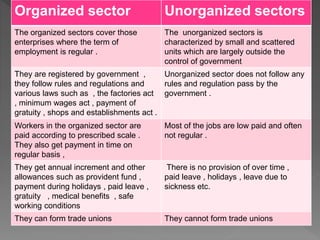
The document discusses organized and unorganized sectors in India. It notes that organized sectors follow government rules and regulations, have employee and employer unions, and include registered companies. Unorganized sectors do not follow standardized norms and include many small, informal businesses. It also discusses differences between public and private sectors, with public sector primarily providing basic government services and private sector made up of private enterprises focused on profit.