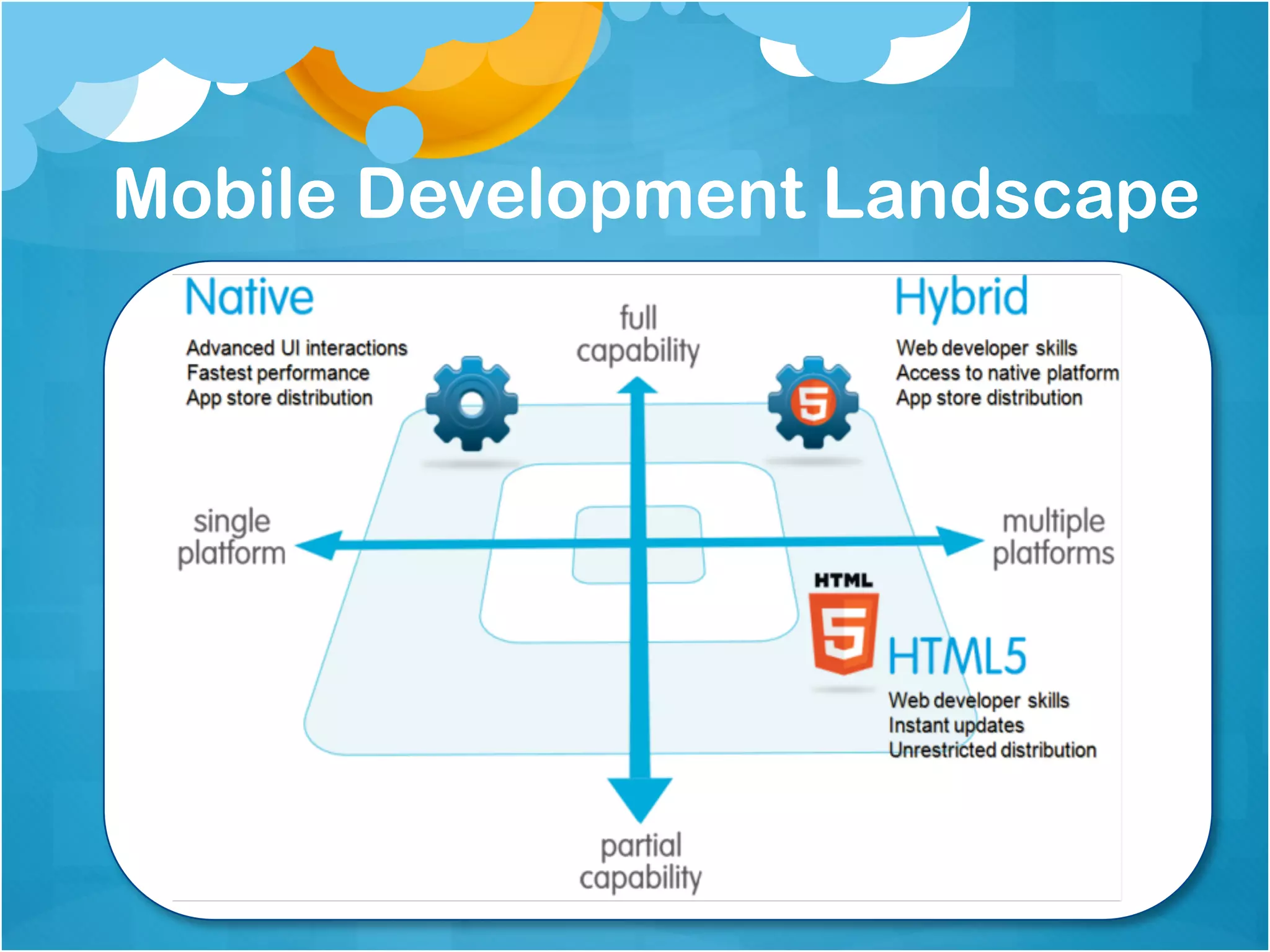
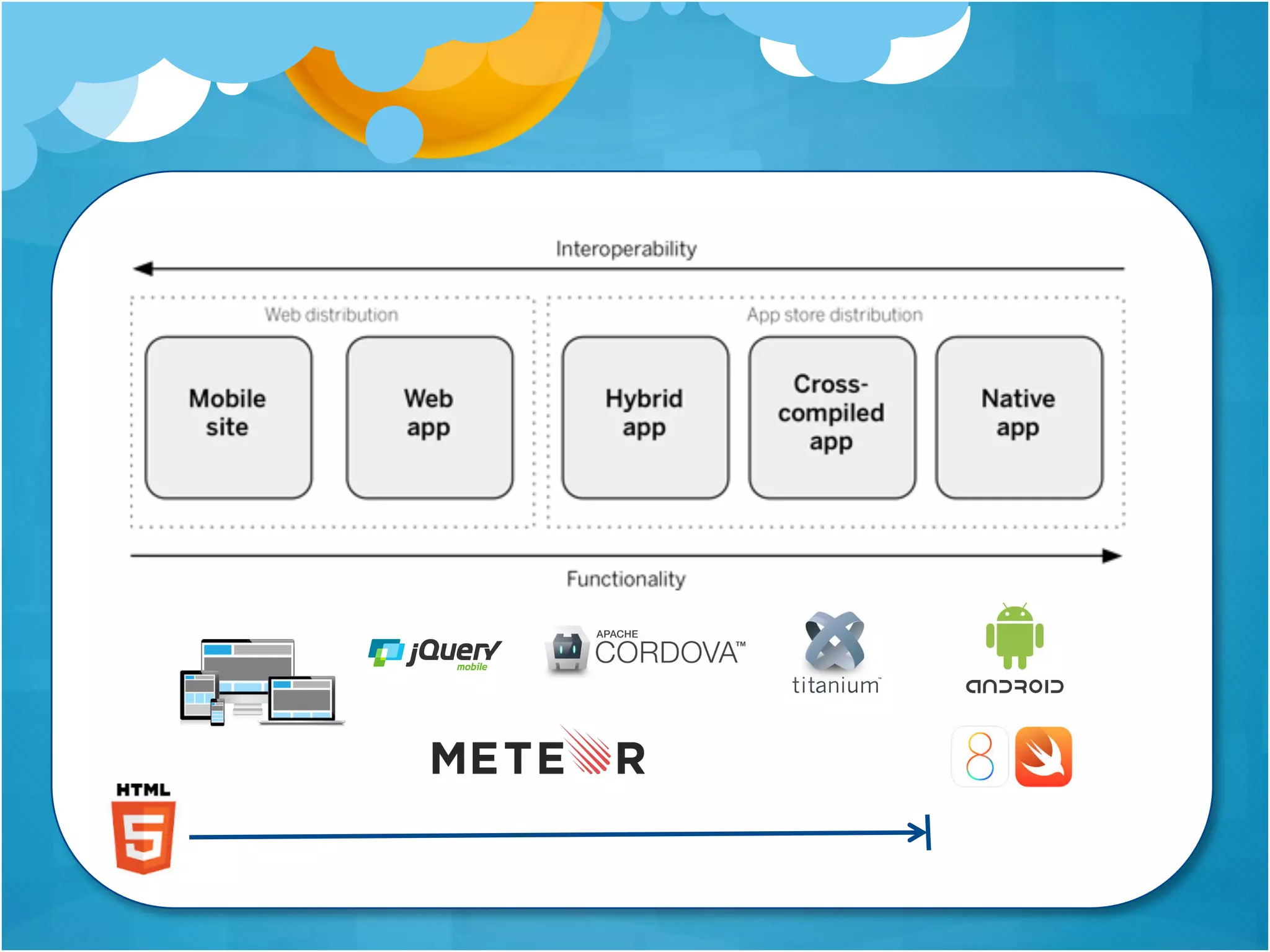
