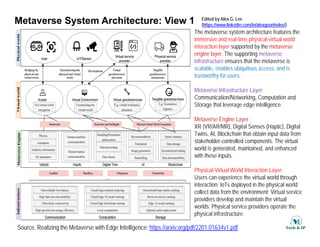
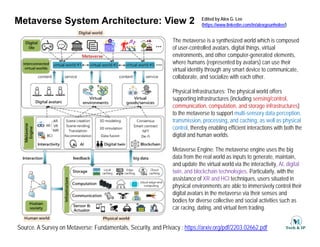
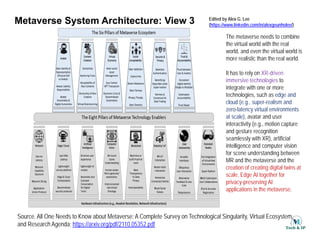
The document outlines the architecture of the metaverse, emphasizing the integration of immersive physical-virtual interactions, supported by a metaverse engine and robust infrastructure for scalability and trustworthiness. It discusses the use of technologies like AI, blockchain, XR, and IoT to enhance user experiences and facilitate interactions within a synthesized virtual world. Overall, it highlights the importance of combining real-world data and advanced technologies to create a realistic and interactive metaverse environment.