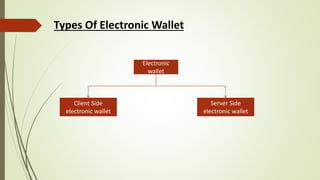
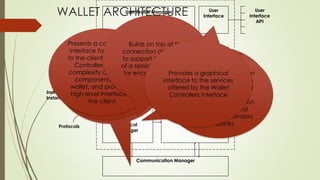
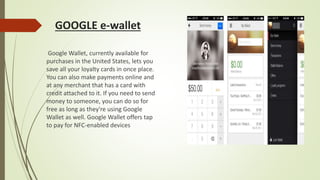
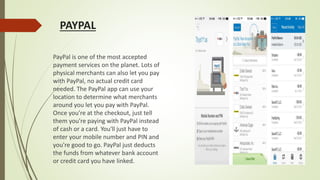
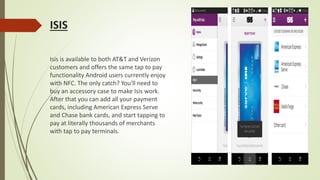
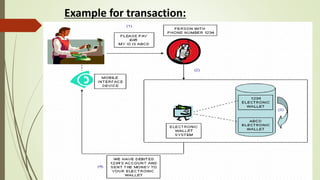
This document provides information about e-wallets. It begins with an introduction that defines an e-wallet as a software component that allows users to make electronic payments by hiding the low-level payment details. It then discusses the types of e-wallets, components, technologies like NFC, payment models, wallet architecture, features, advantages and disadvantages, and how e-wallets are currently being used. Examples of popular e-wallets mentioned include Square Wallet, Google Wallet, PayPal, ISIS, Venmo and Dwolla.