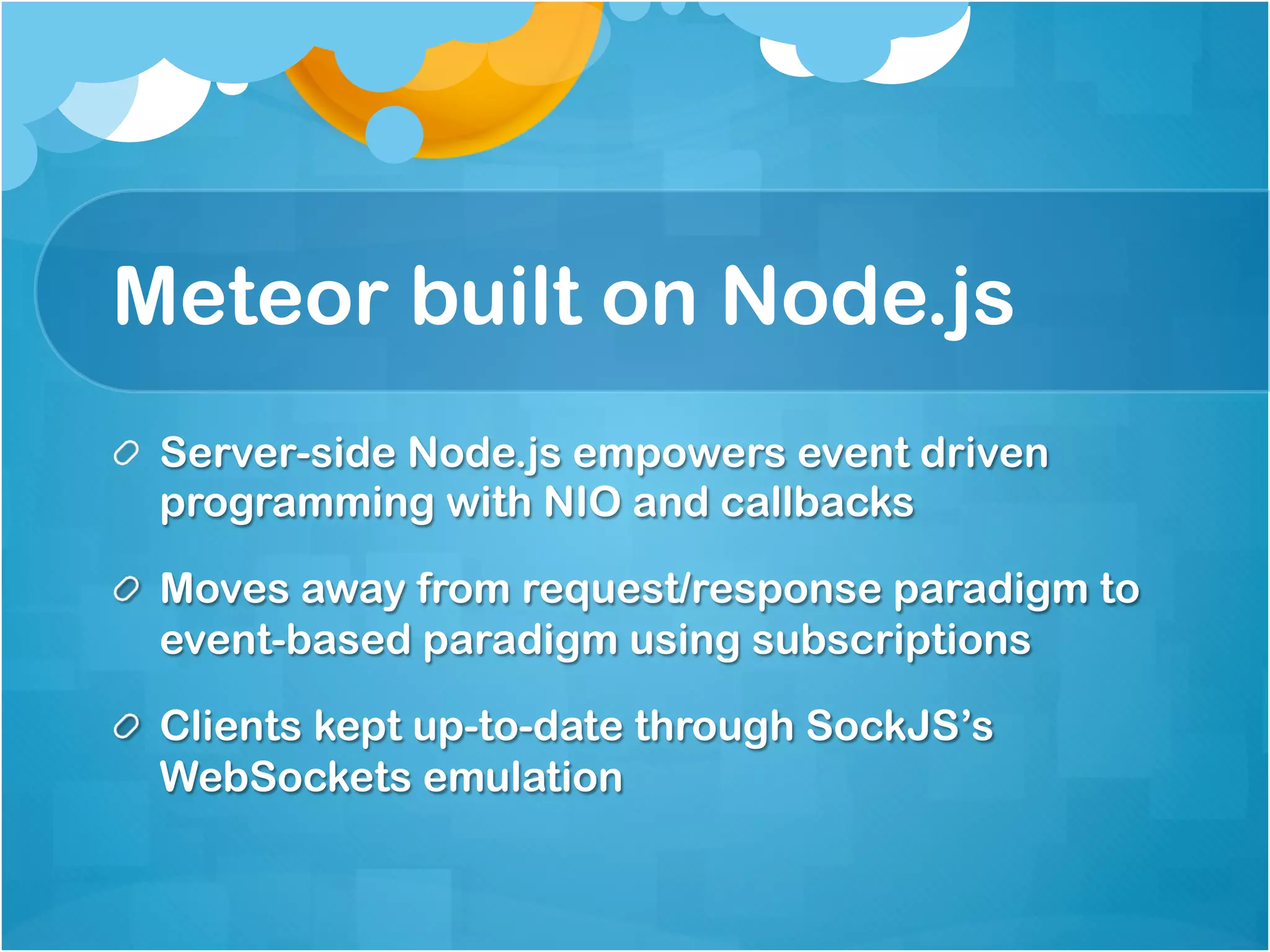
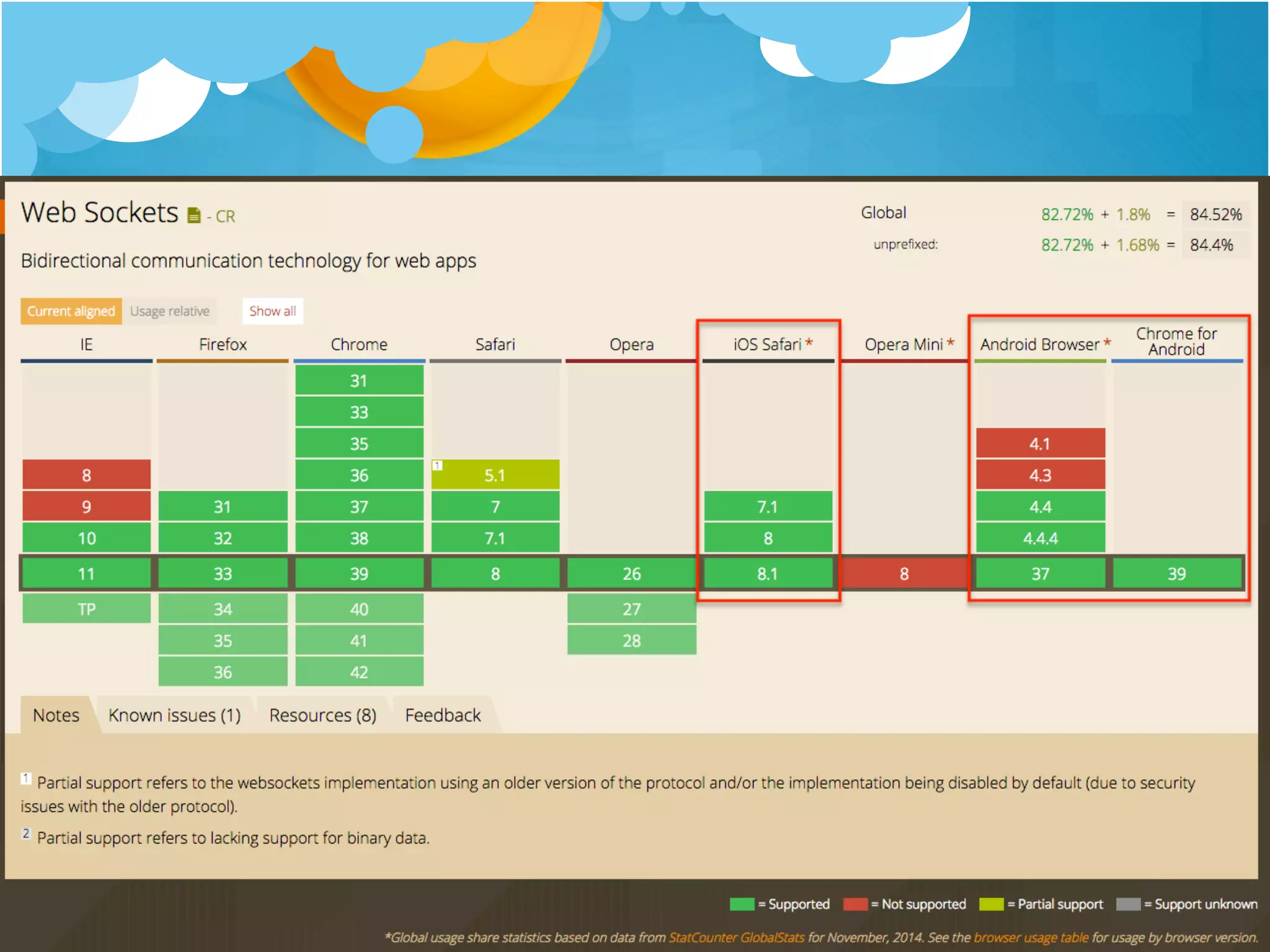
