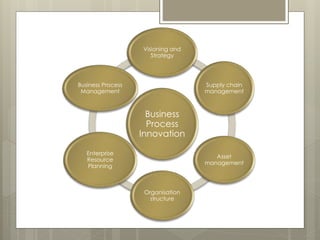
The document discusses strategic innovation and new product development. It outlines the key aspects of strategic innovation including new business models, new markets, and increased value for customers and companies. It also discusses the dimensions and features of strategic innovation.
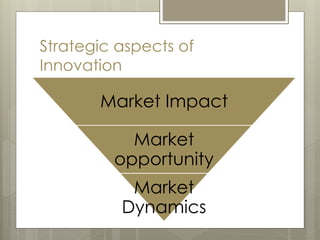
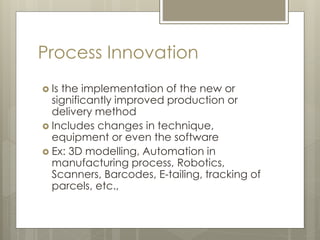
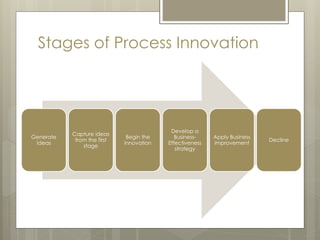
The document then covers various aspects of new product development including identifying market opportunities and dynamics, developing marketing strategies, product testing, and commercialization. It provides examples of innovation platforms from companies like Apple and DSM. Finally, it discusses the process of new product development from strategy to commercialization.