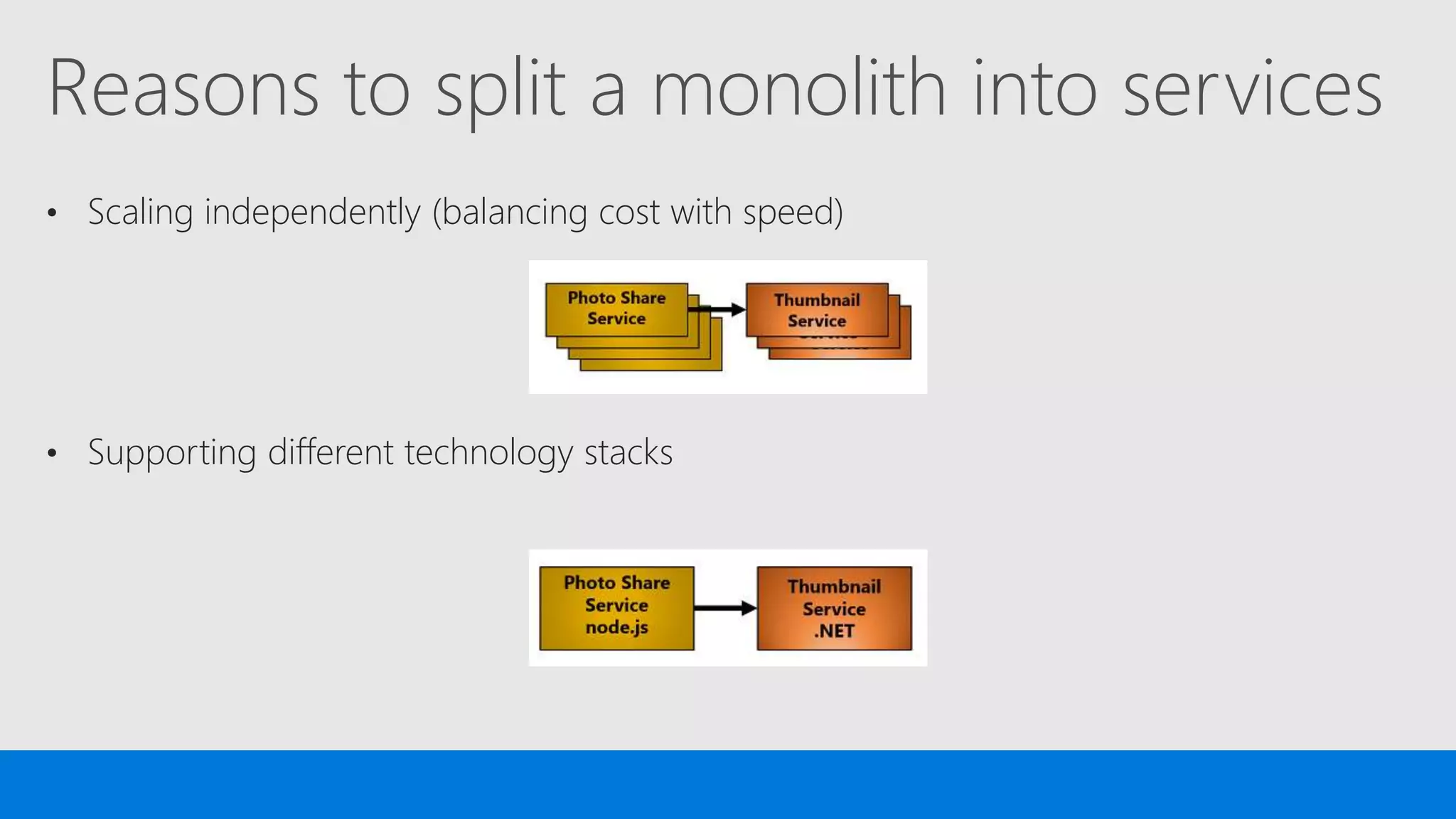
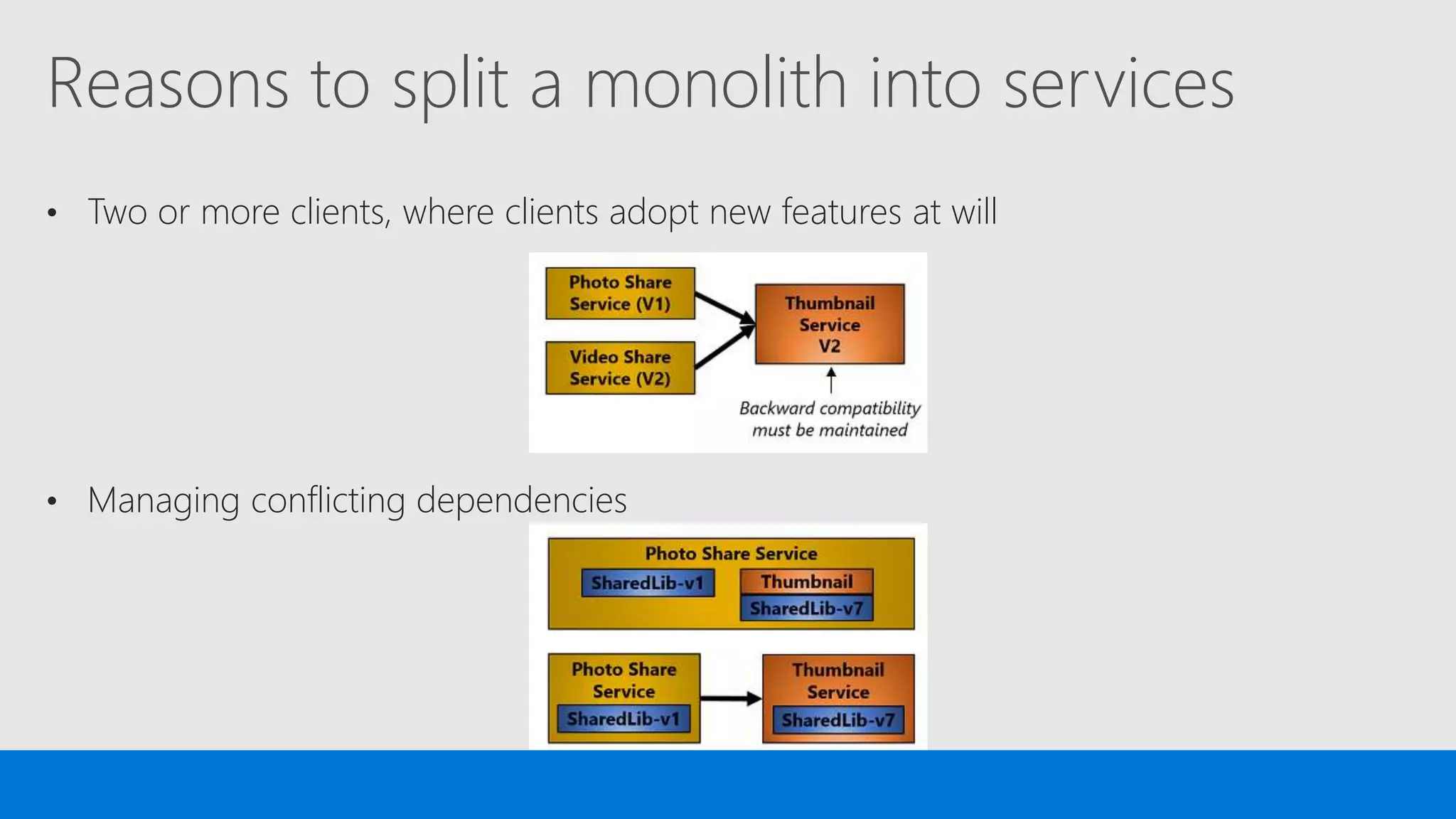
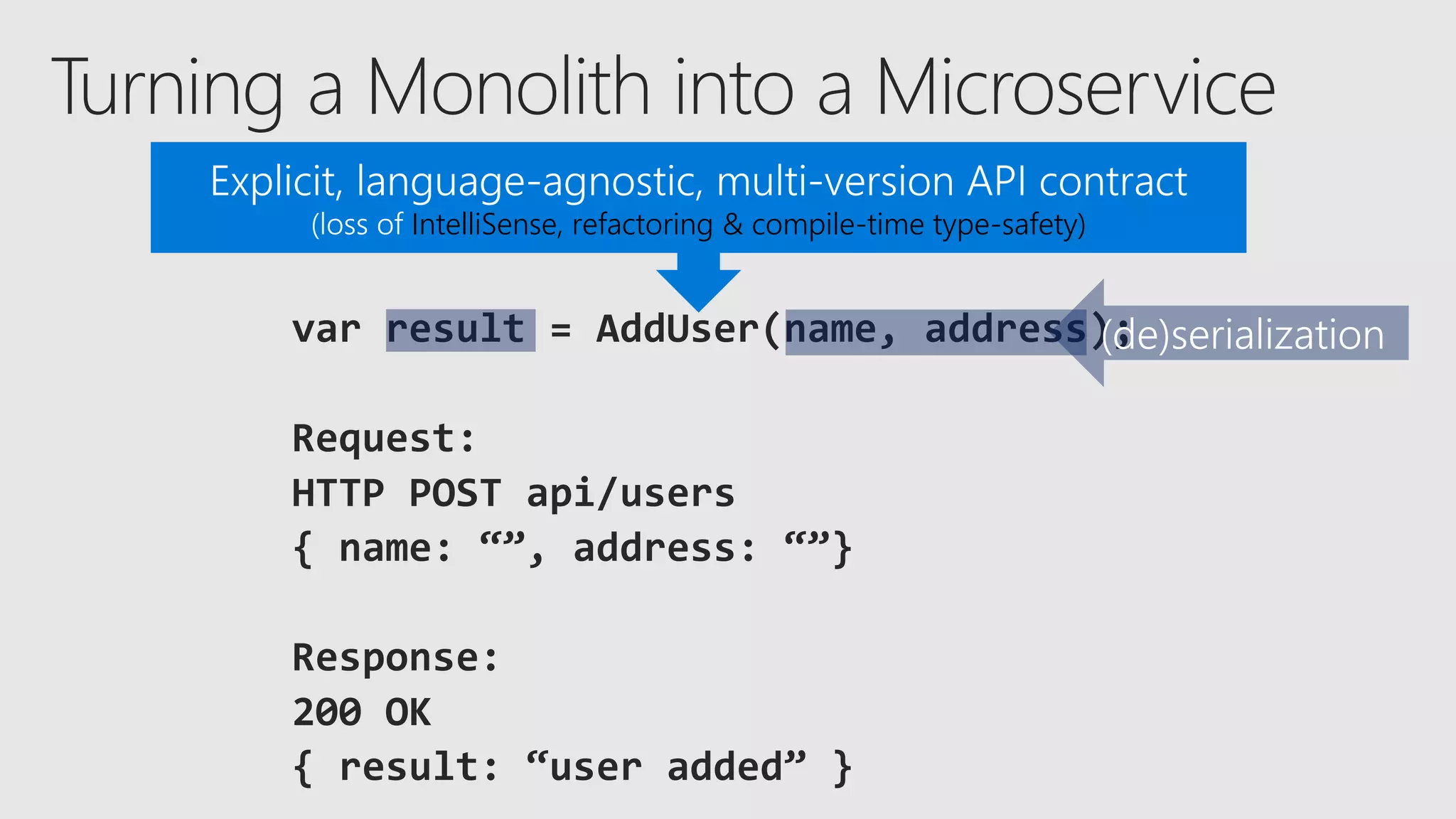
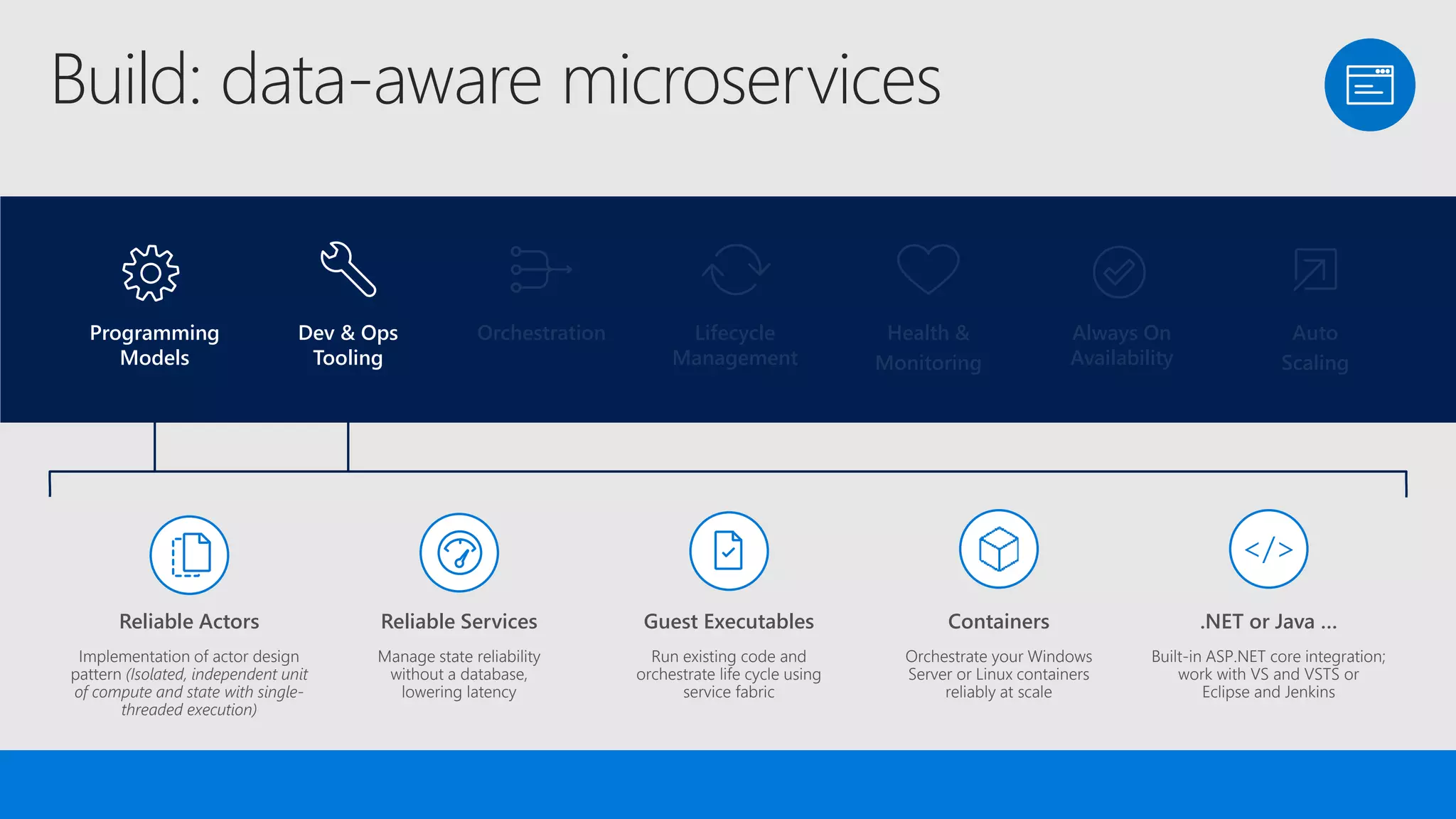
