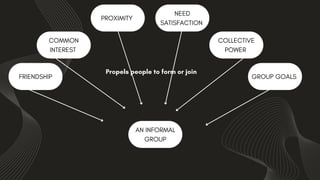
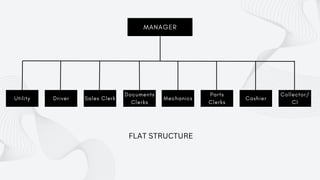
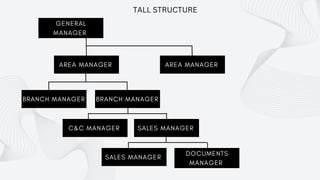
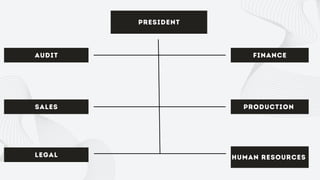
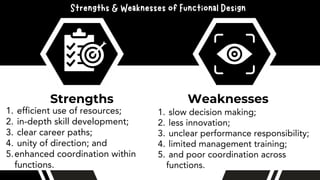
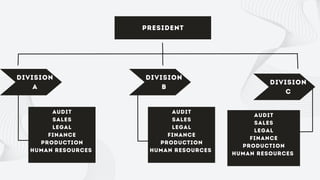
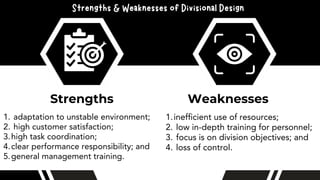
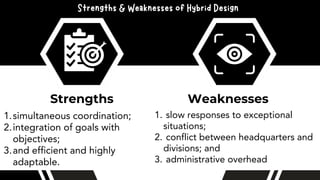
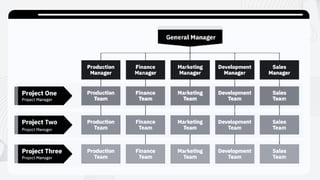
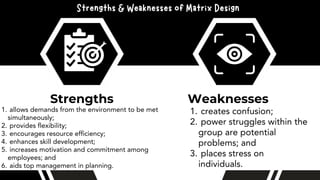
The document discusses the importance of organizational structure and its determinants, including formal and informal groups, levels of management, and different types of organizational designs. It emphasizes that effective organizational skills are critical for managers to enhance efficiency and meet company objectives. The document also details various structures such as flat, tall, functional, divisional, hybrid, and matrix designs, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses in achieving organizational goals.