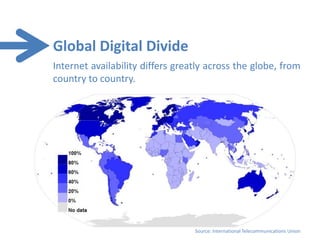
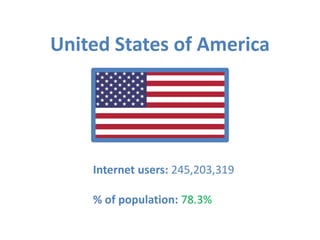
This document provides an overview of the history and development of the internet from its origins as ARPANET in the late 1960s through the present day. It discusses key milestones like the creation of TCP/IP and the world wide web. The document also examines current internet statistics and highlights the global digital divide. Finally, it briefly discusses recent internet controversies and issues of censorship.