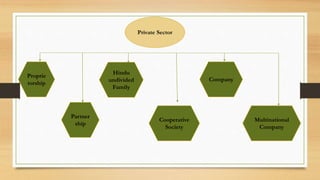
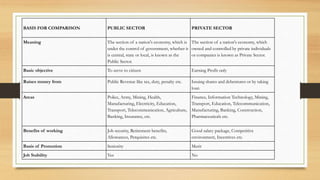
The document discusses opportunities and challenges for India's "Make in India" campaign in the public and private sectors. The public sector encompasses government-run industries and services like postal, education, railways, and more. It generates employment but faces challenges like improving governance. The private sector covers for-profit businesses and contributes through sectors like IT, manufacturing, and infrastructure development, but must raise capital through shares rather than taxes. Both sectors will be crucial for Make in India's success but must address issues such as education quality, trade, and inflation.