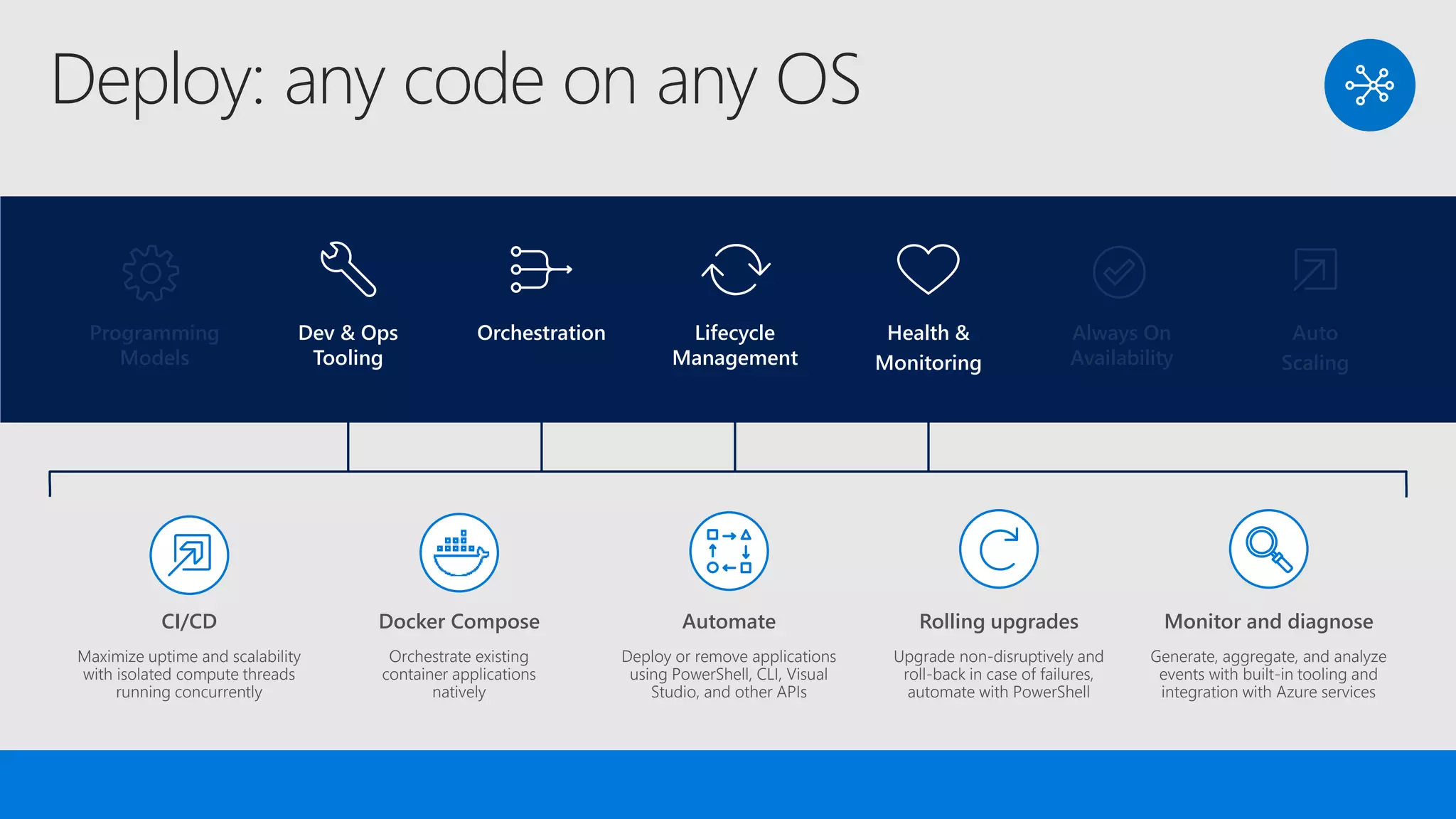
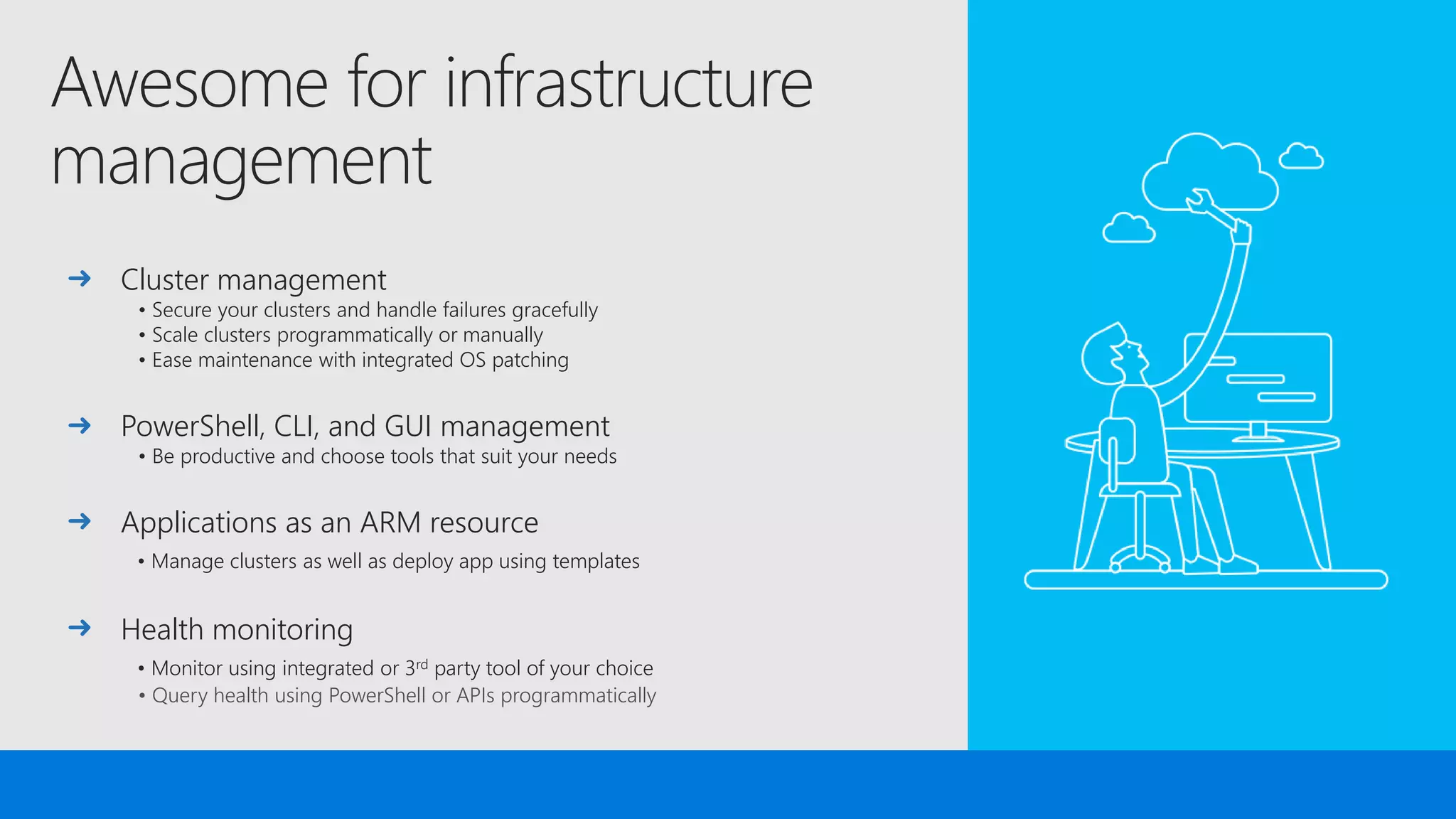
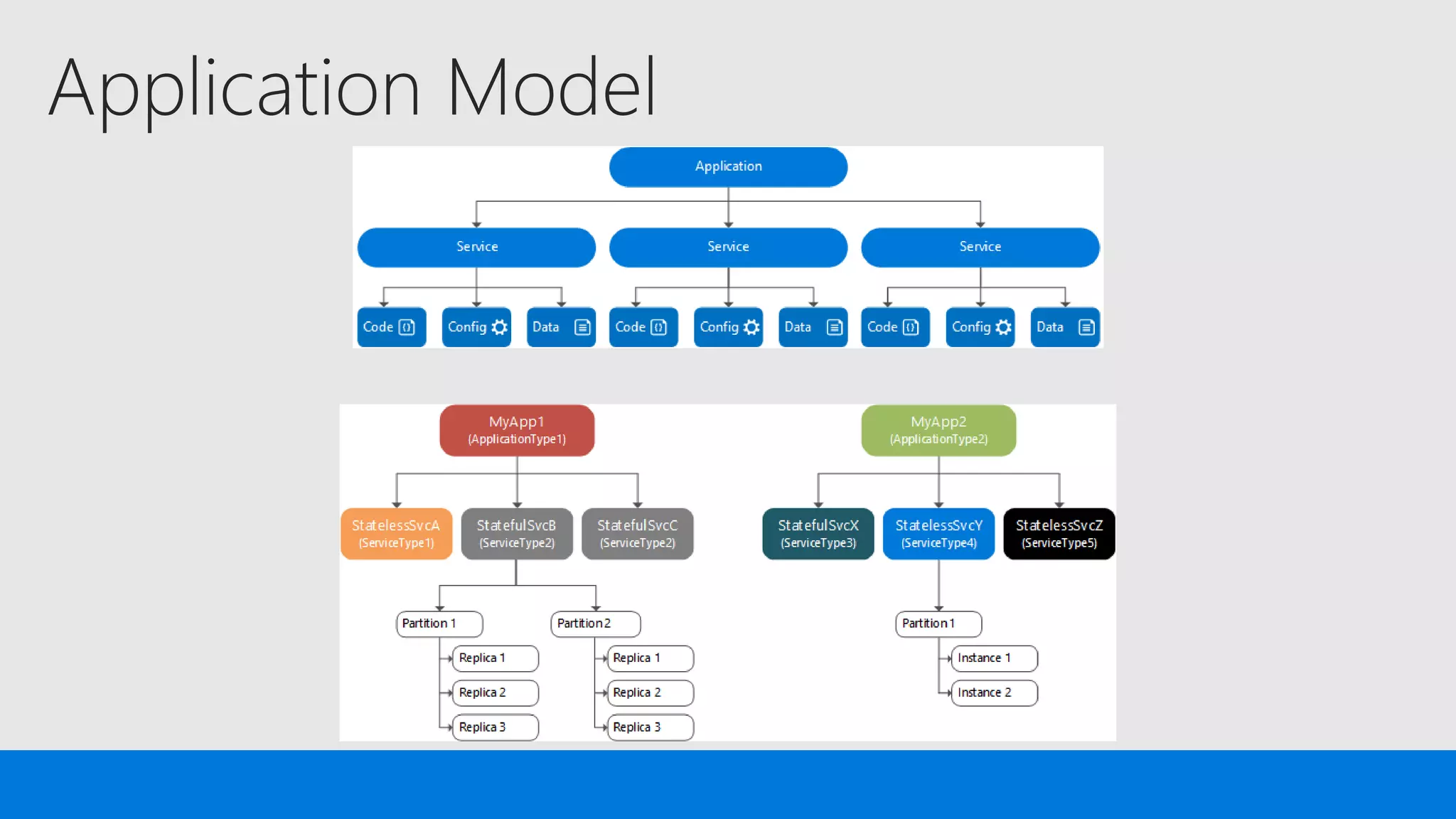
