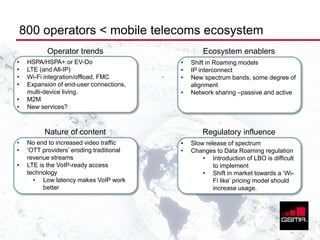
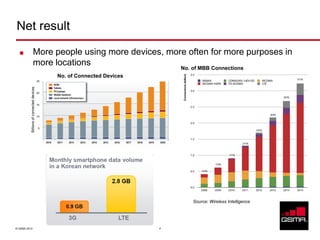
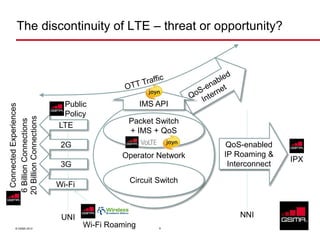
The document discusses the GSMA, a trade group representing mobile operators. It summarizes the GSMA's history and growth. Next, it outlines trends facing mobile operators like increasing video traffic and new services, as well as regulatory influences. To address these challenges, the document recommends strategies like obtaining more spectrum, network sharing, Wi-Fi roaming, and new offload and caching models. Finally, it argues that LTE presents both threats and opportunities, and that operators should embrace changes to prepare for the future.