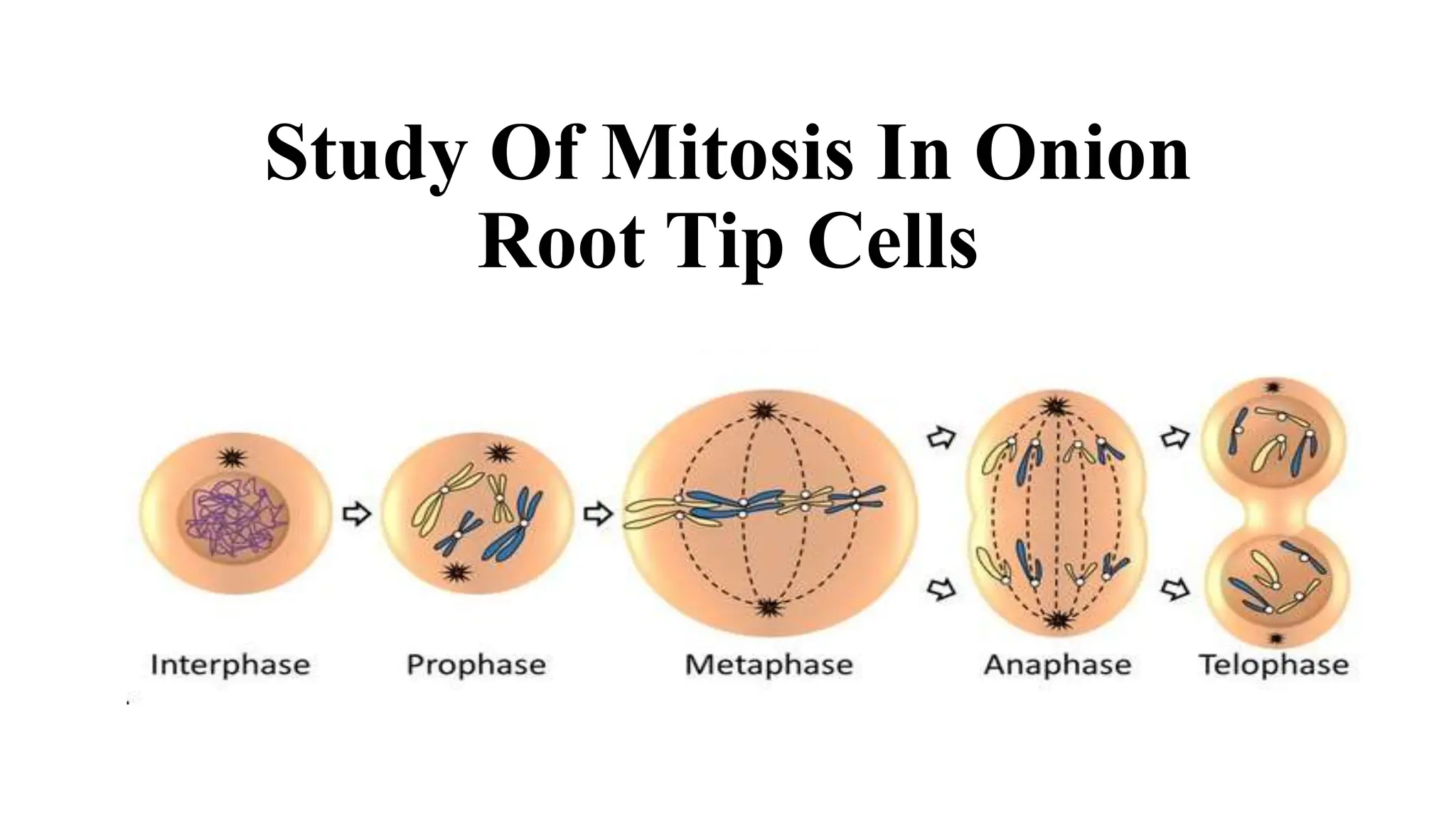
The document details an experiment aimed at studying mitosis in onion root tip cells. It describes the procedure for preparing a slide to observe different stages of mitosis, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Essential materials and specific steps for the experiment are outlined to facilitate the observation of cell division.