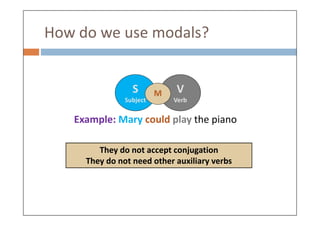
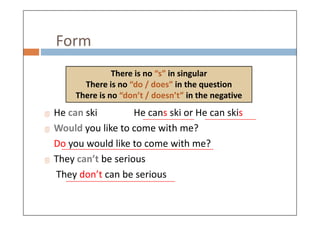
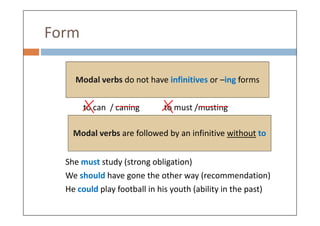
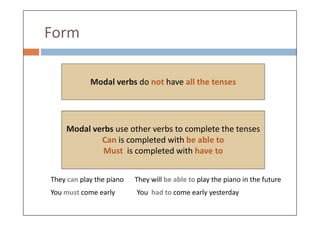
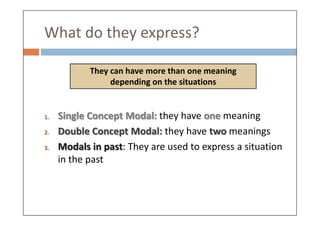
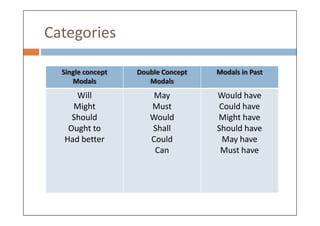
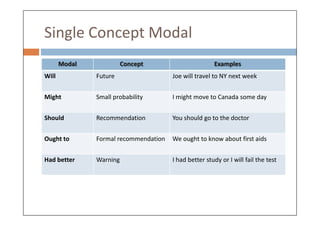
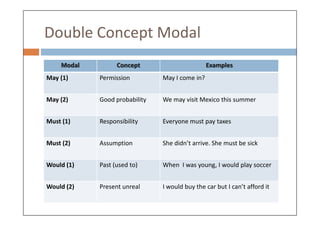
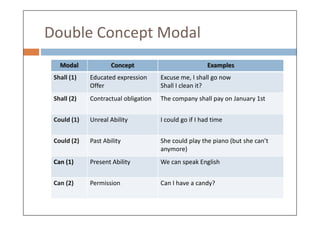
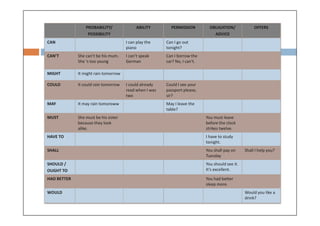
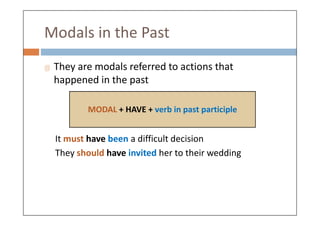
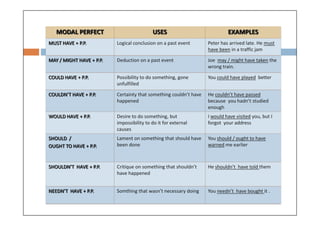
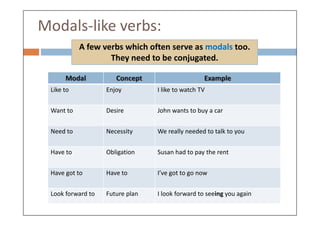
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that add specific meaning to main verbs and do not conjugate or require other auxiliary verbs. They express concepts like ability, permission, obligation, and probability, and can have single or double meanings depending on context. Modal verbs can also form modal perfects to indicate actions in the past, using structures such as 'must have' and 'should have'.