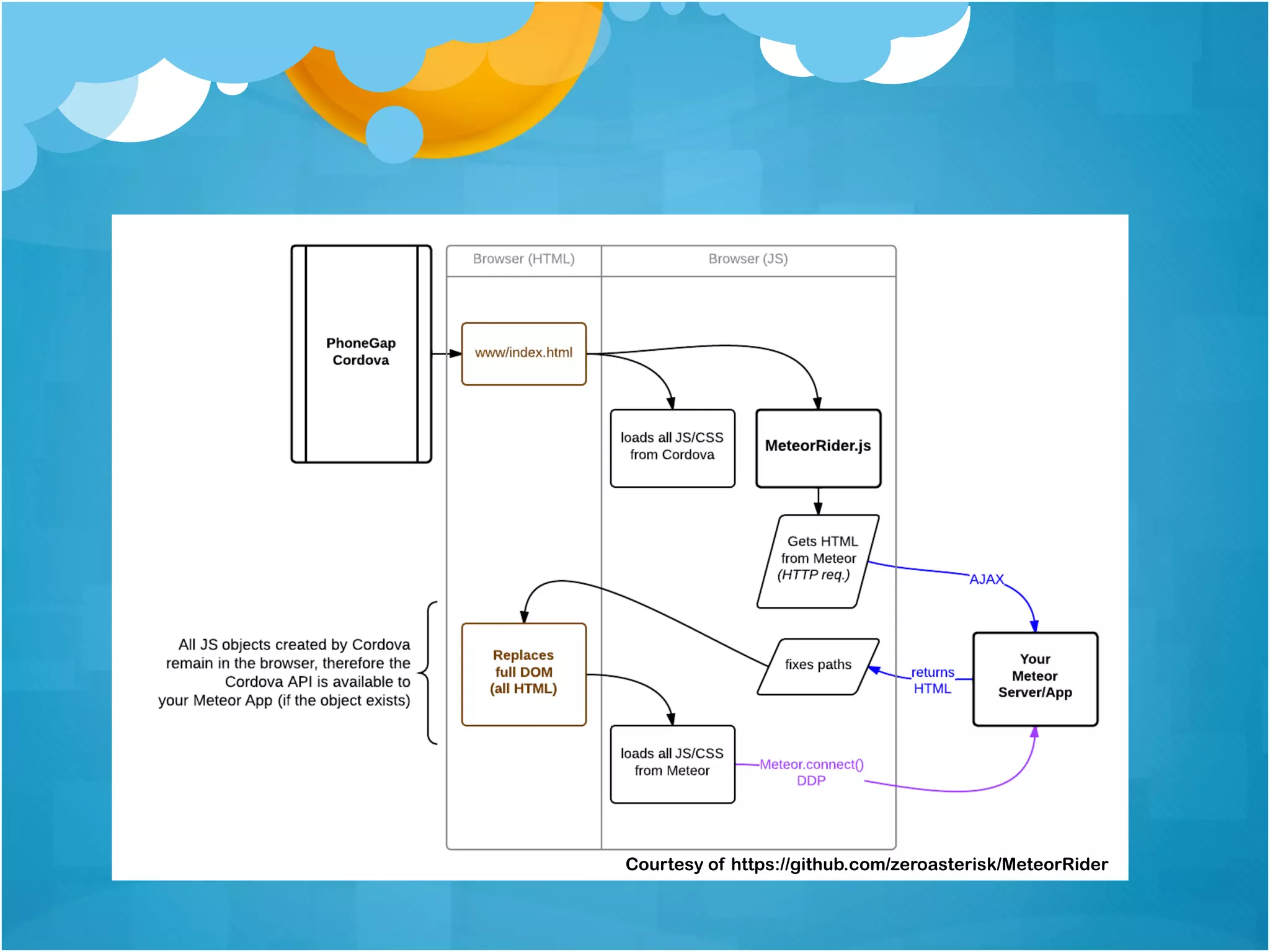
1. The document discusses using Meteor for building mobile applications. Key features of Meteor like automatic data synchronization and Cordova integration are highlighted.
