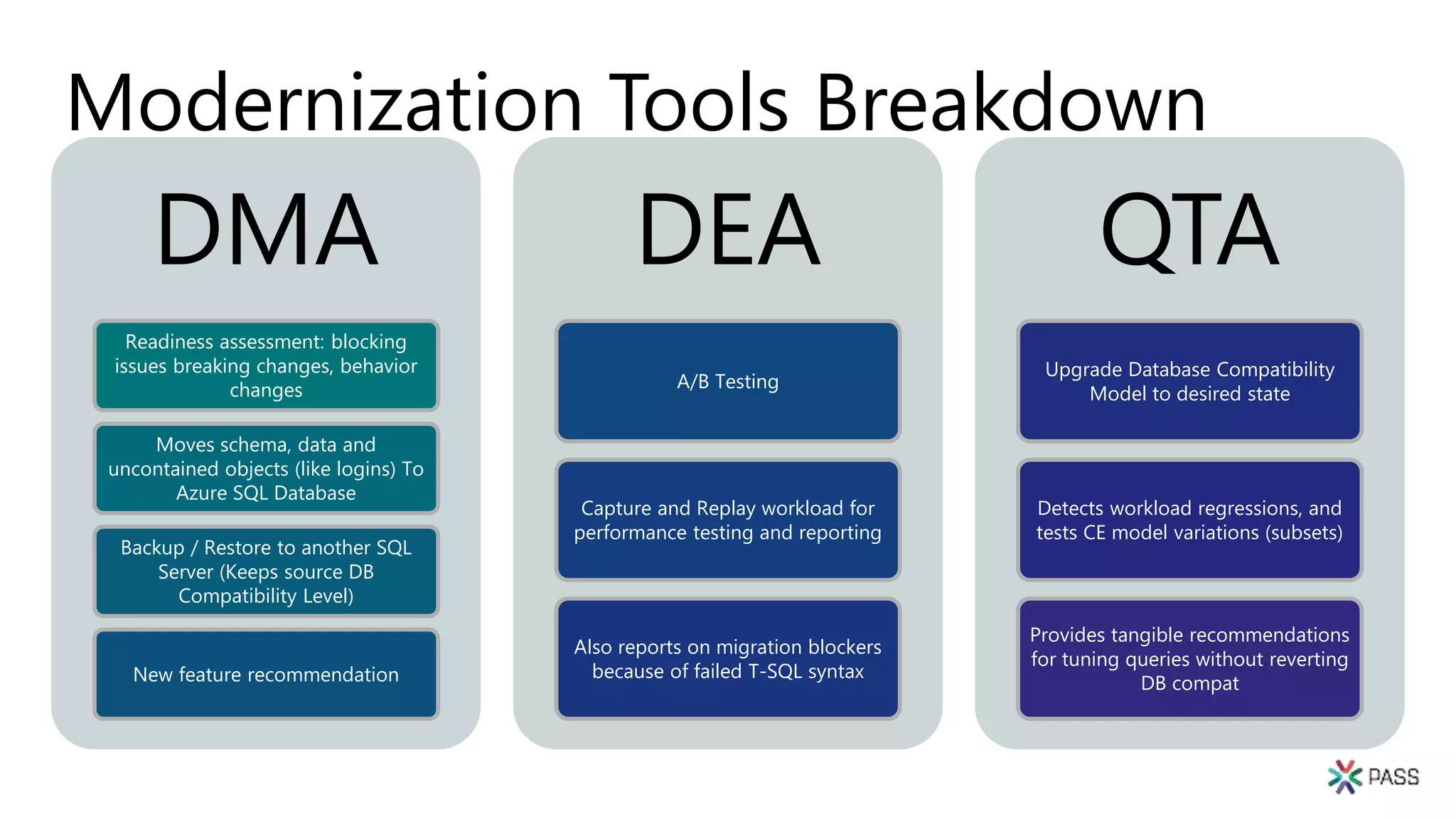
The document discusses the PASS Summit 2019, the largest technical conference for data professionals leveraging the Microsoft data platform, offering various discounts and information on upcoming webinars and sessions. It emphasizes the importance of modernizing SQL Server and introduces tools like the Database Migration Assistant and Database Experimentation Assistant to facilitate smooth upgrades and assess compatibility. Additionally, it outlines the significance of maintaining database compatibility levels for functional protection and risk management during upgrades.