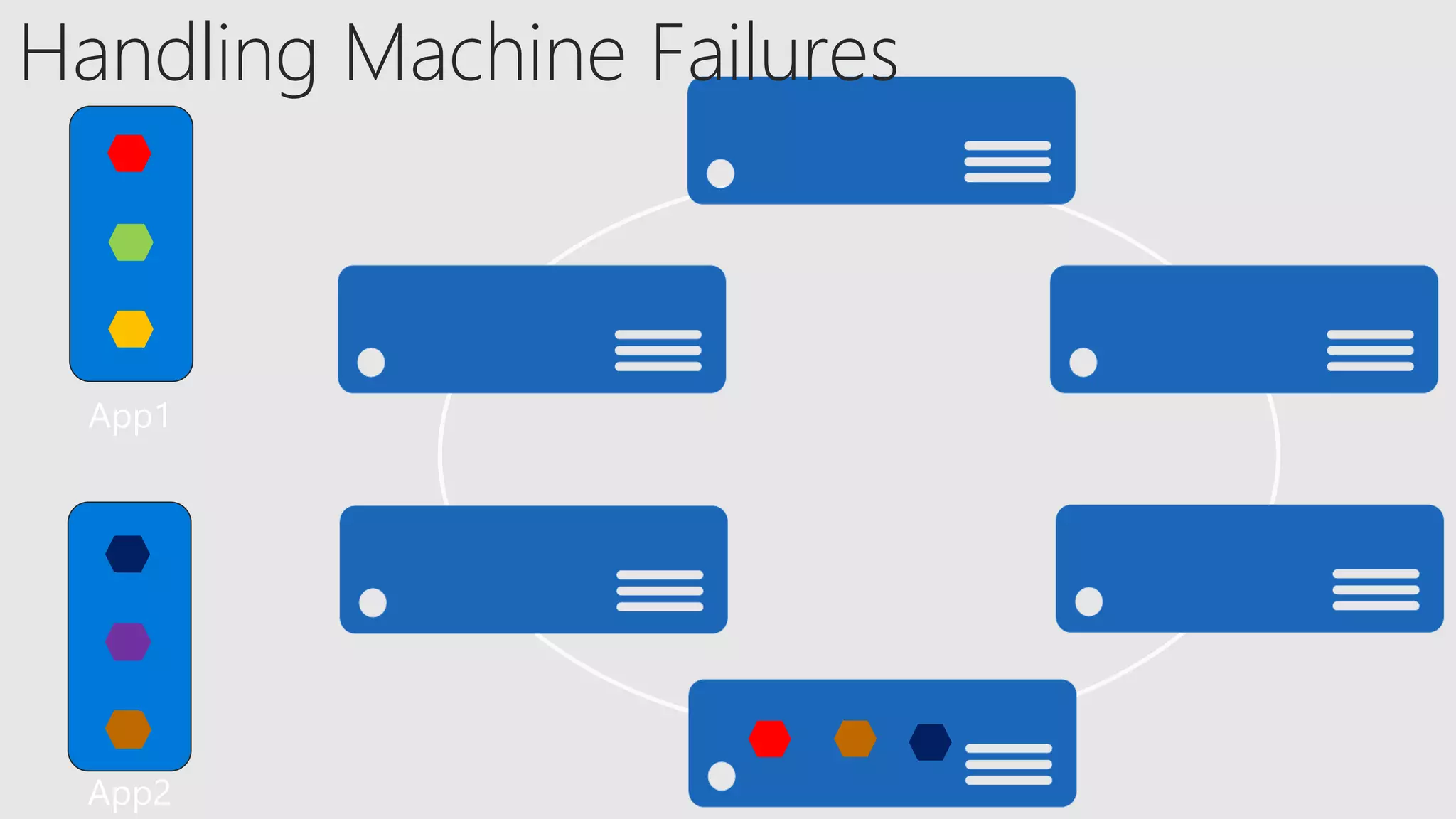
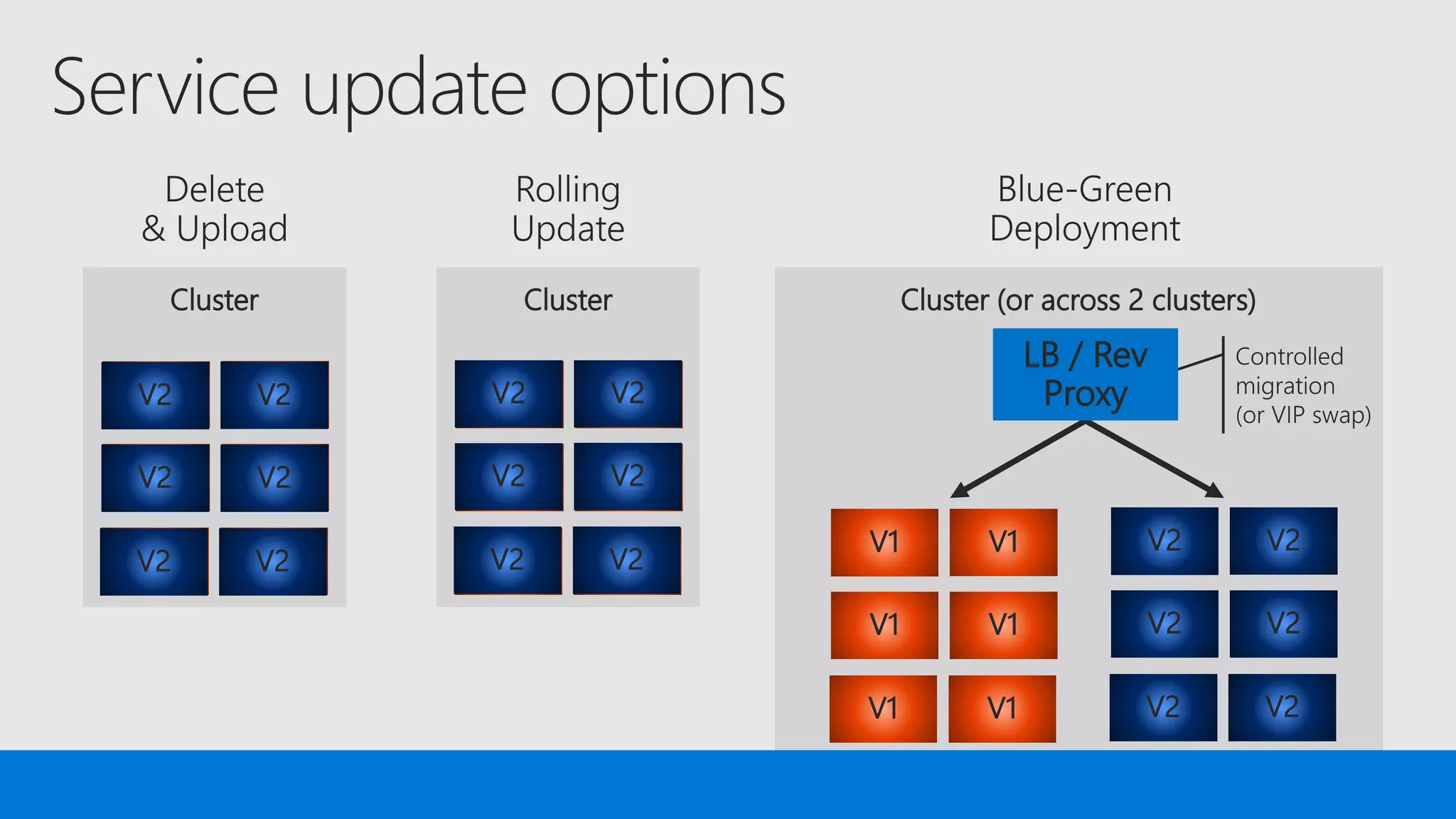
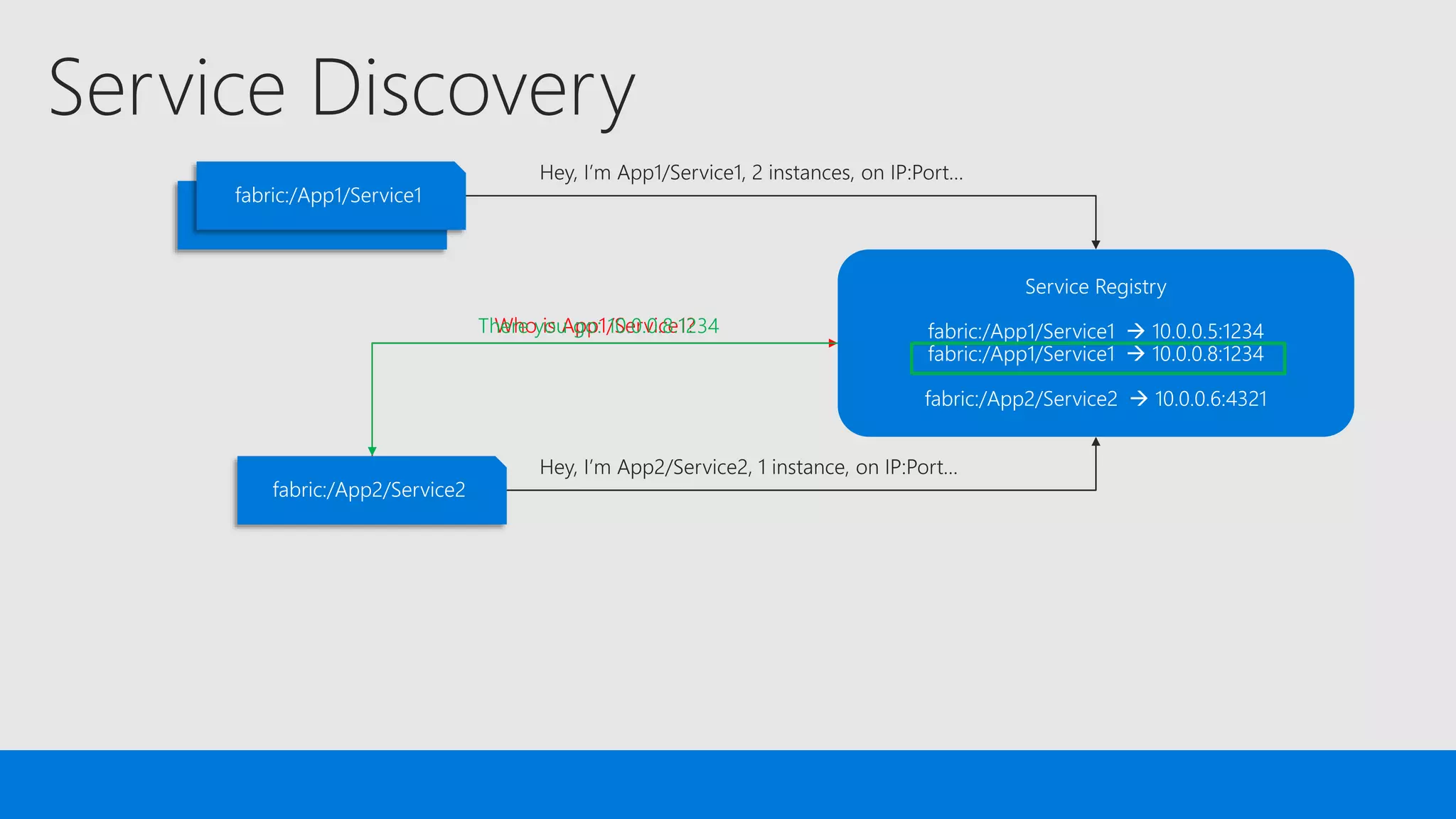
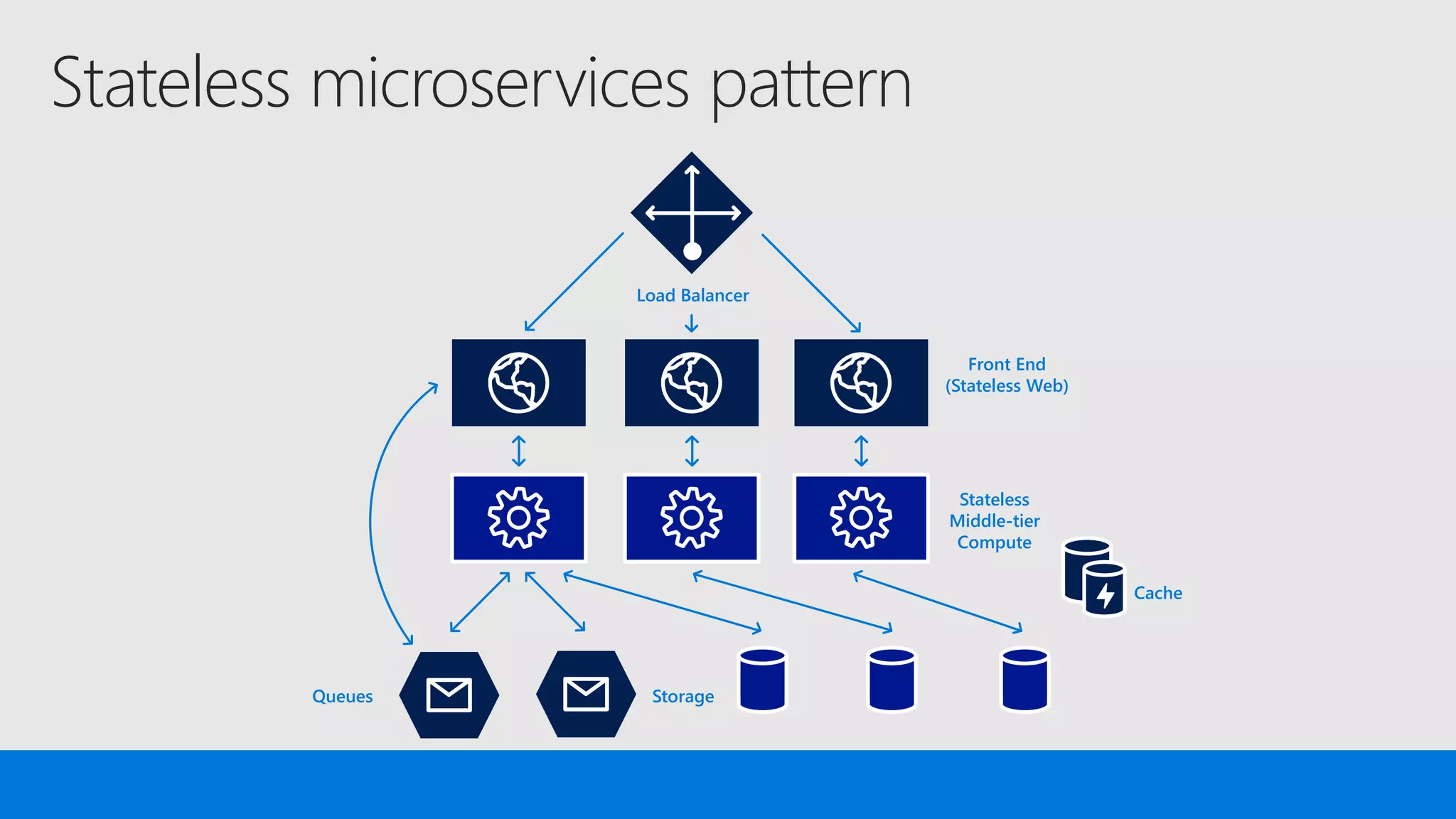