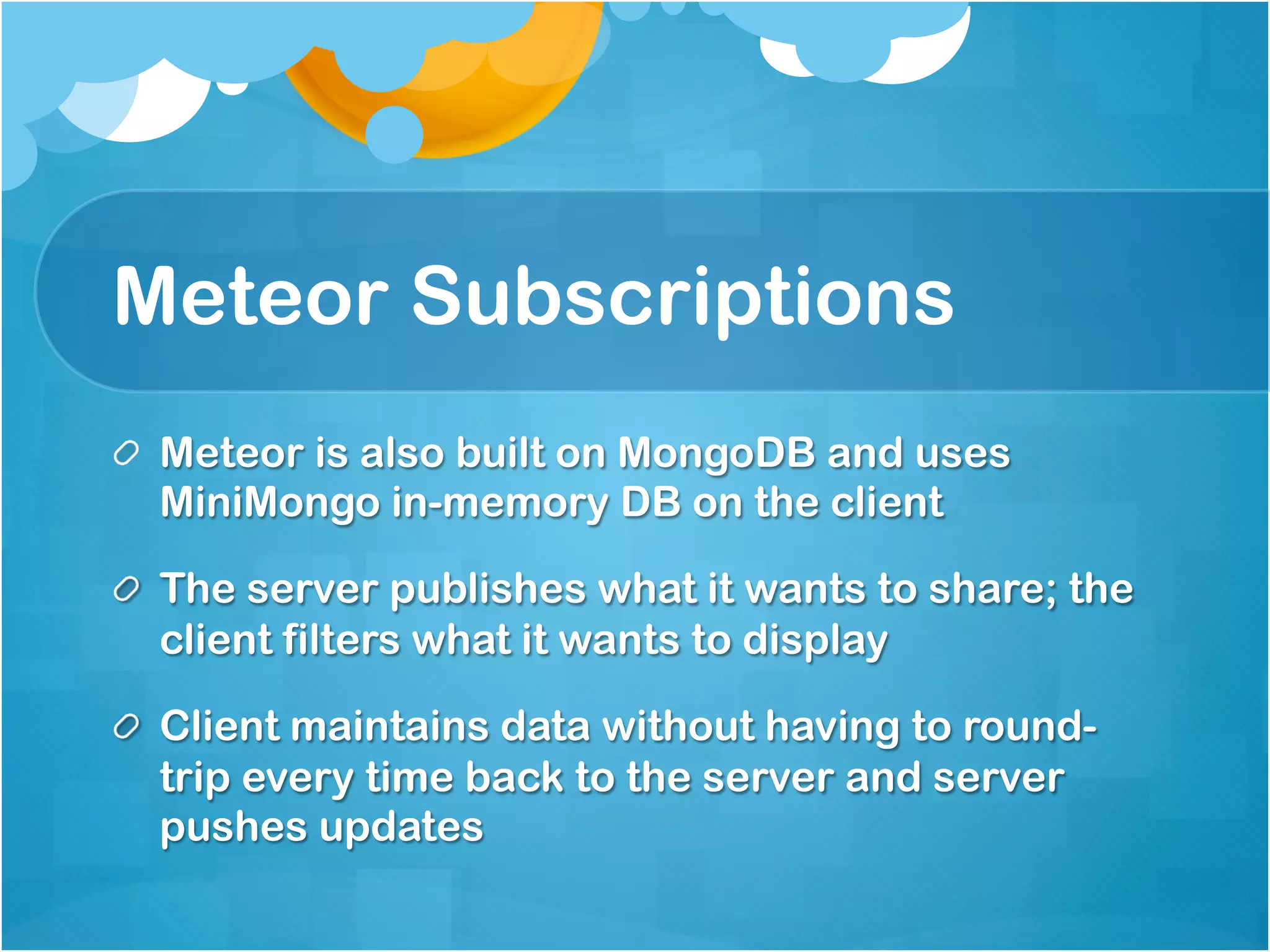
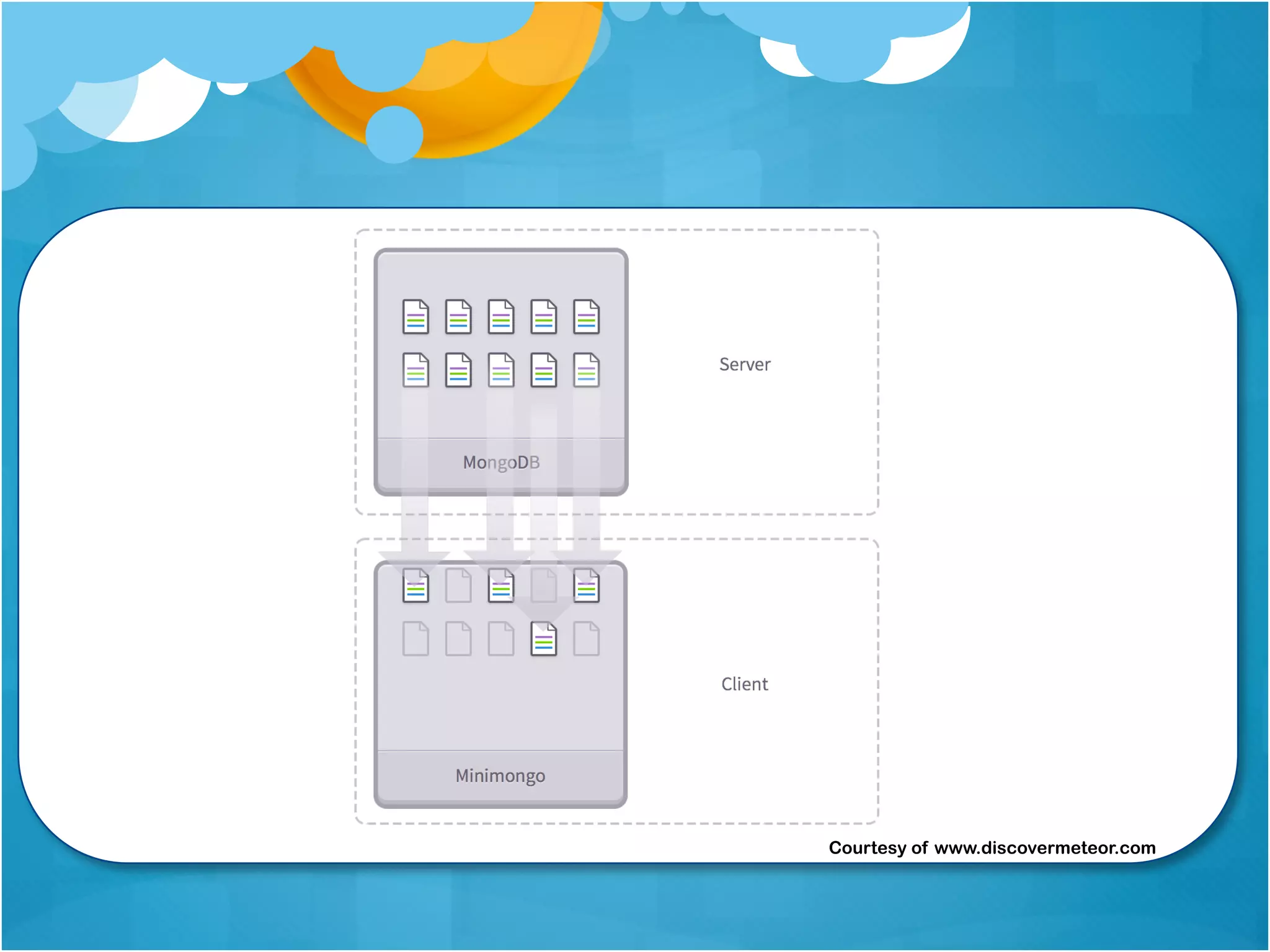
2. Various patterns for structuring Meteor mobile apps are presented, including organizing the project structure, using templates, helpers, and subscriptions to keep data updated.
3. The document also provides an example of how to build a mobile approval application with Meteor that integrates with multiple backend systems and allows approving/denying requests from any device.





![// On the server
Meteor.publish(“requests”, function(limit) {
var userToken = sessionUserAndToken(this.userId, this.connection.id);
var user = userToken.user;
return Requests.find( { $and: [
{uid: user.uid},
{status: {$nin: [‘approved’, ‘failed’, ‘cancelled’]}},
]}, {sort: { ‘timestamp’: 1, ‘requestedFor’: 1, limit: limit});
}
// On the client
Meteor.subscribe(“requests”, Session.get(‘listLimit’), function() {
// Callback function
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meteorpresentationpublic-141212132026-conversion-gate01/75/Meteor-Meet-up-San-Diego-December-2014-12-2048.jpg)










![3. Helpers can be
very…well, helpful!
