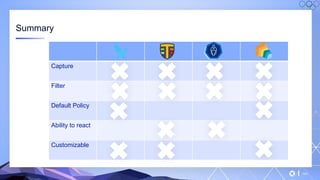
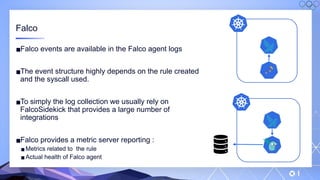
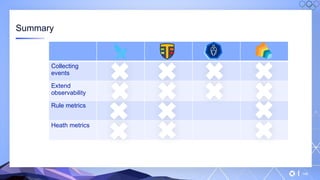
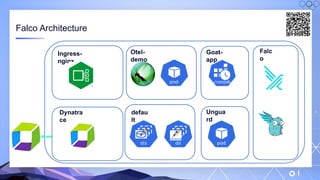
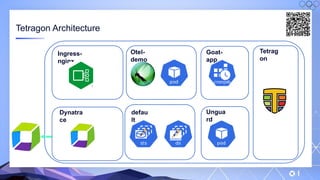
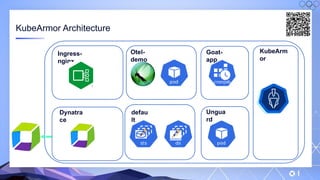
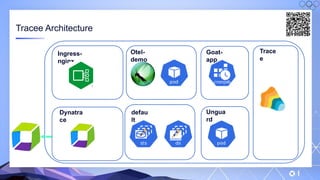
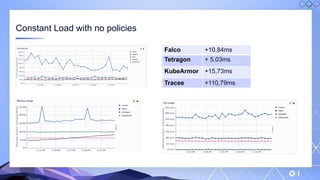
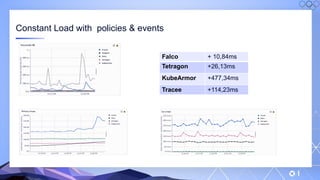
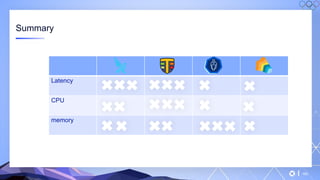
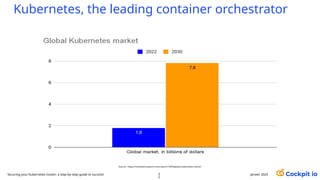
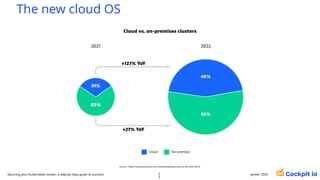
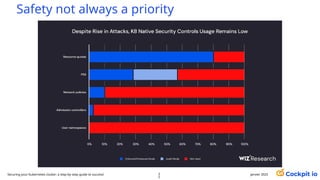
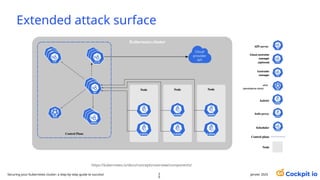
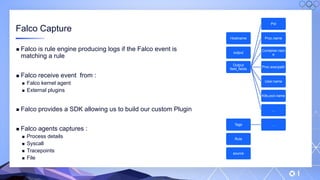
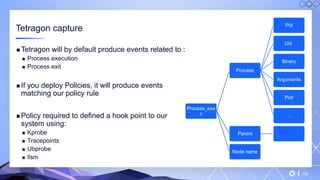
The document outlines a guide for securing Kubernetes clusters, highlighting various aspects such as the importance of proper API server security, identity and access management, and the use of RBAC. It also discusses best practices for managing secrets, auditing logs, and securing containers, alongside emphasizing the need for a zero trust architecture. Additionally, the content features advancements in recruitment and technical expertise provided by Easy Partner, which aids organizations in harnessing tech talent effectively.













































































































![v
138
KubeArmor Policy
▪KubeArmor policies are defined by
building a :
▪KubeArmorClusterPolicy
▪KubeArmorPolicy
▪KubeArmorHostPolicy
▪The policy defines :
▪The Tags
▪The message of the event
▪The Selector to filter to a specific
namespace or workload
▪The rule for the event type ( process, file,
network..Etc)
▪And the action : Block, Audit, Allow
apiVersion: security.kubearmor.com/v1
kind: KubeArmorClusterPolicy
metadata:
name: ksp-nist-remote-access-and-control
spec:
tags: ["NIST","system","ksp","AC-17(1)"]
message: "warning! someone tried to access and
control"
selector:
matchExpressions:
- key: namespace
operator: NotIn
values:
- kube-system
- istio-system
process:
severity: 4
matchPaths:
- path: /usr/bin/ssh
- path: /etc/ssh
action: Audit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2025-01-15-january-250117094427-aab95eb0/85/meetup-devops-aix-marseille-2025-01-125-320.jpg)