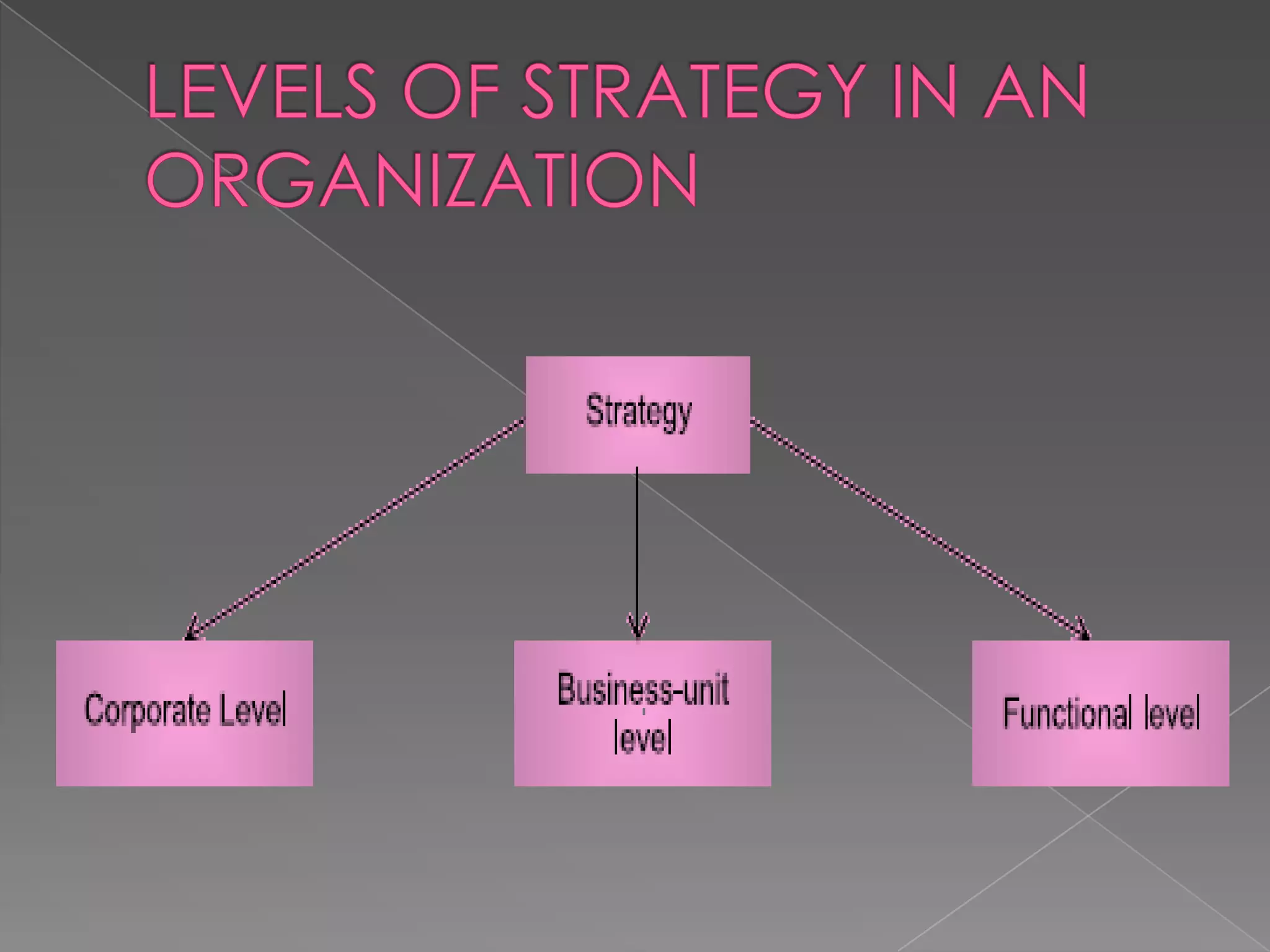
This document discusses mergers and acquisitions from several perspectives. It defines mergers and acquisitions, describes the different types of mergers including horizontal, vertical, conglomerate and concentric mergers. It provides examples of mergers in different industries. It also discusses the common motives behind mergers and acquisitions such as increasing market power, acquiring new technologies, and improving efficiencies. Finally, it outlines some of the benefits that can result from mergers and acquisitions like faster growth, new markets, cost reductions and improved profitability.