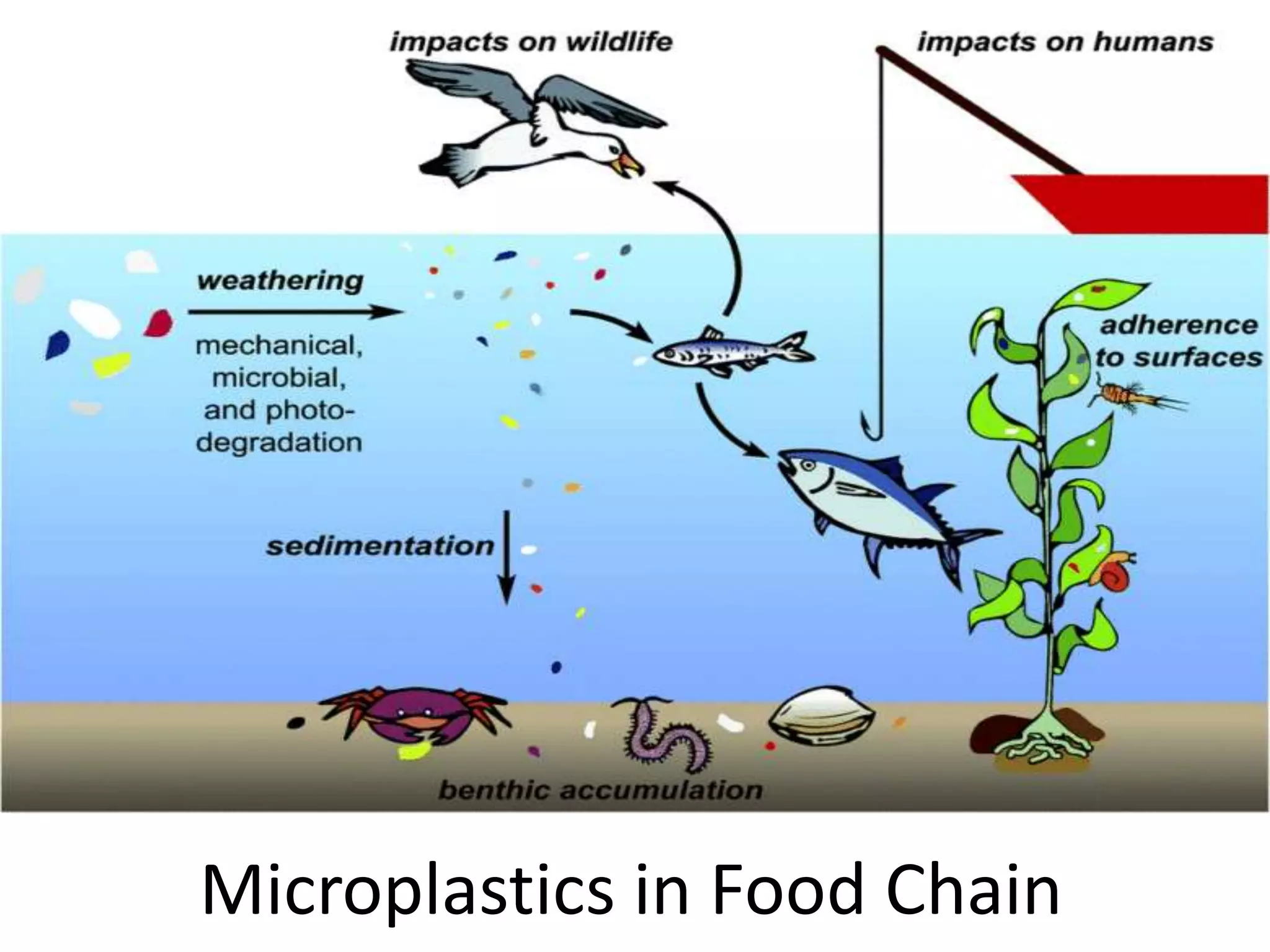
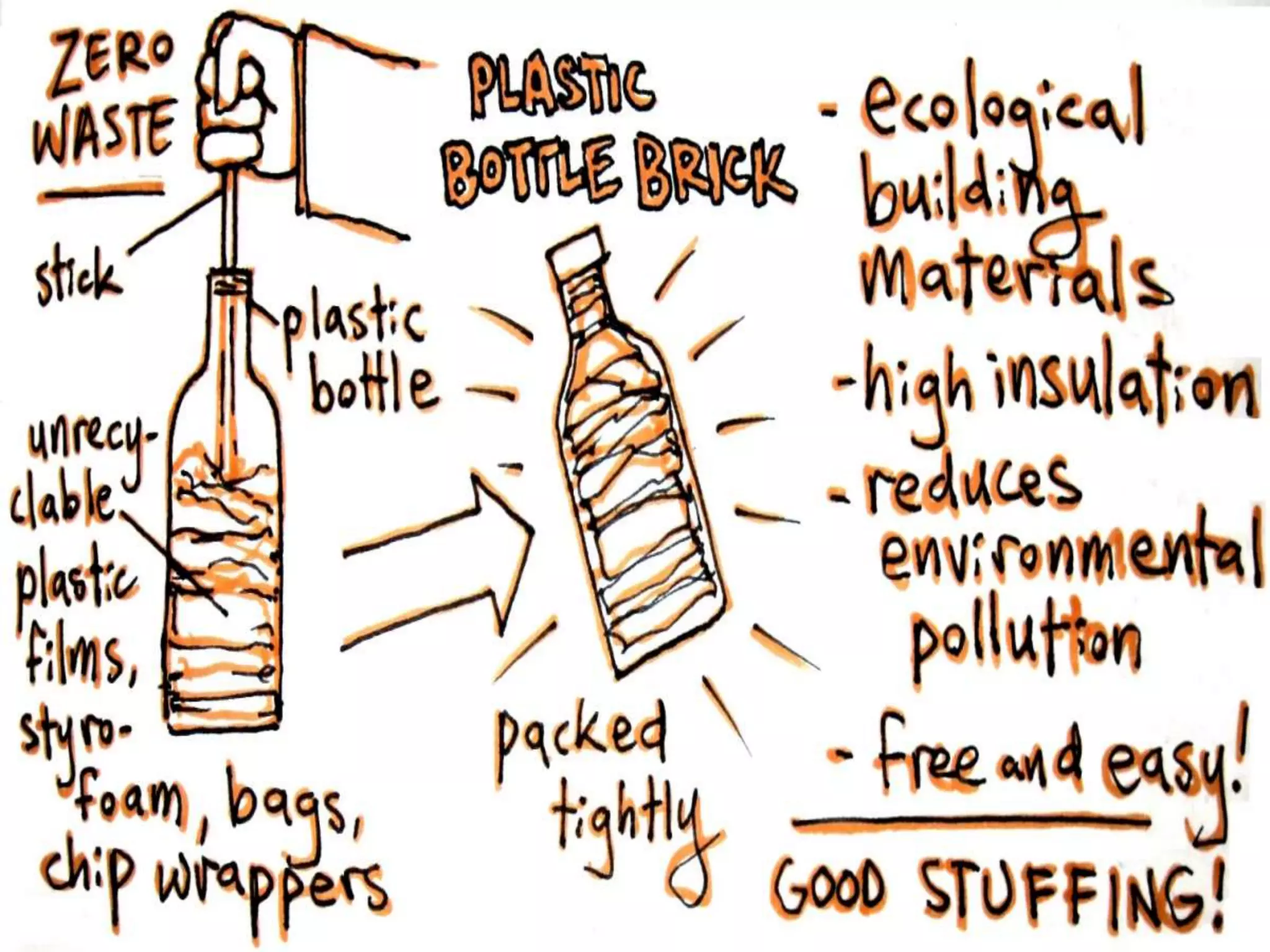
Microplastics are plastic pieces smaller than 5mm that come from two sources: primary microplastics which are originally manufactured at small sizes, and secondary microplastics which are broken down from larger plastic debris. They enter the environment through deterioration of plastic waste, release from products like scrubs, and accidental loss from industry. Microplastics are mistaken for food by marine animals and can accumulate up food chains, releasing harmful chemicals as they break down. Studies found thousands of microplastic pieces per liter in some bottled water brands tested. Eco bricks made by packing waste plastic tightly in bottles provide a way to reuse plastic waste for construction.