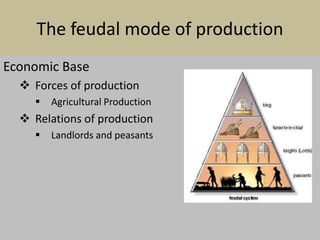
Karl Marx identifies production as essential for human existence and as a social activity that requires cooperation and organization. He describes different modes of production throughout history - from primitive communism to slave societies to feudalism and capitalism - that determine societal class divisions and expressions of culture. Under capitalism, the economic base of forces and relations of production are controlled by the ruling capitalist class, while the social superstructure serves to maintain their interests, but contradictions will lead to revolution and establishment of a communist mode of production without classes.