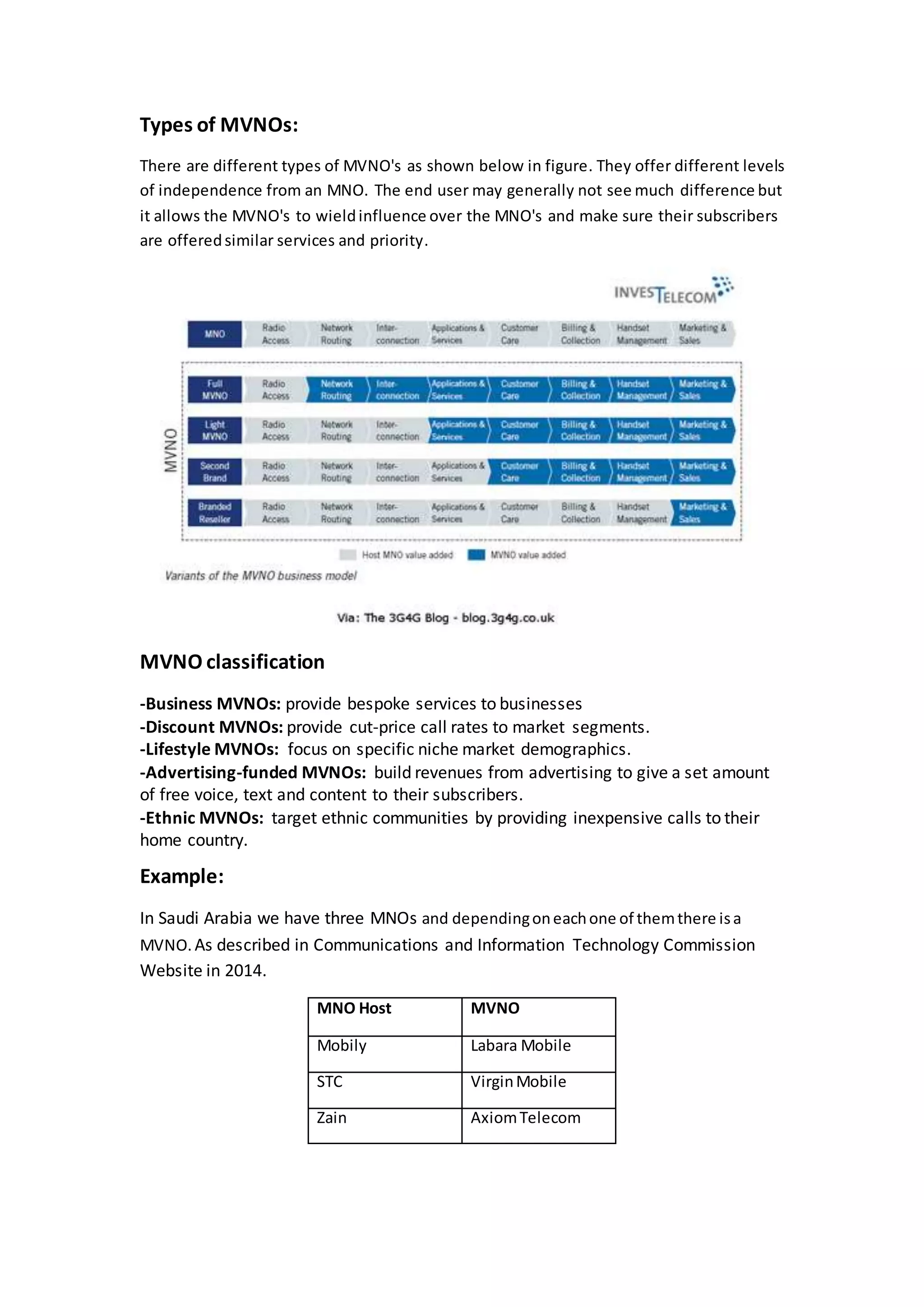
An MVNO is a mobile virtual network operator that provides mobile phone services using another company's network infrastructure and spectrum licenses. MVNOs do not own their own network equipment or spectrum, but instead purchase bulk access to network services from traditional network operators known as mobile network operators or MNOs. There are different types of MVNOs that offer varying levels of independence from MNOs, including business MVNOs, discount MVNOs, lifestyle MVNOs, and ethnic MVNOs. In Saudi Arabia, the three major MNOs - Mobily, STC, and Zain - each host MVNOs that operate using their networks and services.