Mens rea refers to the mental state required for a crime, meaning an intention to commit a prohibited act. For a crime to occur, there must be both an act (actus reus) and a guilty mind (mens rea) coinciding. Mens rea can be established by proving intention, recklessness, or negligence. Intention requires desire or foreseeability of the consequences. Recklessness involves disregarding an obvious risk. Negligence means failing to meet the standard of a reasonable person. The doctrine of transferred malice holds that liability can be established even if the victim differs from the one intended, if the actus reus and mens rea were present. Several cases help define these




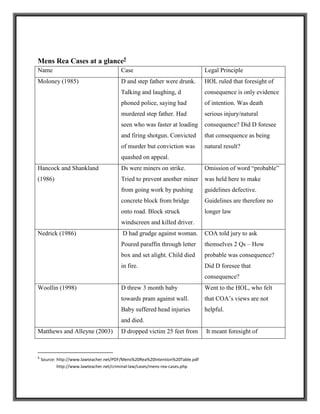
![ R v Moloney (1985)
The defendant and his stepfather drank a large quantity of alcohol at a dinner party. A few hours
later they had a discussion about firearms, and had a shooting contest to see who could load and
fire a shotgun faster. The defendant, who was unaware the gun was pointing at the victim, did
this and killed his stepfather. Defendant was charged with murder.
Held: on appeal the House of Lords quashed the murder conviction and substituted a verdict of
manslaughter, on the ground that only intent to kill or cause really serious injury would be
sufficient mens rea for murder.
R v Hancock and Shankland [1986]
Striking miners threw a concrete block from a bridge onto a road, where it killed a taxi driver.
Held: on appeal a verdict of manslaughter was substituted by the House of Lords who reaffirmed
that the prosecution has to establish an intention to kill or do grievous bodily harm on the part of
the defendant.
R v Woolling [1998]
The defendant lost his temper and threw his three months old son on to a hard surface. His son
sustained a fractured skull and died. Woolling was charged with murder. He refused that he had
intention to cause serious harm.
House of Lord held: having regard to the mental element in murder, a jury was required to
determine whether the defendant had intended to kill or do serious bodily harm. The conviction
for murder was quashed and conviction for manslaughter substituted.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportonmensrea-160805165235/85/Mens-Rea-5-320.jpg)
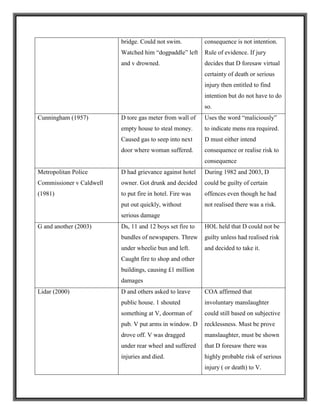
![ Recklessness3
Recklessness is the taking of an unjustified risk. However, two different tests have been
developed by the courts, the result of which is that recklessness now has two different legal
meanings which apply to different offences.
Subjective test
The defendant knows that the risk or willing to take it and takes it deliberately. The question that
must be asked is “was the risk in the defendant’s mind at the time the crime was committed?”
This test was established in:
R v Cunningham [1957]
The defendant had broken a gas meter to steal the money in it with the result that gas escaped
into the next-door house. The victim became ill and her life was endangered. The defendant was
charged under s23 of the Offences Against the Person Act 1861 with “maliciously administering
a noxious thing so as to endanger life”.
Court of Appeal held: that for a defendant to have acted “maliciously” there had to be proof that
he intended to cause the harm in question, or had been reckless as to whether such harm would
be caused. In this context recklessness involved the defendant in being aware of the risk that his
actions might cause the prohibited consequence.
Objective test
The risk must be obvious to the reasonable man, in that any reasonable man would have realized
it if he had thought about it.
A person is reckless in the new wider sense when he performs an act which creates an obvious
risk, and when performing the act, he has either given no thought to the possibility of such a risk
3
Although the House of Lords stated in R v G and another that their Lordships’ definition of recklessness related specifically to
criminal damage, the Court of Appeal in Attorney General’s Reference (No. 3 of 2003) [2004] 2 Cr App R 367 later held that R v
G and another laid down general principles. In practice, it seems likely that the definition of recklessness adopted in R v G and
another will be applied to other statutory offences, unless the contrary is stated within the relevant statute.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportonmensrea-160805165235/85/Mens-Rea-6-320.jpg)
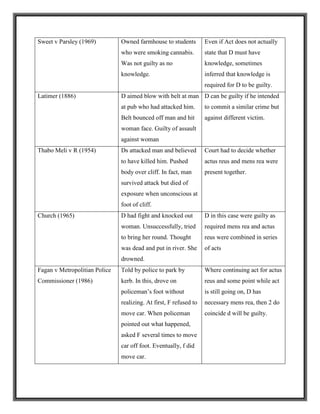
![arising or he recognized that some risk existed, but went on to take it. This test was established
in:
MPC v Caldwell [1982]
The defendant got drunk and set fire to a hotel as an act of revenge against owner. The fire was
discovered and put cut before very serious damage occurred. The defendant was convicted of
damaging property with intent to endanger life or being reckless whether life would be
endangered under s1(2) Criminal Damage Act (CDA 1971). Mens Rea required was intention or
recklessness. Even though the defendant said that he was so drunk at the time that it had never
cross his mind that he may be endangering his life, he was convicted as drunkenness cannot be a
defence to a basic intent crime.
