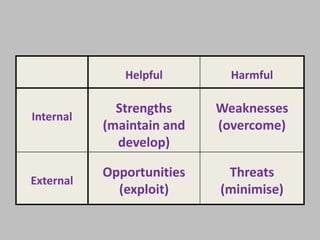
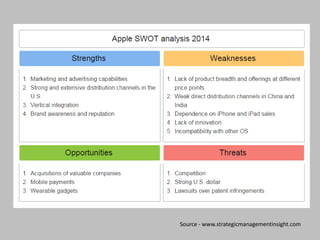
This document discusses SWOT analysis, a tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats involved in a project or business venture. It provides examples of each of the four SWOT factors for McDonald's, including strengths like brand recognition and global operations, weaknesses like unhealthy menus and declining market share, opportunities such as expanding into new markets and breakfast, and threats such as negative publicity and changing social attitudes. The document aims to teach the reader how to properly identify and apply the different SWOT factors to analyze companies or proposals.