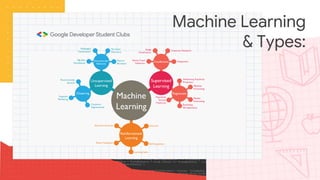
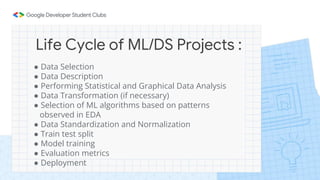
This document provides an introduction to machine learning, including the life cycle of machine learning/data science projects and various algorithms. It discusses the main types of machine learning (supervised vs. unsupervised), describes some common classification and regression algorithms, and gives examples of use cases like healthcare, security, recommendation systems, and more. The life cycle includes steps like data selection, description, transformation, model training, evaluation, and deployment.






![Logistic Regression
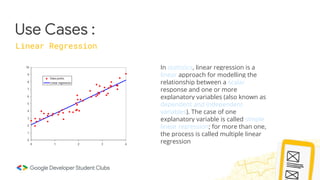
Logistic regression is a
statistical model that in its basic
form uses a logistic function to
model a binary dependent
variable, although many more
complex extensions exist. In
regression analysis, logistic
regression[1] (or logit regression)
is estimating the parameters of
a logistic model (a form of
binary regression).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mlworkshop-220312151649/85/Ml-workshop-11-320.jpg)

