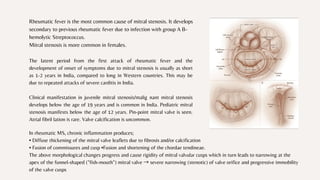
Mitral stenosis is a valvular heart disease characterized by the narrowing of the mitral valve opening due to structural abnormalities of the mitral valve. It occurs when the mitral valve leaflets become thickened, calcified and fused together, decreasing the opening of the valve. Rheumatic fever is the most common cause of mitral stenosis. Symptoms occur when the valve opening decreases to less than 2cm2 and include breathlessness, pulmonary edema and atrial fibrillation.