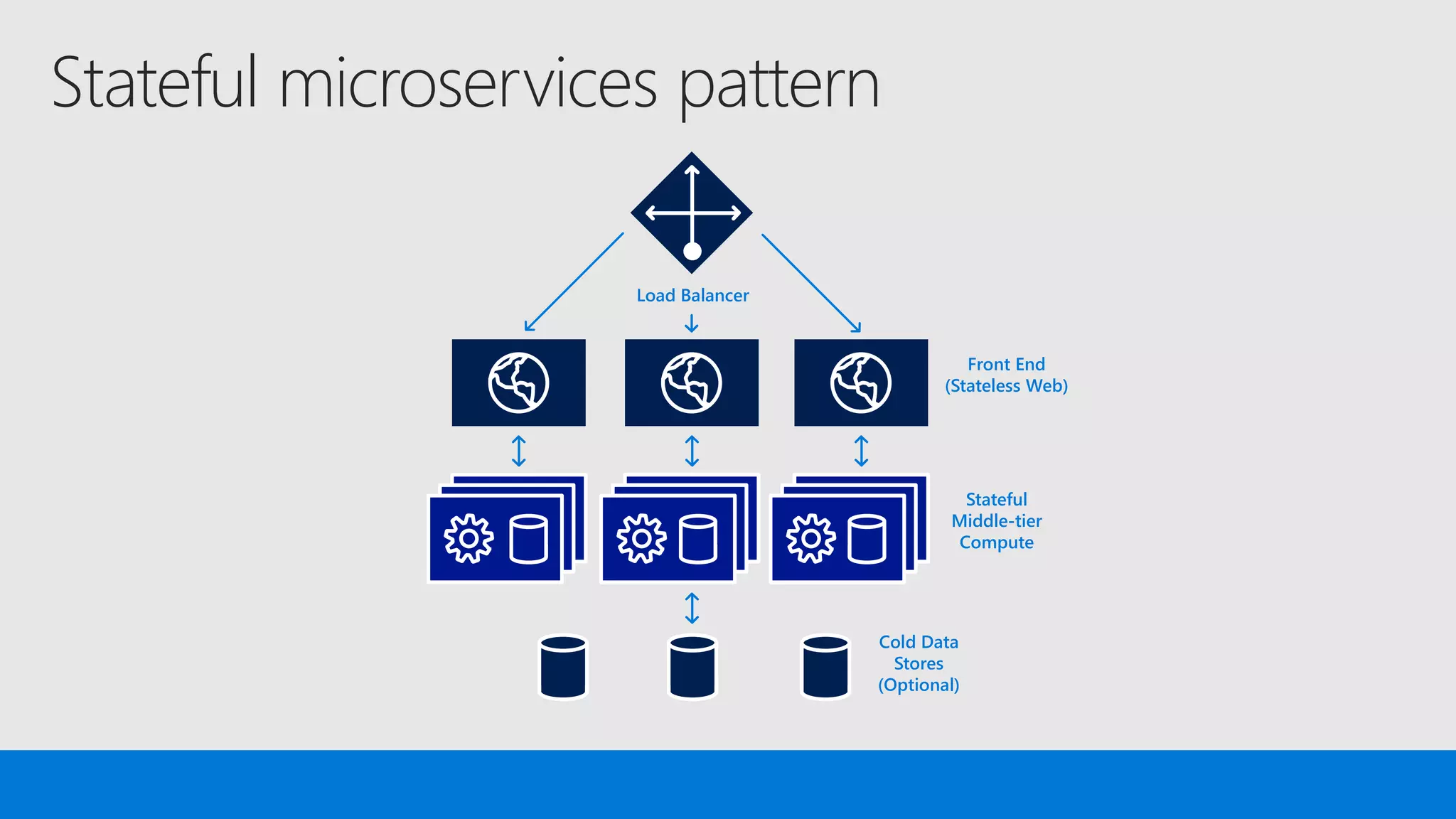
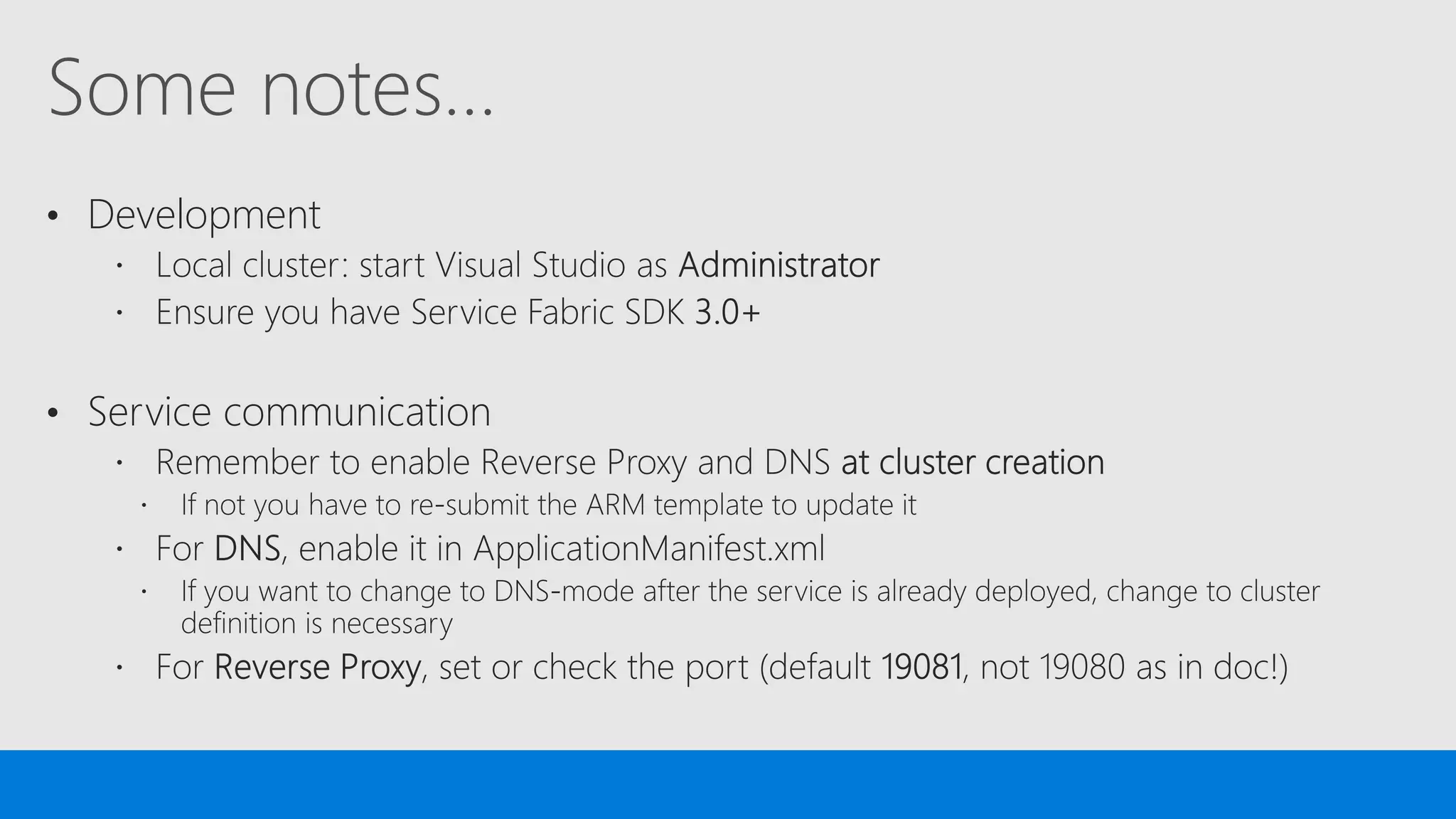
The document discusses the concept of microservices, which encapsulate single capabilities and can be independently developed, deployed, and scaled. It highlights reasons for transitioning from monolithic applications to microservices, including independent scalability and support for diverse technology stacks, while also noting the increased complexity in deployment, management, and security. Additionally, it outlines the capabilities of Azure Service Fabric, a platform facilitating the development and management of microservices, emphasizing its integrated health monitoring, lifecycle management, and support for various programming models.