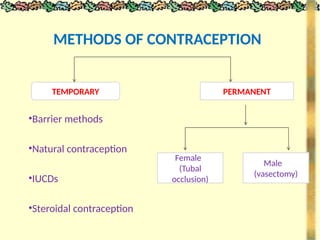
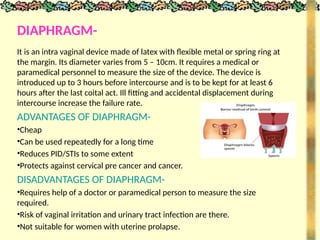
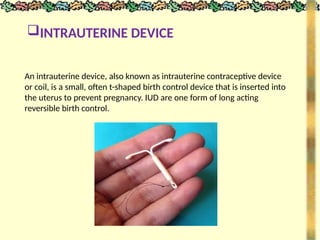
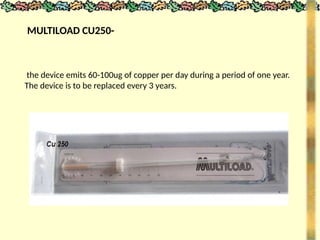
The document outlines various methods of contraception and emergency contraception, detailing definitions, aims, and characteristics of ideal contraceptives. It discusses multiple methods including barrier methods, natural contraception, intrauterine devices (IUDs), steroidal contraception, and surgical options, as well as their advantages and disadvantages. The presentation aims to enhance students' understanding of contraception in relation to family planning and the role of nursing in reproductive health.



























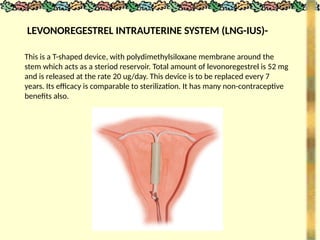



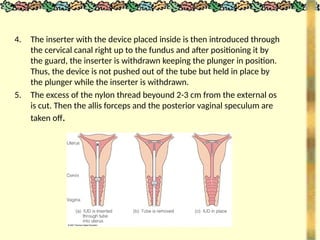




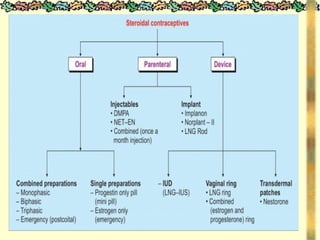











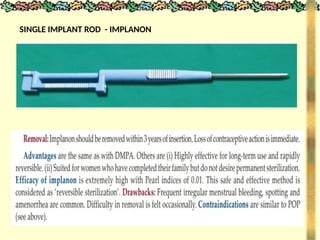




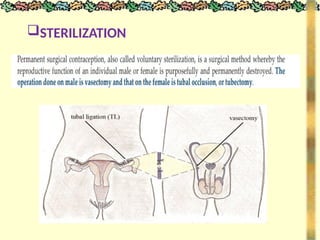
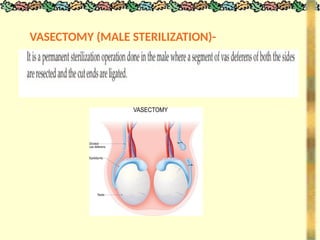



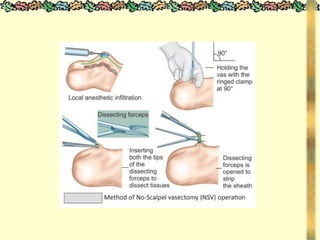

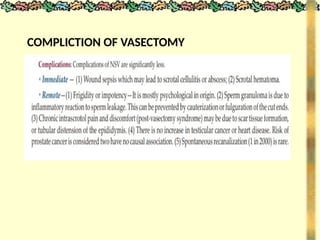
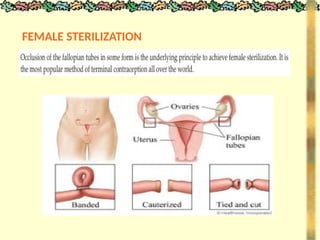



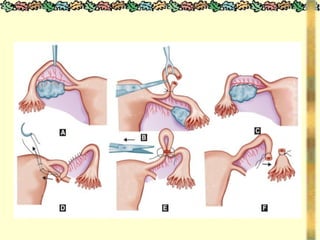



![METHODS_OF_CONTRACEPTION_&_EMERGENCY_CONTRACEPTION[1].pptx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/methodsofcontraceptionemergencycontraception1-250103093523-49b30cae/85/METHODS_OF_CONTRACEPTION_-_EMERGENCY_CONTRACEPTION-1-pptx-74-320.jpg)