R v Reid
The defendant was driving a car with a passenger in the front seat. He attempted to overtake
another car whilst still in the nearside lane. A taxi drivers’ rest hut protruded some six feet into
the nearside lane. The defendant was convicted of causing death by reckless driving, contrary to
s1 of the Road Traffic Act 1972.
The risk must be obvious to the reasonable prudent person; it needs not be obvious to the
defendant.
Elliot v C [1983]
The defendant and educationally subnormal 14 year old school girl had entered a neighbor’s
garden shed, poured white sprit on the floor and ignited it. The defendant then fled as the shed
burst into flames. The magistrates dismissed the charge of criminal damage on the basis that she
gave no though to the risk of damage, and that even if she had, she would not have been capable
of appreciating it. The prosecution appealed and Divisional Court, allowing the appeal, held that
this was irrelevant to the issue of recklessness. When the court in Caldwell had talked about an
“obvious” risk, they had meant obvious to the reasonable man if he had thought about it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportonmensrea-160805165235/85/Mens-Rea-7-320.jpg)
![ Negligence4
Negligence consists of falling below the standard of the ordinary reasonable person. The test is
objective, based on the hypothetical person and involves the defendant either doing something
the reasonable person would not do, or not doing something which the reasonable person would
do.
It does not matter that the defendant was unaware that something dangerous might happen, if the
“reasonable person” would have realized the risk, and taken steps to avoid it.
Mc Crone v Riding [1983]
A learner driver was convicted of driving without due care and attention despite the fact that it
was accepted by the court that he was “exercising all the skill and attention to be expected from a
person with his short experience” because he had failed to attain the required standard.
Transfer of Malice (Bad intention)
Under the doctrine of transferred malice a defendant will be liable for an offence if he has the
necessary mesn rea and commits the actus reus even if the victim differs from the one intended.
The basis for this principle is the decision of the court in:
R v Latimer (1886)
The defendant struck a blow with his belt at X. the defendant was convicted of maliciously
wounding the victim, and appealed on the ground that it had never been his intention to hurt her.
Held: tht the conviction would be affirmed. The defendant had committed the actus reus of the
offence with the necessary mens rea, ie he had acted maliciously. There was no requirement in
the relevant act that his mesn rea should relate to a named victim. Thus Latimer’s malice was
transferred from his intended to his unintended victim.
It is a general principle in criminal law that for a person’s liability to be established it must be
shown that the defendant possessed the necessary mens rea at the time the actus reus was
committed – in other words the two must coincide.
4
Another notable example is the offence of causing or allowing the death of a child or vulnerable adult under s.5 of the Domestic
Violence, Crime and Victims Act 2004](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportonmensrea-160805165235/85/Mens-Rea-8-320.jpg)
![a) Continuing acts
Where the actus reus involves a continuing act a later mens rea during its continuance can
coincide.
Fagan v MPC [1969]
The defendant accidently drove his car on to a policeman’s foot and when he realized, he refused
to remove it immediately.
Held: that the actus reus of the assault was a continuing act which, while started without mens
rea, was still in progress at the time the mesn rea was formed and so there was a coincidence of
actus reus and mens rea sufficient to found criminal liability.
b) Chain of events
The second way the courts have dealt with the problem is to consider a chain of events (i.e. a
continuing series of acts) to be a continuing actus reus for the purposes of the criminal law. If the
actus reus and the mens rea are both present at some time during this chain of events, then there
is liability.
Thabo Meli v R [1954]
The defendant had taken their intended victim to a hut and plied him with drink so that he
became intoxicated. They then hit the victim around the head, intending to kill him. In fact the
defendants only succeeded in knocking him unconscious but believing the victim to be dead,
they threw his body over a cliff. The victim survived but died of exposure some time later. The
defendant were convicted of murder, and appealed to the Privy Council on the ground that there
had been no coincidence of the mens rea and actus reus of murder.
The Privy Council held that the correct view of what the defendants had done was to treat the
chain of events as a continuing actus reaus. The actus reus of causing death started with the
victim being stuck on the head and continued until he died of exposure. It was sufficient for the
prosecution to establish that at some time during that chain of events the defendants had acted
with the requisite mens rea.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reportonmensrea-160805165235/85/Mens-Rea-9-320.jpg)