A helper function can be used globally by all
templates to render things the way you’d like
Examples are Dates, Currency, People’s names, etc.
Create helper one time use directly in HTML as an
expression {{[helper]}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meteorpresentationpublic-141212132026-conversion-gate01/75/Meteor-Meet-up-San-Diego-December-2014-23-2048.jpg)
![//JavaScript
var DateFormats = {
short: "DD-MMM-YYYY”, long: "dddd DD.MM.YYYY hh:mm A"
};
Template.registerHelper("formatDate", function(datetime, format) {
if (moment(datetime).isValid()) {
var f = DateFormats[format],
dt = moment(datetime);
if (format === 'long' || format === 'medium') {
var localTime = moment.utc(dt).valueOf();
return moment(localTime).format(f);
} else {
return moment(dt).format(f);
}
} else {
return '';
}
});
//HTML
<p>This request was {{record.status}} on {{formatDate record.lastModified "medium"}}
</p>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meteorpresentationpublic-141212132026-conversion-gate01/75/Meteor-Meet-up-San-Diego-December-2014-24-2048.jpg)

![//JavaScript
Tracker.autorun(function () {
var conf = Config.findOne();
if (conf) {
Session.set("vordelServer", conf.vordelServer);
if (conf.systemAvailability) {
systems.forEach(function (system) {
var available = conf.systemAvailability[system];
if (available) {
var isDown = available.toUpperCase() === 'OFF' ? true : false;
if (isDown) {
$("." + system).addClass('ui-disabled');
} else {
$("." + system).removeClass('ui-disabled');
}
}
});
}
}
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meteorpresentationpublic-141212132026-conversion-gate01/75/Meteor-Meet-up-San-Diego-December-2014-26-2048.jpg)
![//JavaScript
function processCounts(system) {
var user = Meteor.user(),
queryObject = getSystemQueryObject(system);
if (user && queryObject) {
var query = queryObject.find({$and: [
{approverUid: user.username},
{status: {$nin: status_complete}}
]});
query.observeChanges({
// Only need to observe changes as it relates to this query, not collection
added: function(id, user) { updateListCount(system, false);},
removed: function(id) { updateListCount(system, true);}
});
}
else {
return 0;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meteorpresentationpublic-141212132026-conversion-gate01/75/Meteor-Meet-up-San-Diego-December-2014-27-2048.jpg)


![Getting Started
Cordova supported OOTB since 0.9.2 but much
improved in 1.0
Best reference:
https://github.com/meteor/meteor/wiki/Meteor-
Cordova-Phonegap-integration
Simply run:
meteor add-platform [ios | android]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meteorpresentationpublic-141212132026-conversion-gate01/75/Meteor-Meet-up-San-Diego-December-2014-32-2048.jpg)

![//JavaScript/Cordova plugin hook
comm = function () {
var errorCallback = function (err) {
alert("Native functionality failed with error: " + err);
};
var email = {
message: function (email, subject, callback) {
if (typeof device !== 'undefined' && device.platform === "iOS") {
cordova.exec(callback, errorCallback, "EmailComposer",
"showEmailComposer", [{"toRecipients": [email]}]);
} else {
window.open("mailto:" + email + "?subject=" + subject, '_system');
}
}
};
return {
email: email
};
}();
//Usage
comm.email.message(“lsacco@qualcomm.com”, “Just a test”);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meteorpresentationpublic-141212132026-conversion-gate01/75/Meteor-Meet-up-San-Diego-December-2014-34-2048.jpg)
![Customizing the Experience
mobile-config.js is where you can set:
App Name, version, id, etc.
Icon and splash screens
Cordova preferences
Use cordova-build-override directory to mirror and
customize “native” code
To create build artifacts (IPA/APK) use:
meteor build [bundle path] –server [host]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meteorpresentationpublic-141212132026-conversion-gate01/75/Meteor-Meet-up-San-Diego-December-2014-35-2048.jpg)


