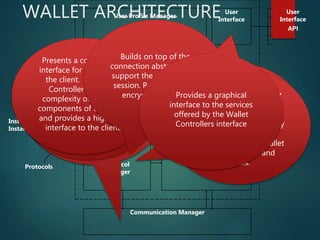
This document presents an empirical study on consumer perception of digital wallets among college students in Faridabad, exploring their adoption, influencing factors, and obstacles. It defines mobile wallets and outlines the technology's features, advantages, and challenges including system outages and security concerns. The study aims to understand students' views on this technological service and its potential impact on payment methods.