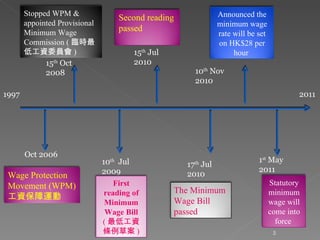
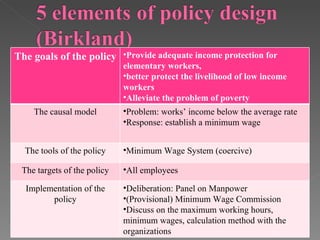
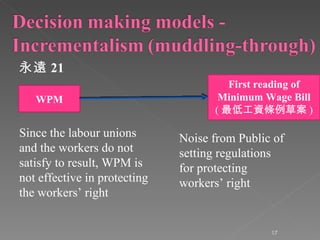
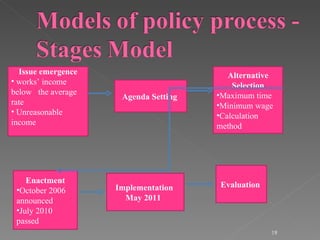
The document discusses Hong Kong's statutory minimum wage policy from 2006 to 2011. It began with the Wage Protection Movement (WPM) in 2006 to protect wages of cleaning and security workers voluntarily, but only 52% benefited. In 2008, the Chief Executive announced a statutory minimum wage would be implemented. A Provisional Minimum Wage Commission was established and conducted public consultations from 2009 to 2010 before recommending the minimum wage be set at $28 per hour, which was enacted in May 2011. The policy used an incremental approach, starting with the voluntary WPM before moving to mandatory legislation.